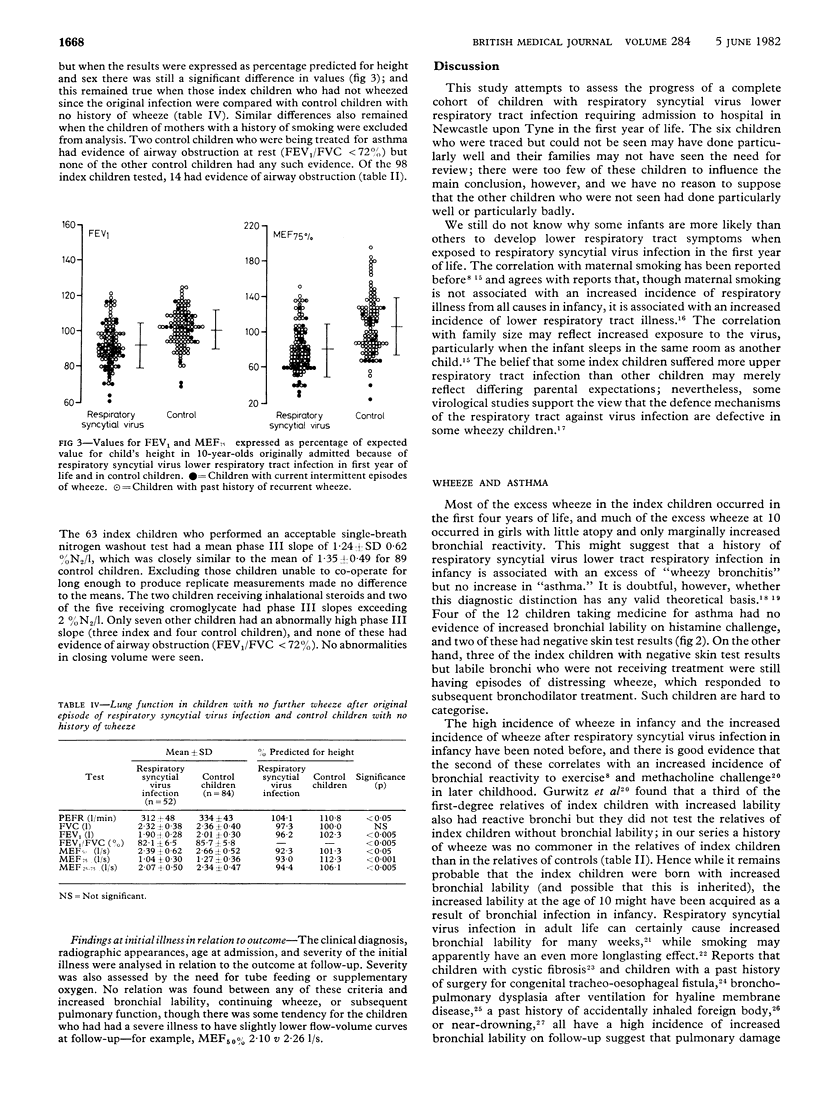
Abstract
Of the 180 children admitted to hospitals in Tyneside in the first year of life with proved respiratory syncytial virus lower respiratory tract infection, 130 were seen for review 10 years later and 34 of the remaining 50 children accounted for. Skin tests, lung function tests, and histamine-challenge and exercise tests for bronchial lability were undertaken in over 100 of the index children and a similar number of control children. A total of 55 (42%) of the 130 index children had had further episodes of wheeze, while only 21 (19%) out of 111 controls had ever wheezed; but few (6.2% v 4.5%) had troublesome symptoms at the age of 10. There was a threefold increase in the incidence of bronchial lability in the index children but no excess of atopy. Maximum expiratory air flow was reduced throughout the vital capacity manoeuvre in the index children, even when those with a history of recurrent wheeze were excluded. Results of single-breath nitrogen washout tests were normal, however, suggesting that ventilation was not appreciably uneven, even though expiratory flow was restricted. These differences might have been caused by infection damaging the growing lung but might also be explained by pre-existing differences in the airway, rendering certain children more susceptible to symptomatic infection when first challenged by the virus in infancy.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anthonisen N. R., Danson J., Robertson P. C., Ross W. R. Airway closure as a function of age. Respir Physiol. 1969 Dec;8(1):58–65. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(69)90044-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becroft D. M. Histopathology of fatal adenovirus infection of the respiratory tract in young children. J Clin Pathol. 1967 Jul;20(4):561–569. doi: 10.1136/jcp.20.4.561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft D. W., Killian D. N., Mellon J. J., Hargreave F. E. Bronchial reactivity to inhaled histamine: a method and clinical survey. Clin Allergy. 1977 May;7(3):235–243. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1977.tb01448.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Court S. D. The definition of acute respiratory illnesses in children. Postgrad Med J. 1973 Nov;49(577):771–776. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.49.577.771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craven N., Sidwall G., West P., McCarthy D. S., Cherniack R. M. Computer analysis of the single-breath nitrogen washout curve. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1976 Apr;113(4):445–449. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1976.113.4.445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fergusson D. M., Horwood L. J., Shannon F. T. Parental smoking and respiratory illness in infancy. Arch Dis Child. 1980 May;55(5):358–361. doi: 10.1136/adc.55.5.358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerrard J. W., Cockcroft D. W., Mink J. T., Cotton D. J., Poonawala R., Dosman J. A. Increased nonspecific bronchial reactivity in cigarette smokers with normal lung function. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1980 Oct;122(4):577–581. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1980.122.4.577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall W. J., Hall C. B., Speers D. M. Respiratory syncytial virus infection in adults: clinical, virologic, and serial pulmonary function studies. Ann Intern Med. 1978 Feb;88(2):203–205. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-88-2-203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn M. E., Brain E. A., Gregg I., Inglis J. M., Yealland S. J., Taylor P. Respiratory viral infection and wheezy bronchitis in childhood. Thorax. 1979 Feb;34(1):23–28. doi: 10.1136/thx.34.1.23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kattan M., Keens T. G., Lapierre J. G., Levison H., Bryan A. C., Reilly B. J. Pulmonary function abnormalities in symptom-free children after bronchiolitis. Pediatrics. 1977 May;59(5):683–688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laing I., Reidel F., Yap P. L., Simpson H. Atopy predisposing to acute bronchiolitis during an epidemic of respiratory syncytial virus. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1982 Apr 10;284(6322):1070–1072. doi: 10.1136/bmj.284.6322.1070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellis C. M., Levison H. Bronchial reactivity in cystic fibrosis. Pediatrics. 1978 Mar;61(3):446–450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan D. W., Levison H. Lung function in children following repair of tracheoesophageal fistula. J Pediatr. 1979 Jul;95(1):24–27. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(79)80076-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minor T. E., Baker J. W., Dick E. C., DeMeo A. N., Ouellette J. J., Cohen M., Reed C. E. Greater frequency of viral respiratory infections in asthmatic children as compared with their nonasthmatic siblings. J Pediatr. 1974 Oct;85(4):472–477. doi: 10.1016/S0022-3476(74)80447-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pullan C. R., Toms G. L., Martin A. J., Gardner P. S., Webb J. K., Appleton D. R. Breast-feeding and respiratory syncytial virus infection. Br Med J. 1980 Oct 18;281(6247):1034–1036. doi: 10.1136/bmj.281.6247.1034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rooney J. C., Williams H. E. The relationship between proved viral bronchiolitis and subsequent wheezing. J Pediatr. 1971 Nov;79(5):744–747. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(71)80385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibbald B., Horn M. E., Gregg I. A family study of the genetic basis of asthma and wheezy bronchitis. Arch Dis Child. 1980 May;55(5):354–357. doi: 10.1136/adc.55.5.354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon G., Jordan W. S., Jr Infectious and allergic aspects of bronchiolitis. J Pediatr. 1967 Apr;70(4):533–538. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(67)80036-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sims D. G., Gardner P. S., Weightman D., Turner M. W., Soothill J. F. Atopy does not predispose to RSV bronchiolitis or postbronchiolitic wheezing. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1981 Jun 27;282(6282):2086–2088. doi: 10.1136/bmj.282.6282.2086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smyth J. A., Tabachnik E., Duncan W. J., Reilly B. J., Levison H. Pulmonary function and bronchial hyperreactivity in long-term survivors of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Pediatrics. 1981 Sep;68(3):336–340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokes G. M., Milner A. D., Hodges I. G., Groggins R. C. Lung function abnormalities after acute bronchiolitis. J Pediatr. 1981 Jun;98(6):871–874. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(81)80577-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WITTIG H. J., GLASER J. The relationship between bronchiolitis and childhood asthma; a follow-up study of 100 cases of bronchiolitis. J Allergy. 1959 Jan-Feb;30(1):19–23. doi: 10.1016/0021-8707(59)90054-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams H., McNicol K. N. Prevalence, natural history, and relationship of wheezy bronchitis and asthma in children. An epidemiological study. Br Med J. 1969 Nov 8;4(5679):321–325. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5679.321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zweiman B., Schoenwetter W. F., Hildreth E. A. The relationship between bronchiolitis and allergic asthma. A prospective study with allergy evaluation. J Allergy. 1966 Jan;37(1):48–53. doi: 10.1016/0021-8707(66)90109-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


