Abstract
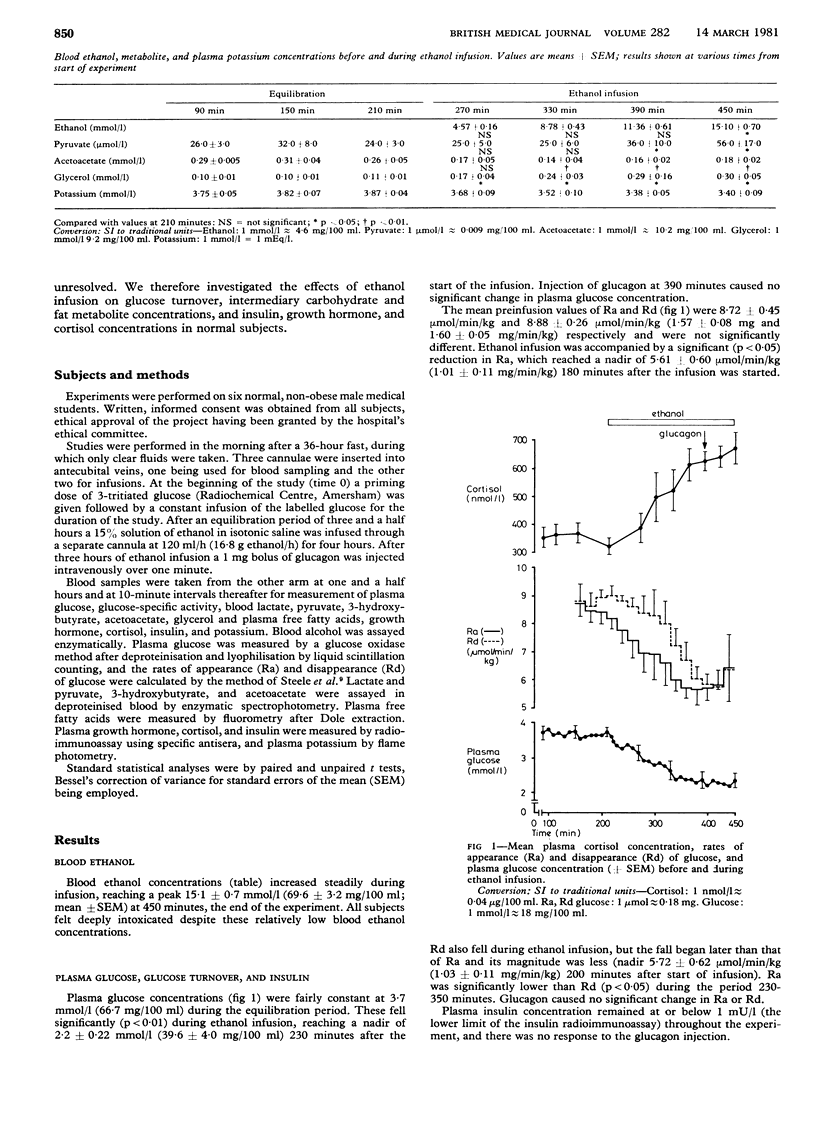
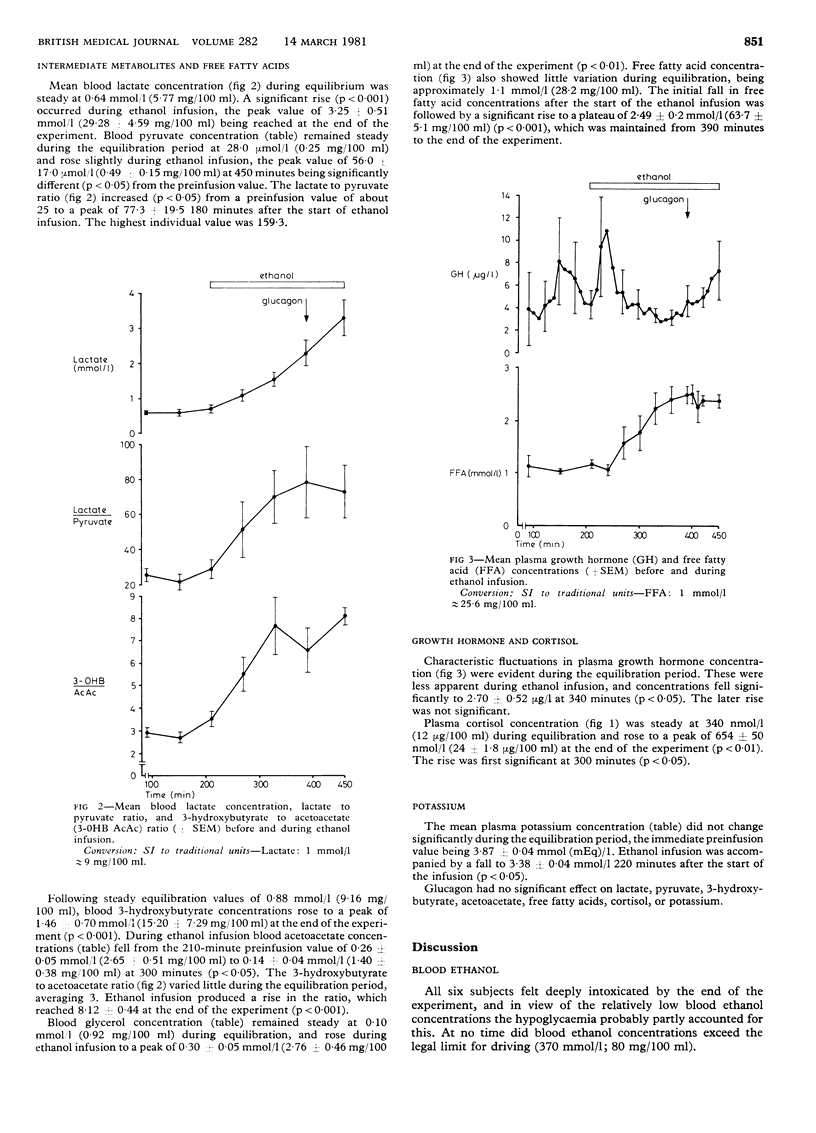
Infusion of 67 g ethanol over four hours in fasted, non-obese normal men (a) induced hypoglycaemia by inhibiting gluconeogenesis; (b) produced noticeable increases in blood lactate, 3-hydroxybutyrate, and free fatty acid concentrations; (c) depressed plasma growth hormone concentrations, despite hypoglycaemia; and (d) raised plasma cortisol concentrations before significant hypoglycaemia occurred. These metabolic changes were explained by the reduction of redox state which accompanies ethanol oxidation. The pronounced changes in metabolic values recorded during this study suggested that the use of parenteral feeding regimens including ethanol needs to be reconsidered.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARKY R. A., FREINKEL N. ALCOHOL HYPOGLYCEMIA. EFFECTS OF ETHANOL ON PLASMA. 3. GLUCOSE, KETONES, AND FREE FATTY ACIDS IN "JUVENILE" DIABETICS: A MODEL FOR "NONKETOTIC DIABETIC ACIDOSIS"? Arch Intern Med. 1964 Oct;114:501–507. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1964.03860100083009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abramson E. A., Arky R. A. Acute antilipolytic effects of ethyl alcohol and acetate in man. J Lab Clin Med. 1968 Jul;72(1):105–117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagdade J. D., Gale C. C., Porte D., Jr Hormone fuel interrelationships during alcohol hypoglycemia in man. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1972 Nov;141(2):540–542. doi: 10.3181/00379727-141-36817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackard W. G., Boylen C. T., Hinson T. C., Nelson N. C. Effect of lipid and ketone infusions on insulin-induced growth hormone elevations in rhesus monkeys. Endocrinology. 1969 Dec;85(6):1180–1185. doi: 10.1210/endo-85-6-1180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P. M., Tompkins C. V., Juul S., Sönksen P. H. Mechanism of action of insulin in diabetic patients: a dose-related effect on glucose production and utilisation. Br Med J. 1978 May 13;1(6122):1239–1242. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6122.1239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREINKEL N., COHEN A. K., ARKY R. A., FOSTER A. E. ALCOHOL HYPOGLYCEMIA. II. A POSTULATED MECHANISM OF ACTION BASED ON EXPERIMENTS WITH RAT LIVER SLICES. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1965 Jan;25:76–94. doi: 10.1210/jcem-25-1-76. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freinkel N., Singer D. L., Arky R. A., Bleicher S. J., Anderson J. B., Silbert C. K. ALCOHOL HYPOGLYCEMIA. I. CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM OF PATIENTS WITH CLINICAL ALCOHOL HYPOGLYCEMIA AND THE EXPERIMENTAL REPRODUCTION OF THE SYNDROME WITH PURE ETHANOL. J Clin Invest. 1963 Jul;42(7):1112–1133. doi: 10.1172/JCI104797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreisberg R. A., Owen W. C., Siegal A. M. Ethanol-induced hyperlacticacidemia: inhibition of lactate utilization. J Clin Invest. 1971 Jan;50(1):166–174. doi: 10.1172/JCI106470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIEBER C. S., LEEVY C. M., STEIN S. W., GEORGE W. S., CHERRICK G. R., ABELMANN W. H., DAVIDSON G. S. Effect of ethanol on plasma free fatty acids in man. J Lab Clin Med. 1962 May;59:826–832. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lochner A., Wulff J., Madison L. L. Ethanol-induced hypoglycemia. I. The acute effects of glucose output and peripheral glucose utilization in fasted dogs. Metabolism. 1967 Jan;16(1):1–18. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(67)90154-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundquist F., Tygstrup N., Winkler K., Jensen K. B. Glycerol metabolism in the human liver: inhibition by ethanol. Science. 1965 Oct 29;150(3696):616–617. doi: 10.1126/science.150.3696.616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Priem H. A., Shanley B. C., Malan C. Effect of alcohol administration on plasma growth hormone response to insulin-induced hypoglycemia. Metabolism. 1976 Apr;25(4):397–403. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(76)90071-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees L. H., Besser G. M., Jeffcoate W. J., Goldie D. J., Marks V. Alcohol-induced pseudo-Cushing's syndrome. Lancet. 1977 Apr 2;1(8014):726–728. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)92169-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEELE R., WALL J. S., DE BODO R. C., ALTSZULER N. Measurement of size and turnover rate of body glucose pool by the isotope dilution method. Am J Physiol. 1956 Sep;187(1):15–24. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1956.187.1.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Searle G. L., Shames D., Cavalieri R. R., Bagdade J. D., Porte D., Jr Evaluation of ethanol hypoglycemia in man: turnover studies with C-6 14C glucose. Metabolism. 1974 Nov;23(11):1023–1035. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(74)90069-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ylikahri R. H. Ethanol-induced hypoglycemia in thyroxine-treated rats. Metabolism. 1970 Jul;19(7):518–528. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(70)90007-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZIERLER K. L., RABINOWITZ D. EFFECT OF VERY SMALL CONCENTRATIONS OF INSULIN ON FOREARM METABOLISM. PERSISTENCE OF ITS ACTION ON POTASSIUM AND FREE FATTY ACIDS WITHOUT ITS EFFECT ON GLUCOSE. J Clin Invest. 1964 May;43:950–962. doi: 10.1172/JCI104981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


