Abstract
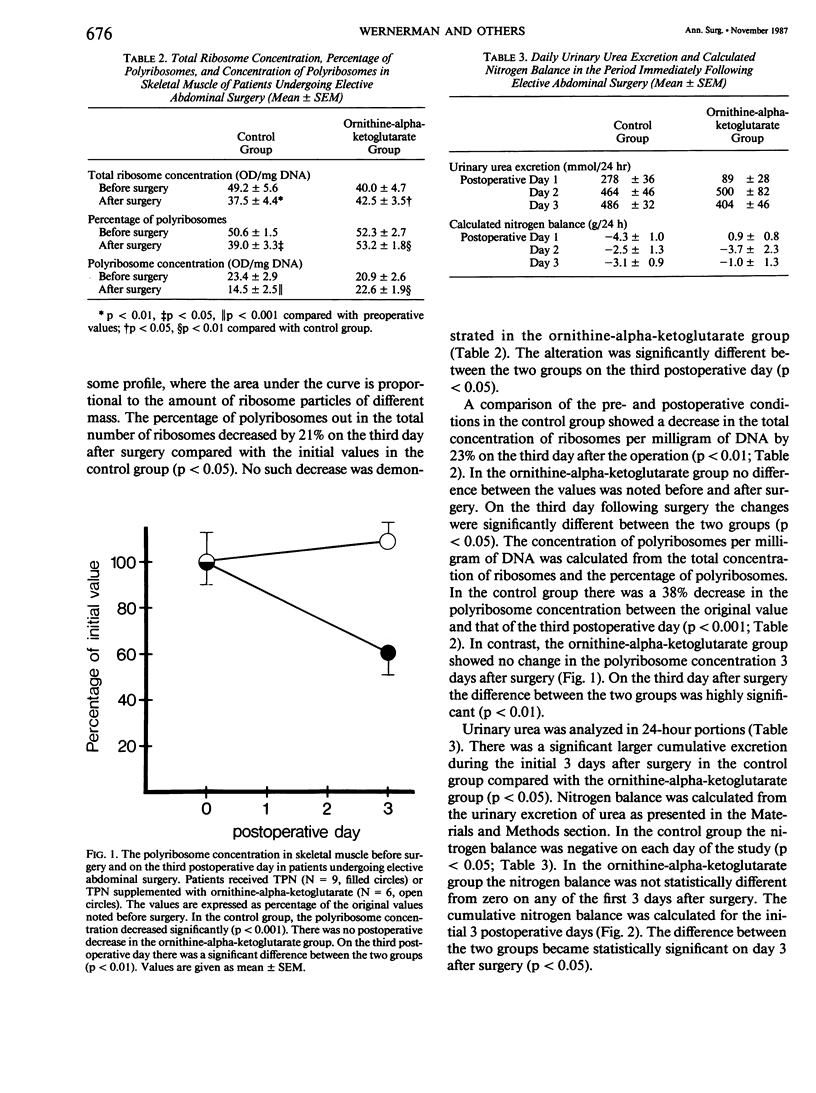
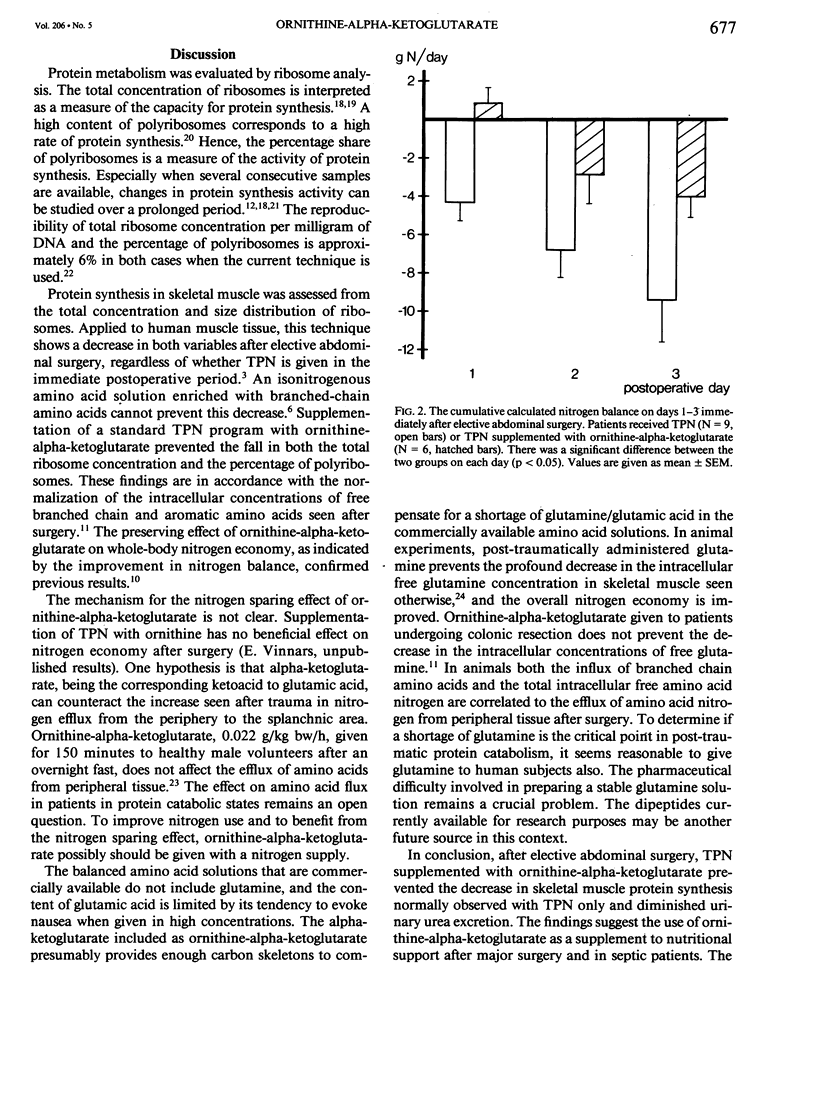
Total parenteral nutrition (TPN) was given for 3 days after elective abdominal surgery. The control group (N = 9) received TPN only and one group of patients (N = 6) received TPN supplemented with ornithine-alpha-ketoglutarate (0.35 g/kg bw/day). Protein synthesis in skeletal muscle was assessed from the total ribosome concentration and the percentage of polyribosomes. In the control group the total concentration of ribosomes decreased after surgery by 23% (p less than 0.05) and the percentage of polyribosomes decreased by 21% (p less than 0.01), whereas in the ornithine-alpha-ketoglutarate group both variables remained unaffected. The cumulative urinary urea excretion was significantly larger in the control group than in the ornithine-alpha-ketoglutarate group (p less than 0.05). The calculated nitrogen balance was negative in the control group on each day of the study (p less than 0.05), but that of the ornithine-alpha-ketoglutarate group was not statistically different from zero. The results show that postoperative maintenance of muscle protein synthesis and a more effective nitrogen use was achieved by supplementing TPN with ornithine-alpha-ketoglutarate, 0.35 g/kg bw/day.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Desai S. P., Bistrian B. R., Moldawer L. L., Blackburn G. L. Whole-body nitrogen and tyrosine metabolism in surgical patients receiving branched-chain amino acid solutions. Arch Surg. 1985 Dec;120(12):1345–1350. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1985.01390360011003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ERIKSEN L. The nature of the intermediate tetrapyrroles in protoporphyrin and heme biosynthesis. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1962;14:11–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson L. S., Reihnér E., Wahren J. Infusion of ornithine-alpha-ketoglutarate in healthy subjects: effects on protein metabolism. Clin Nutr. 1985 May;4(2):73–76. doi: 10.1016/0261-5614(85)90045-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewerth S., Allgen L. G., Fürst P., Holmström B., Odebäck A. C., Schildt B., Vinnars E. Metabolic effects of four intravenous nutritional regimens after elective surgery. I. Clinical data and biochemistry. Clin Nutr. 1983 Mar;1(4):313–324. doi: 10.1016/0261-5614(83)90010-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAWCETT J. K., SCOTT J. E. A rapid and precise method for the determination of urea. J Clin Pathol. 1960 Mar;13:156–159. doi: 10.1136/jcp.13.2.156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. J., Jiang Z. M., Colpoys M., Kapadia C. R., Smith R. J., Wilmore D. W. Branched chain amino acid uptake and muscle free amino acid concentrations predict postoperative muscle nitrogen balance. Ann Surg. 1986 Nov;204(5):513–523. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198611000-00002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapadia C. R., Colpoys M. F., Jiang Z. M., Johnson D. J., Smith R. J., Wilmore D. W. Maintenance of skeletal muscle intracellular glutamine during standard surgical trauma. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1985 Sep-Oct;9(5):583–589. doi: 10.1177/0148607185009005583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinney J. M., Elwyn D. H. Protein metabolism and injury. Annu Rev Nutr. 1983;3:433–466. doi: 10.1146/annurev.nu.03.070183.002245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson J., Liljedahl S. O., Schildt B., Fürst P., Vinnars E. Metabolic studies in multiple injured patients. Clinical features, routine chemical analyses and nitrogen balance. Acta Chir Scand. 1981;147(5):317–324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leander U., Fürst P., Vesterberg K., Vinnars E. Nitrogen sparing effect of Ornicetil in the immediate postoperative state clinical biochemistry and nitrogen balance. Clin Nutr. 1985 Feb;4(1):43–51. doi: 10.1016/0261-5614(85)90037-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackenzie T. A., Clark N. G., Bistrian B. R., Flatt J. P., Hallowell E. M., Blackburn G. L. A simple method for estimating nitrogen balance in hospitalized patients: a review and supporting data for a previously proposed technique. J Am Coll Nutr. 1985;4(5):575–581. doi: 10.1080/07315724.1985.10720100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Keefe S. J., Moldawer L. L., Young V. R., Blackburn G. L. The influence of intravenous nutrition on protein dynamics following surgery. Metabolism. 1981 Dec;30(12):1150–1158. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(81)90034-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rennie M. J., Bennegård K., Edén E., Emery P. W., Lundholm K. Urinary excretion and efflux from the leg of 3-methylhistidine before and after major surgical operation. Metabolism. 1984 Mar;33(3):250–256. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(84)90046-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setaro F., Morley C. G. A modified fluorometric method for the determination of microgram quantities of DNA from cell or tissue cultures. Anal Biochem. 1976 Mar;71(1):313–317. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90043-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wernerman J., von der Decken A., Vinnars E. Polyribosome concentration in human skeletal muscle after starvation and parenteral or enteral refeeding. Metabolism. 1986 May;35(5):447–451. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(86)90136-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wernerman J., von der Decken A., Vinnars E. Protein synthesis in skeletal muscle in relation to nitrogen balance after abdominal surgery: the effect of total parenteral nutrition. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1986 Nov-Dec;10(6):578–582. doi: 10.1177/0148607186010006578. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wernerman J., von der Decken A., Vinnars E. Size distribution of ribosomes in biopsy specimens of human skeletal muscle during starvation. Metabolism. 1985 Jul;34(7):665–669. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(85)90095-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wernerman J., von der Decken A., Vinnars E. The diurnal pattern of protein synthesis in human skeletal muscle. Clin Nutr. 1985 Nov;4(4):203–205. doi: 10.1016/0261-5614(85)90004-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wernerman J., von der Decken A., Vinnars E. The interpretation of ribosome determinations to assess protein synthesis in human skeletal muscle. Infusionsther Klin Ernahr. 1986 Aug;13(4):162–165. doi: 10.1159/000222133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


