Abstract
A new class of steroids has been found that inhibits angiogenesis in the presence of nonanticoagulant heparin. Tetrahydrocortisol is the most potent of the naturally occurring angiostatic steroids. It is a metabolite of cortisone that circulates in the blood, appears in the urine, and was previously believed to be biologically inactive. Both the plasma form and the urinary form are antiangiogenic. The mechanism of action of these steroids depends on their ability to specifically alter basement membrane turnover in growing capillary blood vessels. These steroids represent a prototype of angiogenesis inhibitors that may find potential therapeutic use as adjuncts to anticancer therapy, and in diseases dominated by abnormal neovascularization, i.e., angiogenesis-dependent diseases.
Full text
PDF

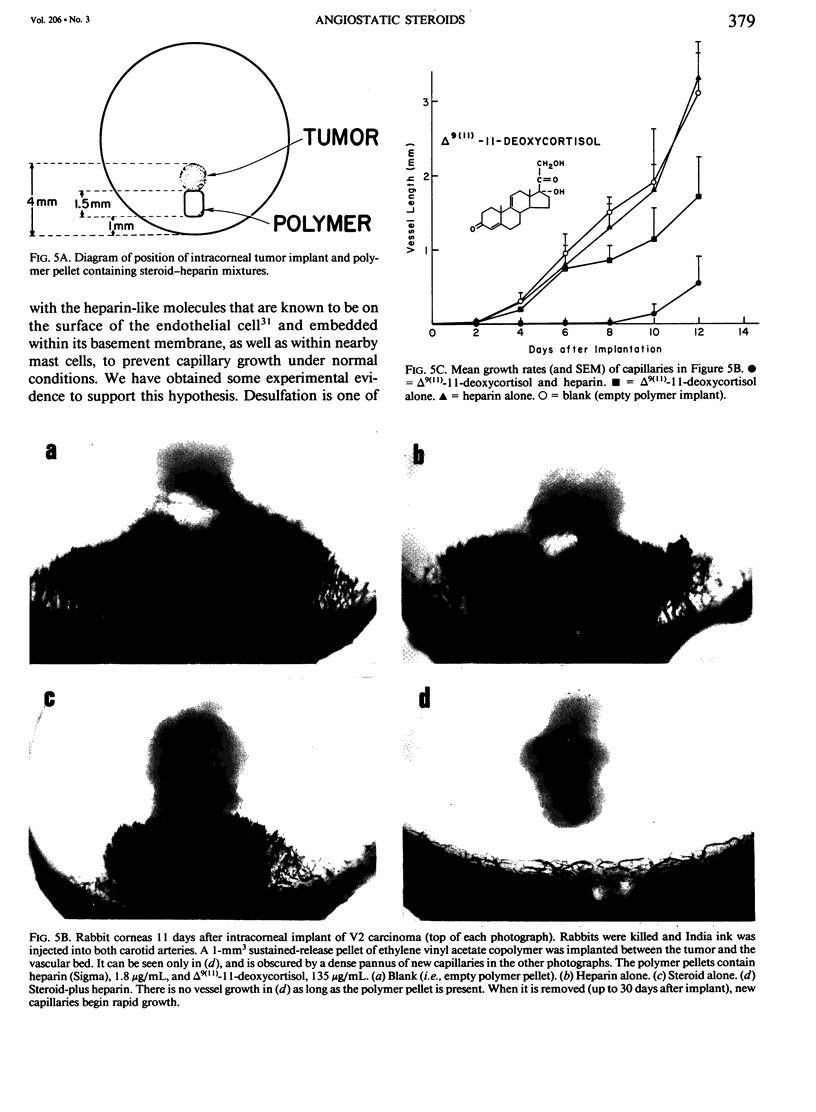
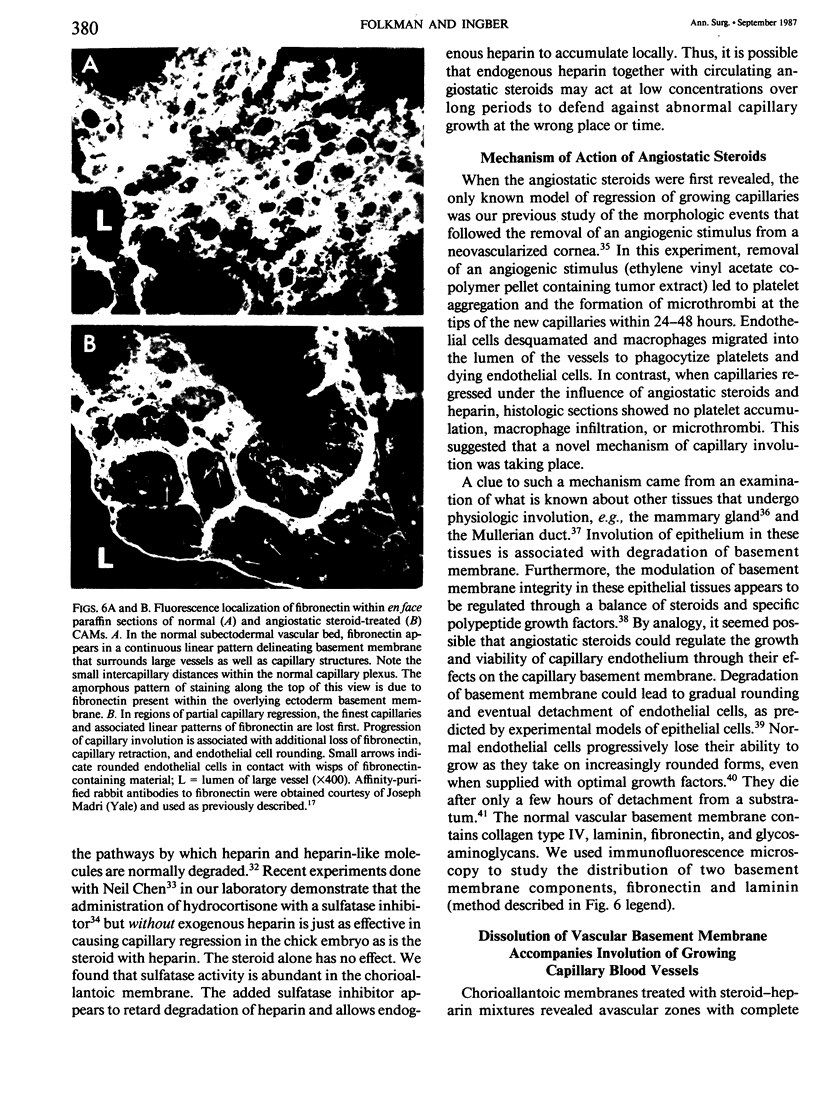


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auerbach R., Kubai L., Knighton D., Folkman J. A simple procedure for the long-term cultivation of chicken embryos. Dev Biol. 1974 Dec;41(2):391–394. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(74)90316-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ausprunk D. H., Falterman K., Folkman J. The sequence of events in the regression of corneal capillaries. Lab Invest. 1978 Mar;38(3):284–294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azizkhan R. G., Azizkhan J. C., Zetter B. R., Folkman J. Mast cell heparin stimulates migration of capillary endothelial cells in vitro. J Exp Med. 1980 Oct 1;152(4):931–944. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.4.931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brem H., Folkman J. Inhibition of tumor angiogenesis mediated by cartilage. J Exp Med. 1975 Feb 1;141(2):427–439. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.2.427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castellot J. J., Jr, Choay J., Lormeau J. C., Petitou M., Sache E., Karnovsky M. J. Structural determinants of the capacity of heparin to inhibit the proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells. II. Evidence for a pentasaccharide sequence that contains a 3-O-sulfate group. J Cell Biol. 1986 May;102(5):1979–1984. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.5.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crum R., Szabo S., Folkman J. A new class of steroids inhibits angiogenesis in the presence of heparin or a heparin fragment. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1375–1378. doi: 10.1126/science.2416056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenstein R., Sorgente N., Soble L. W., Miller A., Kuettner K. E. The resistance of certain tissues to invasion: penetrability of explanted tissues by vascularized mesenchyme. Am J Pathol. 1973 Dec;73(3):765–774. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J. Anti-angiogenesis: new concept for therapy of solid tumors. Ann Surg. 1972 Mar;175(3):409–416. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197203000-00014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J., Klagsbrun M. Angiogenic factors. Science. 1987 Jan 23;235(4787):442–447. doi: 10.1126/science.2432664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J., Langer R., Linhardt R. J., Haudenschild C., Taylor S. Angiogenesis inhibition and tumor regression caused by heparin or a heparin fragment in the presence of cortisone. Science. 1983 Aug 19;221(4612):719–725. doi: 10.1126/science.6192498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J., Moscona A. Role of cell shape in growth control. Nature. 1978 Jun 1;273(5661):345–349. doi: 10.1038/273345a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J. What is the role of endothelial cells in angiogenesis? Lab Invest. 1984 Dec;51(6):601–604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glowacki J., Mulliken J. B. Mast cells in hemangiomas and vascular malformations. Pediatrics. 1982 Jul;70(1):48–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt T. K., Knighton D. R., Thakral K. K., Goodson W. H., 3rd, Andrews W. S. Studies on inflammation and wound healing: angiogenesis and collagen synthesis stimulated in vivo by resident and activated wound macrophages. Surgery. 1984 Jul;96(1):48–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikawa H., Trelstad R. L., Hutson J. M., Manganaro T. F., Donahoe P. K. Changing patterns of fibronectin, laminin, type IV collagen, and a basement membrane proteoglycan during rat Mullerian duct regression. Dev Biol. 1984 Mar;102(1):260–263. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90190-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingber D. E., Madri J. A., Folkman J. A possible mechanism for inhibition of angiogenesis by angiostatic steroids: induction of capillary basement membrane dissolution. Endocrinology. 1986 Oct;119(4):1768–1775. doi: 10.1210/endo-119-4-1768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingber D. E., Madri J. A., Folkman J. Endothelial growth factors and extracellular matrix regulate DNA synthesis through modulation of cell and nuclear expansion. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol. 1987 May;23(5):387–394. doi: 10.1007/BF02620997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler D. A., Langer R. S., Pless N. A., Folkman J. Mast cells and tumor angiogenesis. Int J Cancer. 1976 Nov 15;18(5):703–709. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910180520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klagsbrun M., Knighton D., Folkman J. Tumor angiogenesis activity in cells grown in tissue culture. Cancer Res. 1976 Jan;36(1):110–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer R., Conn H., Vacanti J., Haudenschild C., Folkman J. Control of tumor growth in animals by infusion of an angiogenesis inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4331–4335. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer R., Folkman J. Polymers for the sustained release of proteins and other macromolecules. Nature. 1976 Oct 28;263(5580):797–800. doi: 10.1038/263797a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen A. K., Lund D. P., Langer R., Folkman J. Oral heparin results in the appearance of heparin fragments in the plasma of rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2964–2968. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polverini P. J., Leibovich S. J. Induction of neovascularization in vivo and endothelial proliferation in vitro by tumor-associated macrophages. Lab Invest. 1984 Dec;51(6):635–642. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg R. D., Fritze L. M., Castellot J. J., Jr, Karnovsky M. J. Heparin-like molecules as regulators of atherogenesis. Nouv Rev Fr Hematol. 1984;26(4):255–260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salomon D. S., Liotta L. A., Kidwell W. R. Differential response to growth factor by rat mammary epithelium plated on different collagen substrata in serum-free medium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):382–386. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shing Y., Folkman J., Haudenschild C., Lund D., Crum R., Klagsbrun M. Angiogenesis is stimulated by a tumor-derived endothelial cell growth factor. J Cell Biochem. 1985;29(4):275–287. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240290402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S., Folkman J. Protamine is an inhibitor of angiogenesis. Nature. 1982 May 27;297(5864):307–312. doi: 10.1038/297307a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wicha M. S., Liotta L. A., Vonderhaar B. K., Kidwell W. R. Effects of inhibition of basement membrane collagen deposition on rat mammary gland development. Dev Biol. 1980 Dec;80(2):253–256. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90402-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zetter B. R. Migration of capillary endothelial cells is stimulated by tumour-derived factors. Nature. 1980 May 1;285(5759):41–43. doi: 10.1038/285041a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker-Franklin D., Nabi Z. F. A substrate analog inhibitor for arylsulfatase reduces NK cell cytotoxicity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Jan 16;126(1):540–543. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90639-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]