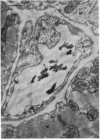
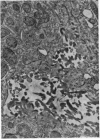
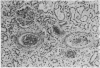
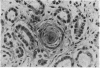
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BAHNSON H. T., ZIEGLER R. F. A consideration of the causes of death following operation for congenital heart disease of the cyanotic type. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1950 Jan;90(1):60–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BORGSTROM S., GELIN L. E., ZEDERFELDT B. The formation of vein thrombi following tissue injury: an experimental study in rabbits. Acta Chir Scand Suppl. 1959;Suppl 247:1–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaisdell F. W., Lim R. C., Jr, Amberg J. R., Choy S. H., Hall A. D., Thomas A. N. Pulmonary microembolism. A cause of morbidity and death after major vascular surgery. Arch Surg. 1966 Nov;93(5):776–786. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1966.01330050080012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodsky I., Gill D. N., Lusch C. J. Fibrinolysis in congenital heart disease. Preoperative treatment with epsilon-aminocaproic acid. Am J Clin Pathol. 1969 Jan;51(1):51–57. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/51.1.51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COON W. W., HODGSON P. E. Fibrinolysis in surgery patients. I. Possible relationship to a hemorrhagic diathesis. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1952 Dec;95(6):717–724. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COPENHAVER W. M., MOORE D. H., RUSKA H. Electron microscopic and histochemical observations of muscle degeneration after tourniquet. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1956 Nov 25;2(6):755–764. doi: 10.1083/jcb.2.6.755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CROWELL J. W., READ W. L. In vivo coagulation; a probable cause of irreversible shock. Am J Physiol. 1955 Dec;183(3):565–569. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1955.183.3.565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CROWELL J. W., SHARPE G. P., LAMBRIGHT R. L., READ W. L. The mechanism of death after resuscitation following acute circulatory failure. Surgery. 1955 Oct;38(4):696–702. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis L. H., Stewart J. L., Conrad M. E. A consumption coagulation defect in congenital cyanotic heart disease and its treatment with heparin. J Pediatr. 1967 Sep;71(3):407–410. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(67)80302-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis L. H., Stewart J. L., Conrad M. E. Heparin treatment of haemorrhagic diathesis in cyanotic congenital heart-disease. Lancet. 1967 May 20;1(7499):1088–1089. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)92655-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GASSER C., GAUTIER E., STECK A., SIEBENMANN R. E., OECHSLIN R. Hämolytisch-urämische Syndrome: bilaterale Nierenrindennekrosen bei akuten erworbenen hämolytischen Anämien. Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1955 Sep 20;85(38-39):905–909. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIANANTONIO C., VITACCO M., MENDILAHARZU F., RUTTY A., MENDILAHARZU J. THE HEMOLYTIC-UREMIC SYNDROME. J Pediatr. 1964 Apr;64:478–491. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(64)80337-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glasgow L. A., Balduzzi P. Isolation of Coxsackie virus group A, type 4, from a patient with hemolytic-uremic syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1965 Sep 30;273(14):754–756. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196509302731407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARTMANN R. C. A hemorrhagic disorder occurring in patients with cyanotic congenital heart disease. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1952 Jul;91(1):49–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HITZIG W. H. THERAPIE MIT ANTIKOAGULANTIEN IN DER PAEDIATRIE. Helv Paediatr Acta. 1964 Aug;19:213–222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hathaway W. E., Mull M. M., Pechet G. S. Disseminated intravascular coagulation in the newborn. Pediatrics. 1969 Feb;43(2):233–240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsh J., McBride J. A. Increased platelet adhesiveness in recurrent venous thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. Br Med J. 1965 Oct 2;2(5465):797–799. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5465.797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim R. C., Jr, Blaisdell F. W., Choy S. H., Hall A. D., Thomas A. N. Massive pulmonary microembolism in regional shock. Surg Forum. 1966;17:13–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay D. G., Franciosi R., Zeller J. Symposium on thrombohemorrhagic phenomena. II. Am J Cardiol. 1967 Sep;20(3):374–380. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(67)90061-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay D. G., Margaretten W., Csavossy I. An electron microscope study of endotoxin shock in rhesus monkeys. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1967 Oct;125(4):825–832. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHOENFELD M. R., LEPOW H., WOLL F., EDIS G. Acid hyperphenylphosphatasia in thrombophlebitis and pulmonary embolism. Ann Intern Med. 1962 Sep;57:468–471. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-57-3-468. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHEEHAN H. L., DAVIS J. C. Renal ischaemia with failed reflow. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1959 Jul;78:105–120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starzl T. E., Lerner R. A., Dixon F. J., Groth C. G., Brettschneider L., Terasaki P. I. Shwartzman reaction after human renal homotransplantation. N Engl J Med. 1968 Mar 21;278(12):642–648. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196803212781202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. P. Treatment of pulmonary embolic disease. A critical review of some aspects of current therapy. N Engl J Med. 1965 Oct 21;273(17):885–892. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196510212731701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitaker A. N., McKay D. G. Induction of hypotension in rhesus monkeys and rabbits by intravenous thrombin infusion. Lab Invest. 1969 Jan;20(1):79–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams G. M., Hume D. M., Hudson R. P., Jr, Morris P. J., Kano K., Milgrom F. "Hyperacute" renal-homograft rejection in man. N Engl J Med. 1968 Sep 19;279(12):611–618. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196809192791201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]