Abstract
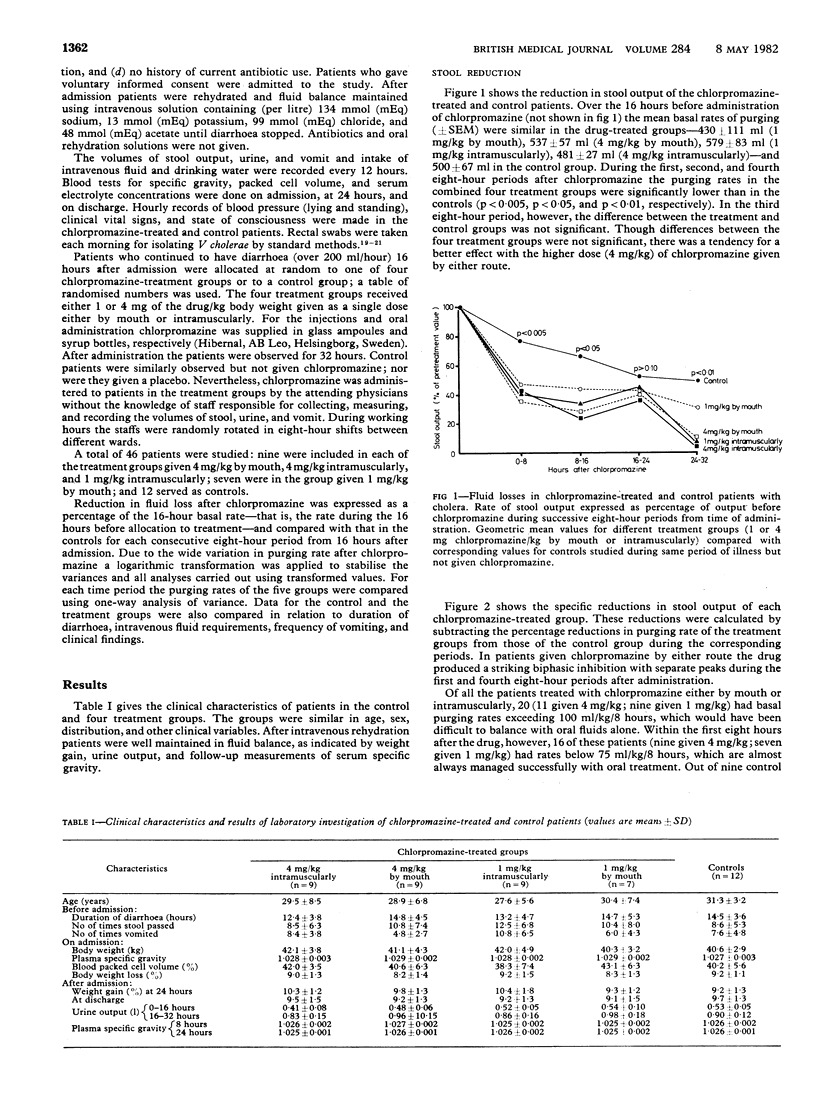
A randomised controlled trial was conducted to investigate the ability of chlorpromazine to reduce intestinal secretion in cholera. Chlorpromazine had reduced loss of intestinal fluid in animals with diarrhoea induced by cholera toxin, and in a preliminary study the drug had reduced purging in patients with cholera. Forty-six adults with cholera were included in the randomised trial. Of these, 34 were treated with chlorpromazine (1 mg/kg or 4 mg/kg either by mouth or intramuscularly) and 12 served as controls. After treatment with the drug there was a significantly greater reduction in the rate of fluid loss in the treated patients than in the controls during the first (p less than 0.005), second (p less than 0.05), and fourth (p less than 0.01) eight-hour periods, but not during the third eight-hour period; the dose of 4 mg/kg was only marginally more effective than 1 mg/kg. The effect of chlorpromazine was strikingly biphasic, with one peak during the first eight hours and another 24-32 hours after administration. Chlorpromazine also significantly reduced the duration of diarrhoea, frequency of vomiting, and amount of intravenous fluid required. The drug induced mild sedation and no hypotension in these well-hydrated patients. These findings confirm the effectiveness of chlorpromazine in reducing fluid loss in cholera. A sedative effect, however, especially in children, may limit its usefulness and requires further study.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BENENSON A. S., ISLAM M. R., GREENOUGH W. B., 3rd RAPID IDENTIFICATION OF VIBRIO CHOLERAE BY DARKFIELD MICROSCOPY. Bull World Health Organ. 1964;30:827–831. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FEELEY J. C. Isolation of cholera vibrios by positive-recognition plating procedures. J Bacteriol. 1962 Oct;84:866–867. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.4.866-867.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field M., Fromm D., al-Awqati Q., Greenough W. B., 3rd Effect of cholera enterotoxin on ion transport across isolated ileal mucosa. J Clin Invest. 1972 Apr;51(4):796–804. doi: 10.1172/JCI106874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren J., Lange S., Lönnroth I. Reversal of cyclic AMP-mediated intestinal secretion in mice by chlorpromazine. Gastroenterology. 1978 Dec;75(6):1103–1108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ilundain A., Naftalin R. J. Role of Ca(2+)-dependent regulator protein in intestinal secretion. Nature. 1979 May 31;279(5712):446–448. doi: 10.1038/279446a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakiuchi S., Rall T. W. The influence of chemical agents on the accumulation of adenosine 3',5'-Phosphate in slices of rabbit cerebellum. Mol Pharmacol. 1968 Jul;4(4):367–378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimbert D. V. Cyclic nucleotides and their role in gastrointestinal secretion. Gastroenterology. 1974 Nov;67(5):1023–1064. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lönnroth I., Andrén B., Lange S., Martinsson K., Holmgren J. Chlorpromazine reverses diarrhea in piglets caused by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):900–905. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.900-905.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lönnroth I., Holmgren J., Lange S. Chlorpromazine inhibits cholera toxin-induced intestinal hypersecretion. Med Biol. 1977 Jun;55(3):126–129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nalin D. R., Cash R. A., Islam R., Molla M., Phillips R. A. Oral maintenance therapy for cholera in adults. Lancet. 1968 Aug 17;2(7564):370–373. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)90591-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osnes J. B., Christoffersen T., Morland J., Oye I. Chlorpromazine and hormonal elevation of cyclic AMP contents in turkey erythrocytes and in perfused rat heart and liver. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1976 Mar;38(3):195–208. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1976.tb03112.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson D. K., Ebel H., DiBona D. R., Sharp G. W. Localization of the action of cholera toxin on adenyl cyclase in mucosal epithelial cells of rabbit intestine. J Clin Invest. 1972 Sep;51(9):2292–2298. doi: 10.1172/JCI107039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce N. F., Sack R. B., Mitra R. C., Banwell J. G., Brigham K. L., Fedson D. S., Mondal A. Replacement of water and electrolyte losses in cholera by an oral glucose-electrolyte solution. Ann Intern Med. 1969 Jun;70(6):1173–1181. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-70-6-1173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabbani G. H., Greenough W. B., 3rd, Holmgren J., Lönnroth I. Chlorpromazine reduces fluid-loss in cholera. Lancet. 1979 Feb 24;1(8113):410–412. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)90885-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schafer D. E., Lust W. D., Sircar B., Goldberg N. D. Elevated concentration of adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate in intestinal mucosa after treatment with cholera toxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Oct;67(2):851–856. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.2.851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeman P. The membrane actions of anesthetics and tranquilizers. Pharmacol Rev. 1972 Dec;24(4):583–655. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp G. W., Hynie S. Stimulation of intestinal adenyl cyclase by cholera toxin. Nature. 1971 Jan 22;229(5282):266–269. doi: 10.1038/229266a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. L., Field M. In vitro antisecretory effects of trifluoperazine and other neuroleptics in rabbit and human small intestine. Gastroenterology. 1980 Jun;78(6):1545–1553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff J., Jones A. B. Inhibition of hormone-sensitive adenyl cyclase by phenothiazines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Feb;65(2):454–459. doi: 10.1073/pnas.65.2.454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


