Abstract
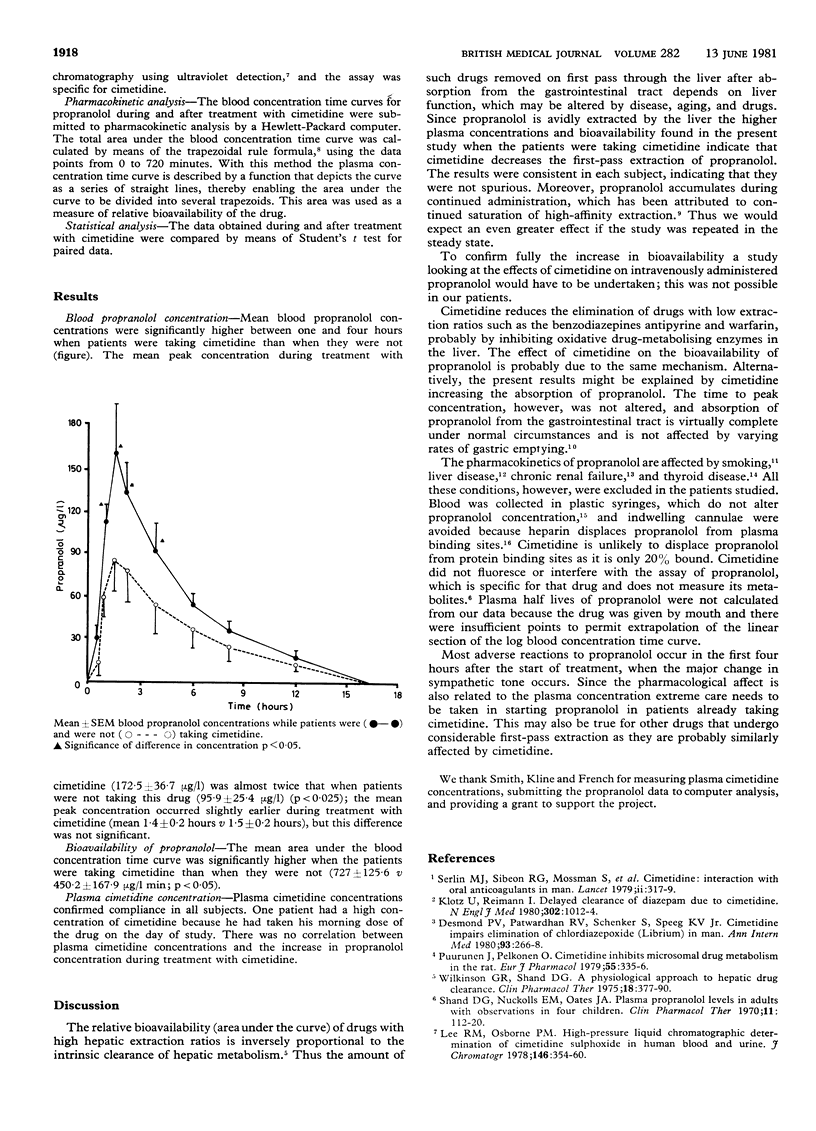
Whole-blood propranolol concentrations were estimated for 12 hours after a single 80 mg oral dose was given in six patients taking cimetidine and two weeks after they had stopped the drug. Mean blood propranolol concentrations were higher throughout the sampling period when the patients were taking cimetidine than when they were not, and the difference was statistically significant between one and four hours (p less than 0.05). The mean relative bioavailability of propranolol, measured as the area under the concentration time curve, was significantly higher when the patients were taking cimetidine (p less than 0.025). The mean increase in bioavailability was 136.5 +/- 57.6%, and the results were consistent in each subject. It is concluded from these results that cimetidine reduces the hepatic first-pass extraction of propranolol.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Castleden C. M., George C. F., Short M. D. Contribution of individual differences in gastric emptying to variability in plasma propranolol concentrations. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1978 Feb;5(2):121–122. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1978.tb01610.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotham R. H., Shand D. Spuriously low plasma propranolol concentrations resulting from blood collection methods. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1975 Nov;18(5 Pt 1):535–538. doi: 10.1002/cpt1975185part1535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desmond P. V., Patwardhan R. V., Schenker S., Speeg K. V., Jr Cimetidine impairs elimination of chlordiazepoxide (Librium) in man. Ann Intern Med. 1980 Aug;93(2):266–268. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-93-2-266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans G. H., Shand D. G. Disposition of propranolol. V. Drug accumulation and steady-state concentrations during chronic oral administration in man. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1973 Jul-Aug;14(4):487–493. doi: 10.1002/cpt1973144part1487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klotz U., Reimann I. Delayed clearance of diazepam due to cimetidine. N Engl J Med. 1980 May 1;302(18):1012–1014. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198005013021807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee R. M., Osborne P. M. High-pressure liquid chromatographic determination of cimetidine sulphoxide in human blood and urine. J Chromatogr. 1978 Sep 1;146(2):354–360. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)81903-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowenthal D. T., Briggs W. A., Gibson T. P., Nelson H., Cirksena W. J. Pharmacokinetics of oral propranolol in chronic renal disease. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1974 Nov;16(5 Pt 1):761–769. doi: 10.1002/cpt1974165part1761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puurunen J., Pelkonen O. Cimetidine inhibits microsomal drug metabolism in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol. 1979 May 1;55(3):335–336. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(79)90205-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders L., Natunen T. A four parameter model for oral drug absorption. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1976 Jul;28(7):572–579. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1976.tb02798.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serlin M. J., Sibeon R. G., Mossman S., Breckenridge A. M., Williams J. R., Atwood J. L., Willoughby J. M. Cimetidine: interaction with oral anticoagulants in man. Lancet. 1979 Aug 18;2(8138):317–319. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)90340-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vestal R. E., Wood A. J., Branch R. A., Shand D. G., Wilkinson G. R. Effects of age and cigarette smoking on propranolol disposition. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1979 Jul;26(1):8–15. doi: 10.1002/cpt19792618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson G. R., Shand D. G. Commentary: a physiological approach to hepatic drug clearance. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1975 Oct;18(4):377–390. doi: 10.1002/cpt1975184377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood A. J., Kornhauser D. M., Wilkinson G. R., Shand D. G., Branch R. A. The influence of cirrhosis on steady-state blood concentrations of unbound propranolol after oral administration. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1978 Nov-Dec;3(6):478–487. doi: 10.2165/00003088-197803060-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood M., Shand D. G., Wood A. J. Altered drug binding due to the use of indwelling heparinized cannulas (heparin lock) for sampling. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1979 Jan;25(1):103–107. doi: 10.1002/cpt1979251103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


