Abstract
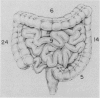
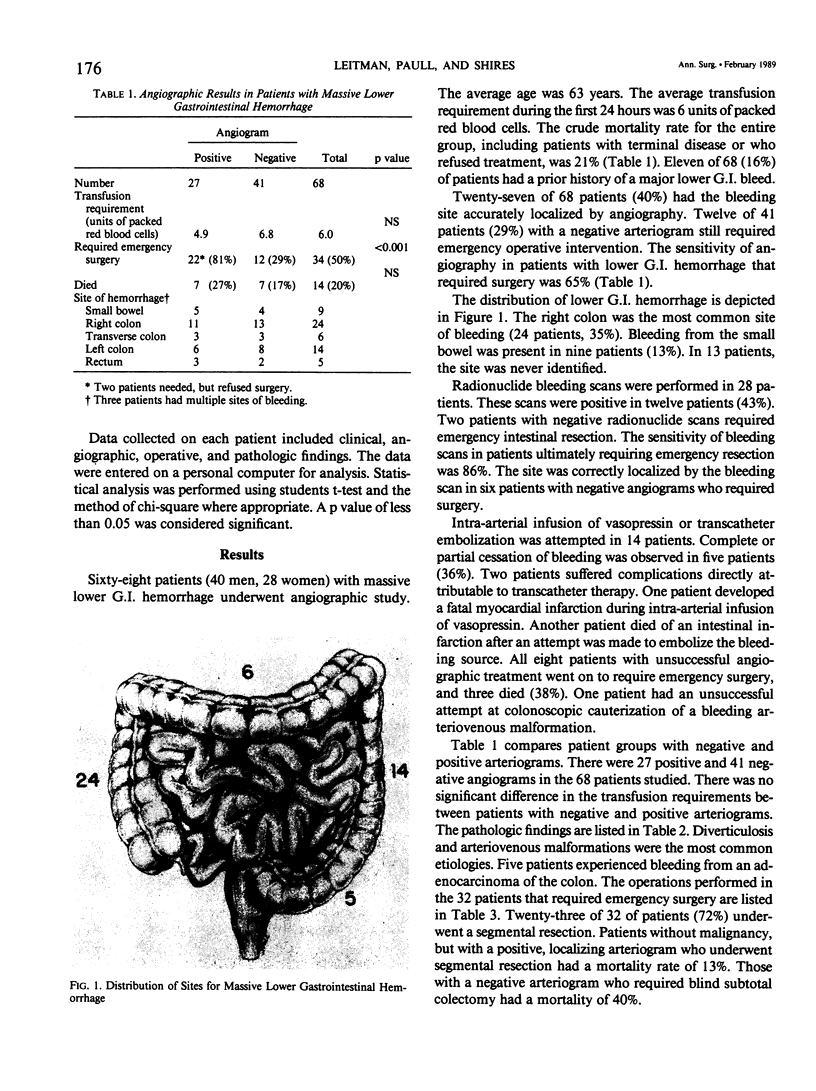
Sixty-eight patients with massive lower gastrointestinal (G.I.) hemorrhage underwent emergency arteriography. Patients were transfused an average of six units of packed red blood cells within 24 hours of admission. The bleeding source was localized arteriographically in 27 (40%), with a sensitivity of 65% among patients requiring emergency resection. However, twelve of the 41 patients with a negative arteriogram still required emergency intestinal resection for continued hemorrhage. Radionuclide bleeding scans had a sensitivity of 86%. The right colon was the most common site of bleeding (35%). Diverticulosis and arteriovenous malformation were the most common etiologies. Selective intra-arterial infusion of vasopressin and embolization were successful in 36% of cases in which they were employed and contributed to fatality in two patients. Twenty-three patients underwent segmental resection, whereas seven patients required subtotal colectomy for multiple bleeding sites or negative studies in the face continued hemorrhage. Intraoperative infusion of methylene blue via angiographic catheters allowed successful localization and resection of bleeding small bowel segments in three patients. Overall mortality was 21%. The mortality for patients without a malignancy, with a positive preoperative arteriogram, and emergency segmental resection was 13%.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alavi A., Ring E. J. Localization of gastrointestinal bleeding: superiority of 99mTc sulfur colloid compared with angiography. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1981 Oct;137(4):741–748. doi: 10.2214/ajr.137.4.741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Athanasoulis C. A., Baum S., Rösch J., Waltman A. C., Ring E. J., Smith J. C., Jr, Sugarbaker E., Wood W. Mesenteric arterial infusions of vasopressin for hemorrhage from colonic diverticulosis. Am J Surg. 1975 Feb;129(2):212–216. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(75)90300-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Athanasoulis C. A., Moncure A. C., Greenfield A. J., Ryan J. A., Dodson T. F. Intraoperative localization of small bowel bleeding sites with combined use of angiographic methods and methylene blue injection. Surgery. 1980 Jan;87(1):77–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baum S., Athanasoulis C. A., Waltman A. C., Galdabini J., Schapiro R. H., Warshaw A. L., Ottinger L. W. Angiodysplasia of the right colon: a cause of gastrointestinal bleeding. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1977 Nov;129(5):789–794. doi: 10.2214/ajr.129.5.789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baum S., Rösch J., Dotter C. T., Ring E. J., Athanasoulis C., Waltman A. C., Courey W. R. Selective mesenteric arterial infusions in the management of massive diverticular hemorrhage. N Engl J Med. 1973 Jun 14;288(24):1269–1272. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197306142882404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaton H. L. Small intestinal bleeding. Method for intraoperative localization. N Y State J Med. 1982 Feb;82(2):171–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boley S. J., Brandt L. J., Frank M. S. Severe lower intestinal bleeding: diagnosis and treatment. Clin Gastroenterol. 1981 Jan;10(1):65–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boley S. J., DiBiase A., Brandt L. J., Sammartano R. J. Lower intestinal bleeding in the elderly. Am J Surg. 1979 Jan;137(1):57–64. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(79)90011-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boley S. J., Sammartano R., Brandt L. J., Sprayregen S. Vascular ectasias of the colon. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1979 Sep;149(3):353–359. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt L. J., Boley S. J. The role of colonoscopy in the diagnosis and management of lower intestinal bleeding. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1984;102:61–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britt L. G., Warren L., Moore O. F., 3rd Selective management of lower gastrointestinal bleeding. Am Surg. 1983 Mar;49(3):121–125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Browder W., Cerise E. J., Litwin M. S. Impact of emergency angiography in massive lower gastrointestinal bleeding. Ann Surg. 1986 Nov;204(5):530–536. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198611000-00004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casarella W. J., Galloway S. J., Taxin R. N., Follett D. A., Pollock E. J., Seaman W. B. "Lower" gastrointestinal tract hemorrhage: new concepts based on arteriography. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med. 1974 Jun;121(2):357–368. doi: 10.2214/ajr.121.2.357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho S. R., Tisnado J., Liu C. I., Beachley M. C., Shaw C. I., Kipreos B. E., Schneider V. Bleeding cytomegalovirus ulcers of the colon: barium enema nad angiography. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1981 Jun;136(6):1213–1215. doi: 10.2214/ajr.136.6.1213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colacchio T. A., Forde K. A., Patsos T. J., Nunez D. Impact of modern diagnostic methods on the management of active rectal bleeding. Ten year experience. Am J Surg. 1982 May;143(5):607–610. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(82)90175-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckstein M. R., Athanasoulis C. A. Gastrointestinal bleeding. An angiographic perspective. Surg Clin North Am. 1984 Feb;64(1):37–51. doi: 10.1016/s0039-6109(16)43231-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans W. E., O'Dorisio T. M., Molnar W., Martin E. W., Jr, Wooley C. F., Cooperman M. Intraoperative localization of intestinal arteriovenous malformation. Arch Surg. 1978 Apr;113(4):410–412. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1978.01370160068010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giacchino J. L., Geis W. P., Pickleman J. R., Dado D. V., Hadcock W. E., Freeark R. J. Changing perspectives in massive lower intestinal hemorrhage. Surgery. 1979 Sep;86(3):368–376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomes A. S., Lois J. F., McCoy R. D. Angiographic treatment of gastrointestinal hemorrhage: comparison of vasopressin infusion and embolization. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1986 May;146(5):1031–1037. doi: 10.2214/ajr.146.5.1031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta S., Luna E., Kingsley S., Prince M., Herrera N. Detection of gastrointestinal bleeding by radionuclide scintigraphy. Am J Gastroenterol. 1984 Jan;79(1):26–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvin G. L., 3rd, Horsley J. S., 3rd, Caruana J. A., Jr The morbidity and mortality of emergent operations for colorectal disease. Ann Surg. 1984 May;199(5):598–603. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198405000-00015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawler G., Bircher M., Spencer J., Hemingway A. P., Allison D. J. Embolisation in colonic bleeding. Br J Radiol. 1985 Jan;58(685):83–84. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-58-685-83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Max M. H., Richardson J. D., Flint L. M., Jr, Knutson C. O., Schwesinger W. Colonoscopic diagnosis of angiodysplasias of the gastrointestinal tract. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1981 Feb;152(2):195–199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers M. A., Alonso D. R., Gray G. F., Baer J. W. Pathogenesis of bleeding colonic diverticulosis. Gastroenterology. 1976 Oct;71(4):577–583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore J. D., Thompson N. W., Appelman H. D., Foley D. Arteriovenous malformations of the gastrointestinal tract. Arch Surg. 1976 Apr;111(4):381–389. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1976.01360220077013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nath R. L., Sequeira J. C., Weitzman A. F., Birkett D. H., Williams L. F., Jr Lower gastrointestinal bleeding. Diagnostic approach and management conclusions. Am J Surg. 1981 Apr;141(4):478–481. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(81)90143-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nusbaum M., Baum S., Blakemore W. S., Tumen H. Clinical experience with selective intra-arterial infusion of vasopressin in the control of gastrointestinal bleeding from arterial sources. Am J Surg. 1972 Feb;123(2):165–172. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(72)90328-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenkrantz H., Bookstein J. J., Rosen R. J., Goff W. B., 2nd, Healy J. F. Postembolic colonic infarction. Radiology. 1982 Jan;142(1):47–51. doi: 10.1148/radiology.142.1.6975953. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tedesco F. J., Gottfried E. B., Corless J. K., Brownstein R. E. Prospective evaluation of hospitalized patients with nonactive lower intestinal bleeding--timing and role of barium enema and colonoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 1984 Oct;30(5):281–283. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5107(84)72418-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch C. E., Athanasoulis C. A., Galdabini J. J. Hemorrhage from the large bowel with special reference to angiodysplasia and diverticular disease. World J Surg. 1978 Jan;2(1):73–83. doi: 10.1007/BF01574466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright H. K., Pelliccia O., Higgins E. F., Jr, Sreenivas V., Gupta A. Controlled, semielective, segmental resection for massive colonic hemorrhage. Am J Surg. 1980 Apr;139(4):535–538. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(80)90333-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]