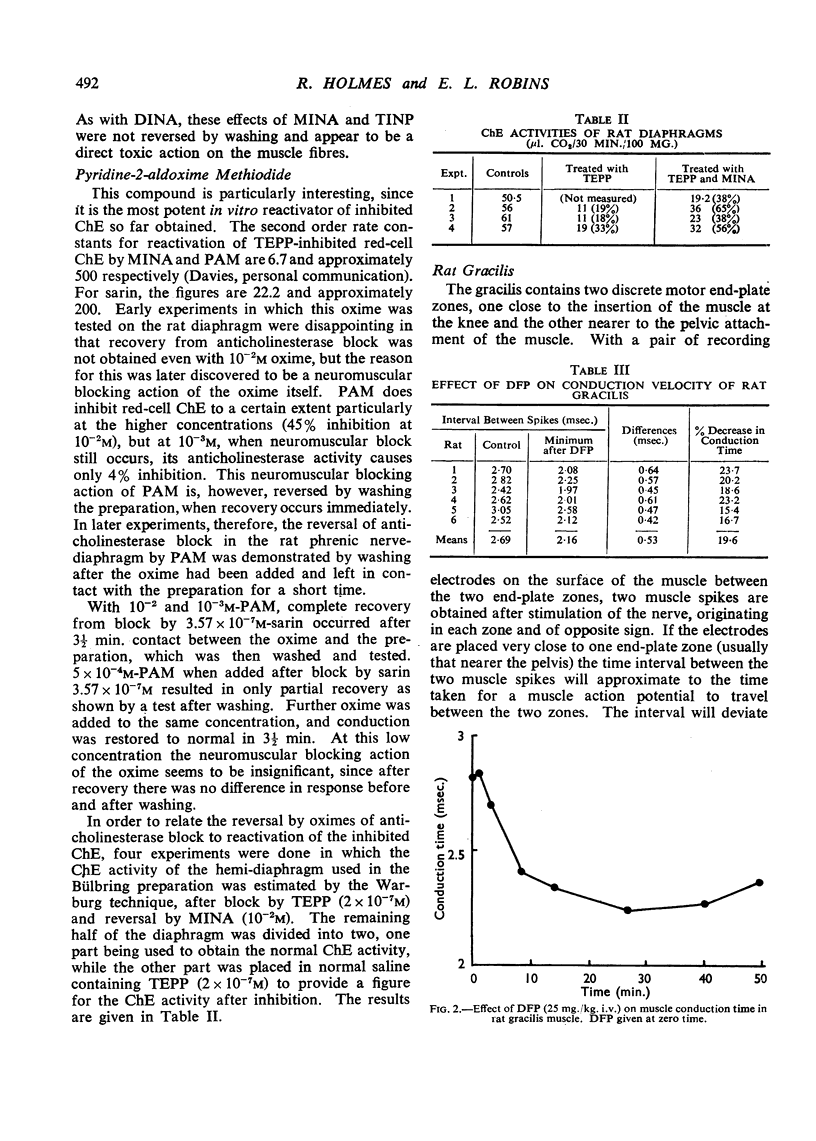
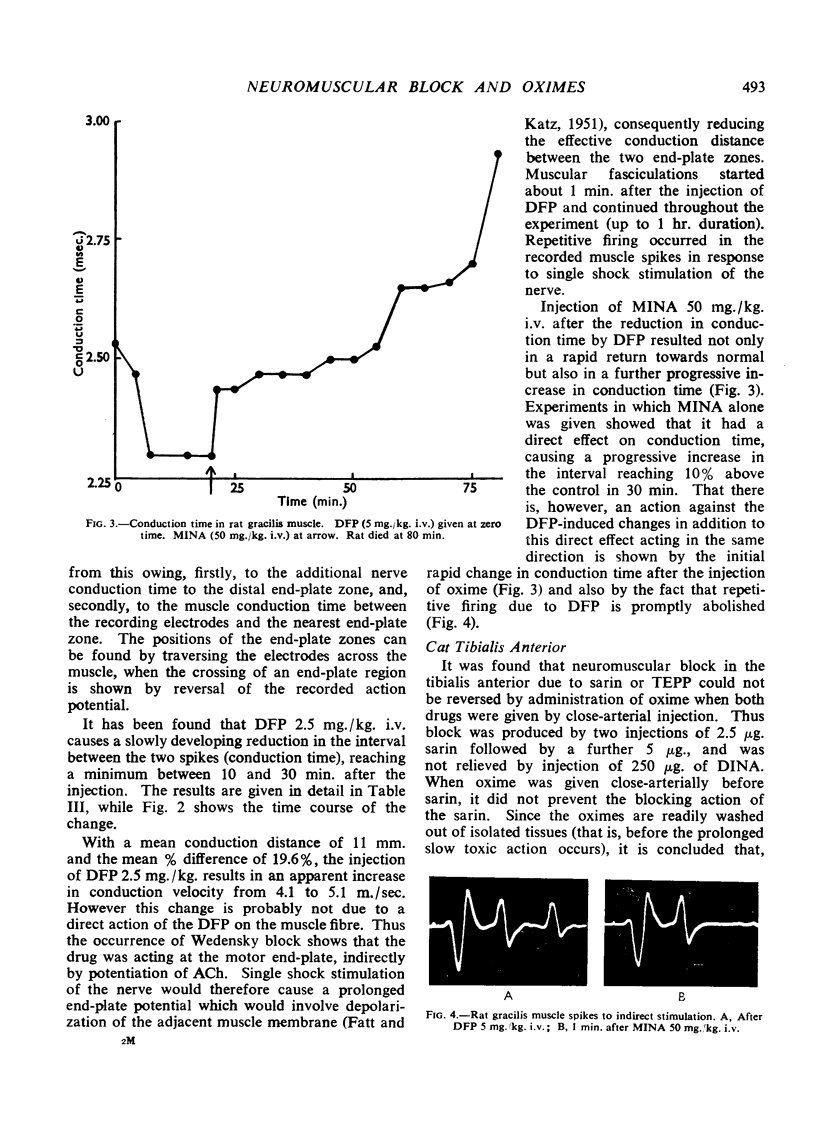
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CHILDS A. F., DAVIES D. R., GREEN A. L., RUTLAND J. P. The reactivation by oximes and hydroxamic acids of cholinesterase inhibited by organo-phosphorus compounds. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1955 Dec;10(4):462–465. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1955.tb00106.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOUGLAS W. W., MATHEWS P. B. C. Acute tetraethylpyrophosphate poisoning in cats and its modification by atropine or hyoscine. J Physiol. 1952 Feb;116(2):202–218. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FATT P., KATZ B. An analysis of the end-plate potential recorded with an intracellular electrode. J Physiol. 1951 Nov 28;115(3):320–370. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1951.sp004675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JARCHO L. W., EYZAGUIRRE C., TALBOT S. A., LILIENTHAL J. L., Jr Neuromuscular excitation: responses of normal and denervated mammalian muscle to bis-trimethylammonium decane (C10) and to alpha-tubocurarine. Am J Physiol. 1950 Aug 1;162(2):475–488. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1950.162.2.475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JEFFRIES G. H. The effect of varying glucose concentrations on the mammalian end-plate potential. J Physiol. 1953 Jun 29;120(4):611–617. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp004921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROY B. B., KUPERMAN A. S. Reversal of the actions of tetraethyl pyrophosphate in surviving mammalian tissue. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1955 Jun;89(2):255–258. doi: 10.3181/00379727-89-21775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILSON I. B., GINSBURG S. Reactivation of acetylcholinesterase inhibited by alkylphosphates. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1955 Feb;54(2):569–571. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(55)90075-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


