Abstract
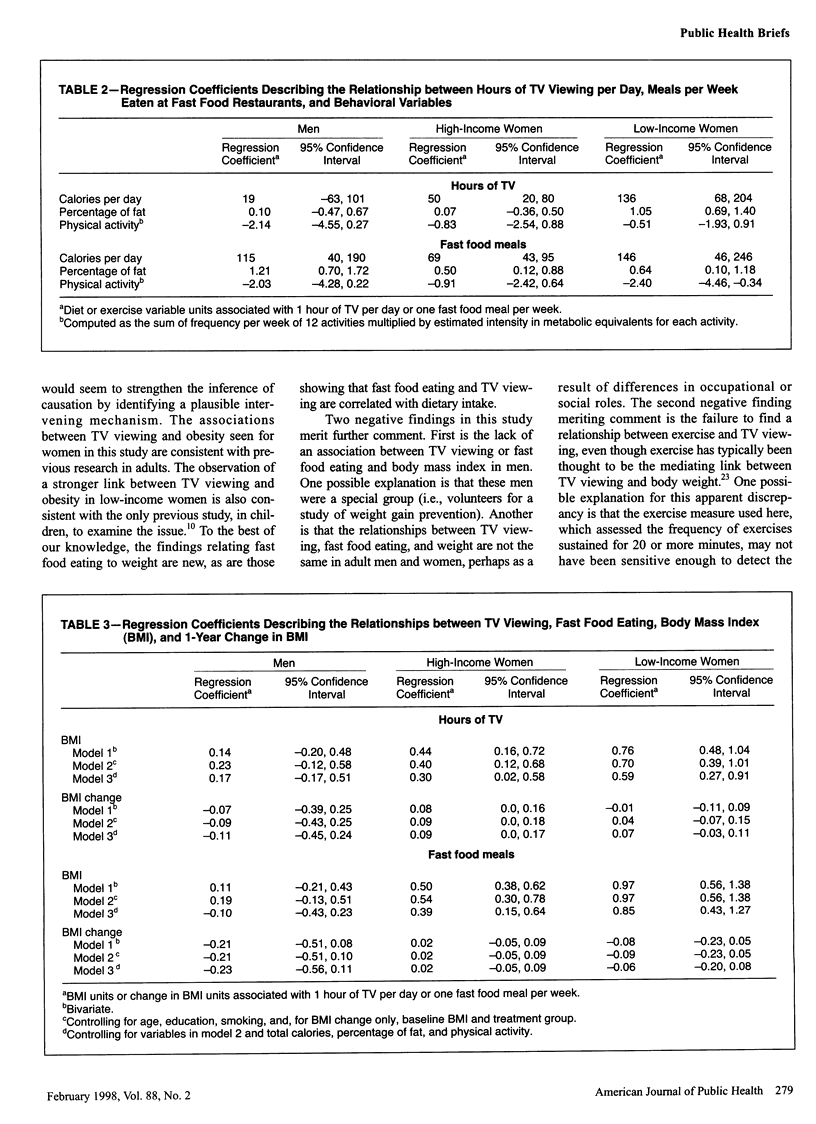
OBJECTIVES: This study examined the association between TV viewing, fast food eating, and body mass index. METHODS: Associations between hours of TV viewing, frequency of eating at fast food restaurants, body mass index, and behaviors were assessed cross sectionally and longitudinally over 1 year in 1059 men and women. RESULTS: Fast food meals and TV viewing hours were positively associated with energy intake and body mass index in women but not in men. TV viewing predicted weight gain in high-income women. CONCLUSIONS: Secular increases in fast food availability and access to televised entertainment may contribute to increasing obesity rates in the United States.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernard L., Lavallée C., Gray-Donald K., Delisle H. Overweight in Cree schoolchildren and adolescents associated with diet, low physical activity, and high television viewing. J Am Diet Assoc. 1995 Jul;95(7):800–802. doi: 10.1016/S0002-8223(95)00221-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Block G., Hartman A. M., Dresser C. M., Carroll M. D., Gannon J., Gardner L. A data-based approach to diet questionnaire design and testing. Am J Epidemiol. 1986 Sep;124(3):453–469. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a114416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caspersen C. J., Merritt R. K. Physical activity trends among 26 states, 1986-1990. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1995 May;27(5):713–720. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietz W. H., Jr, Gortmaker S. L. Do we fatten our children at the television set? Obesity and television viewing in children and adolescents. Pediatrics. 1985 May;75(5):807–812. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DuRant R. H., Baranowski T., Johnson M., Thompson W. O. The relationship among television watching, physical activity, and body composition of young children. Pediatrics. 1994 Oct;94(4 Pt 1):449–455. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- French S. A., Jeffery R. W., Forster J. L., McGovern P. G., Kelder S. H., Baxter J. E. Predictors of weight change over two years among a population of working adults: the Healthy Worker Project. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 1994 Mar;18(3):145–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris J. K., French S. A., Jeffery R. W., McGovern P. G., Wing R. R. Dietary and physical activity correlates of long-term weight loss. Obes Res. 1994 Jul;2(4):307–313. doi: 10.1002/j.1550-8528.1994.tb00069.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinsey J. D. Food and families' socioeconomic status. J Nutr. 1994 Sep;124(9 Suppl):1878S–1885S. doi: 10.1093/jn/124.suppl_9.1878S. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuczmarski R. J., Flegal K. M., Campbell S. M., Johnson C. L. Increasing prevalence of overweight among US adults. The National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys, 1960 to 1991. JAMA. 1994 Jul 20;272(3):205–211. doi: 10.1001/jama.272.3.205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locard E., Mamelle N., Billette A., Miginiac M., Munoz F., Rey S. Risk factors of obesity in a five year old population. Parental versus environmental factors. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 1992 Oct;16(10):721–729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rissel C. E. Overweight and television watching. Aust J Public Health. 1991 Jun;15(2):147–150. doi: 10.1111/j.1753-6405.1991.tb00325.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson T. N., Hammer L. D., Killen J. D., Kraemer H. C., Wilson D. M., Hayward C., Taylor C. B. Does television viewing increase obesity and reduce physical activity? Cross-sectional and longitudinal analyses among adolescent girls. Pediatrics. 1993 Feb;91(2):273–280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sallis J. F., Broyles S. L., Frank-Spohrer G., Berry C. C., Davis T. B., Nader P. R. Child's home environment in relation to the mother's adiposity. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 1995 Mar;19(3):190–197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szilagyi P. G., Rodewald L. E., Humiston S. G., Raubertas R. F., Cove L. A., Doane C. B., Lind P. H., Tobin M. S., Roghmann K. J., Hall C. B. Missed opportunities for childhood vaccinations in office practices and the effect on vaccination status. Pediatrics. 1993 Jan;91(1):1–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker L. A., Bagwell M. Television viewing and obesity in adult females. Am J Public Health. 1991 Jul;81(7):908–911. doi: 10.2105/ajph.81.7.908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker L. A., Friedman G. M. Television viewing and obesity in adult males. Am J Public Health. 1989 Apr;79(4):516–518. doi: 10.2105/ajph.79.4.516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


