Abstract
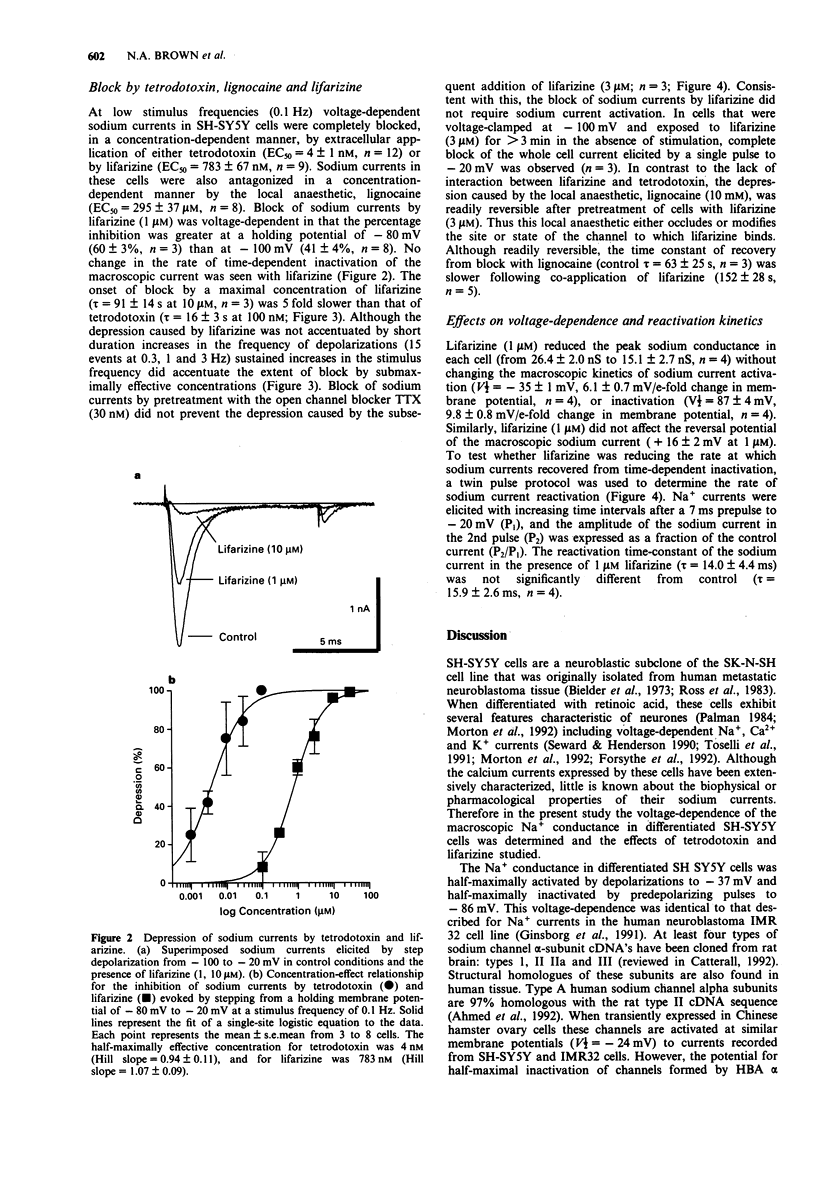
1. The ability of lifarizine (RS-87476) to block human voltage-sensitive Na+ channel currents was studied by use of whole cell patch clamp recording from differentiated neuroblastoma cells (SH-SY5Y). 2. The Na+ conductance in differentiated SH-SY5Y cells (24.0 +/- 2.4 nS, n = 11) was half-maximally activated by 10 ms depolarizations to -37 +/- 2 mV and was half-maximally inactivated by predepolarizing pulses of 200 ms duration to -86 +/- 3 mV (n = 11). 3. At low stimulus frequencies (0.1 to 0.33 Hz) voltage-dependent sodium currents were completely blocked, in a concentration-dependent manner, by extracellular application of either tetrodotoxin (EC50 = 4 +/- 1 nM, n = 12) or by lifarizine (EC50 = 783 +/- 67 nM, n = 9). The onset of block by lifarizine (tau = 91 +/- 14 s at 10 microM) was considerably slower than that of tetrodotoxin (tau = 16 +/- 3 s at 100 nM). 4. Lifarizine (1 microM) reduced the peak sodium conductance in each cell (from 26.4 +/- 2.0 nS to 15.1 +/- 2.7 nS, n = 4) without changing the macroscopic kinetics of sodium current activation or inactivation (V1/2 = -35 1 mV and -87 +/- 4 mV respectively, n = 4). Similarly, lifarizine (1 microM) did not affect the reversal potential of the macroscopic sodium current (+14 +/- 5 mV in control and +16 +/- 2 mV in 1 microM lifarizine; n = 4) or reactivation time-constant (tau = 14.0 +/- 4.4 ms).(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF
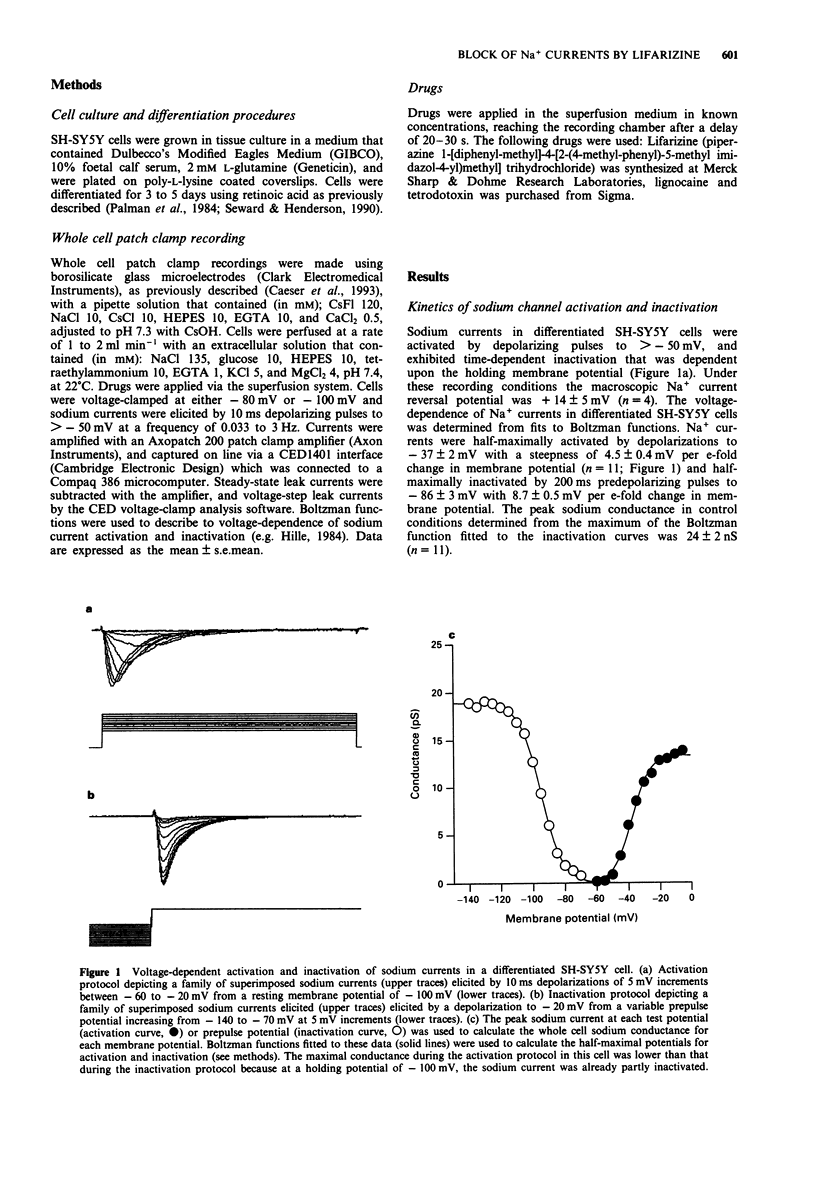
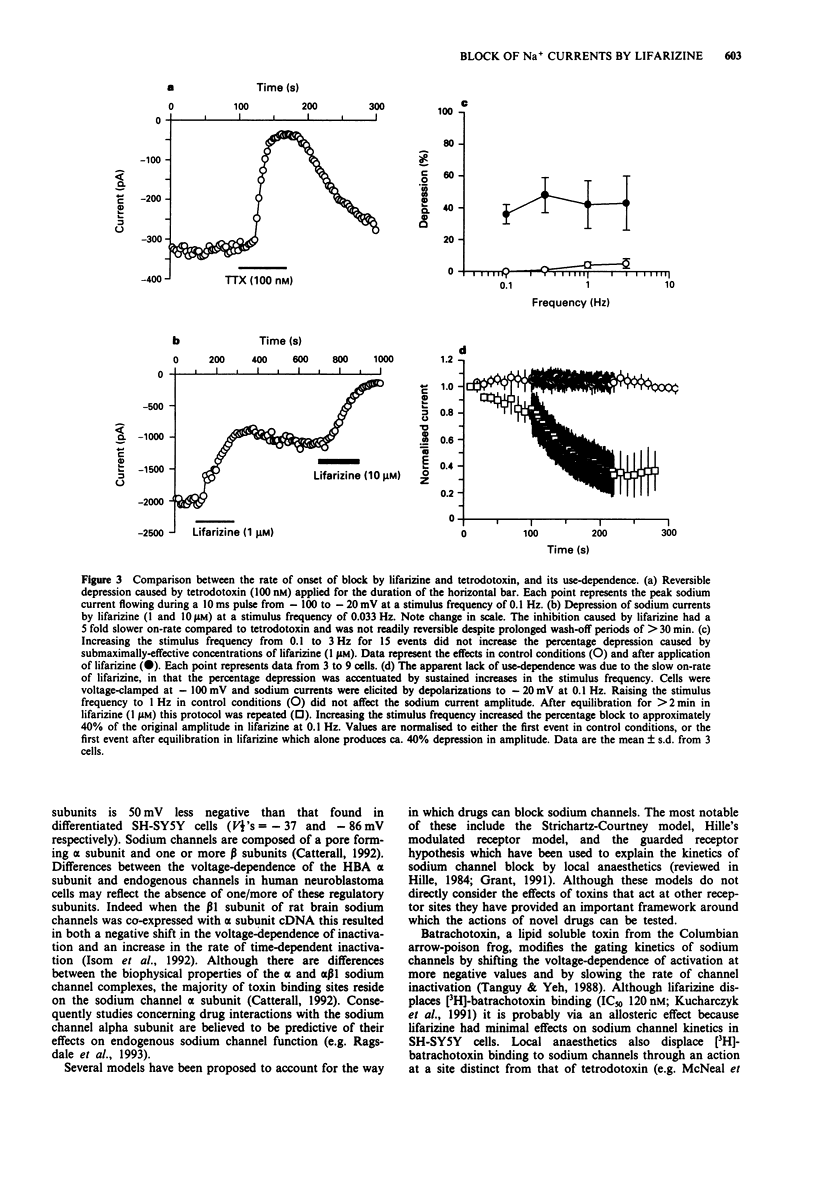
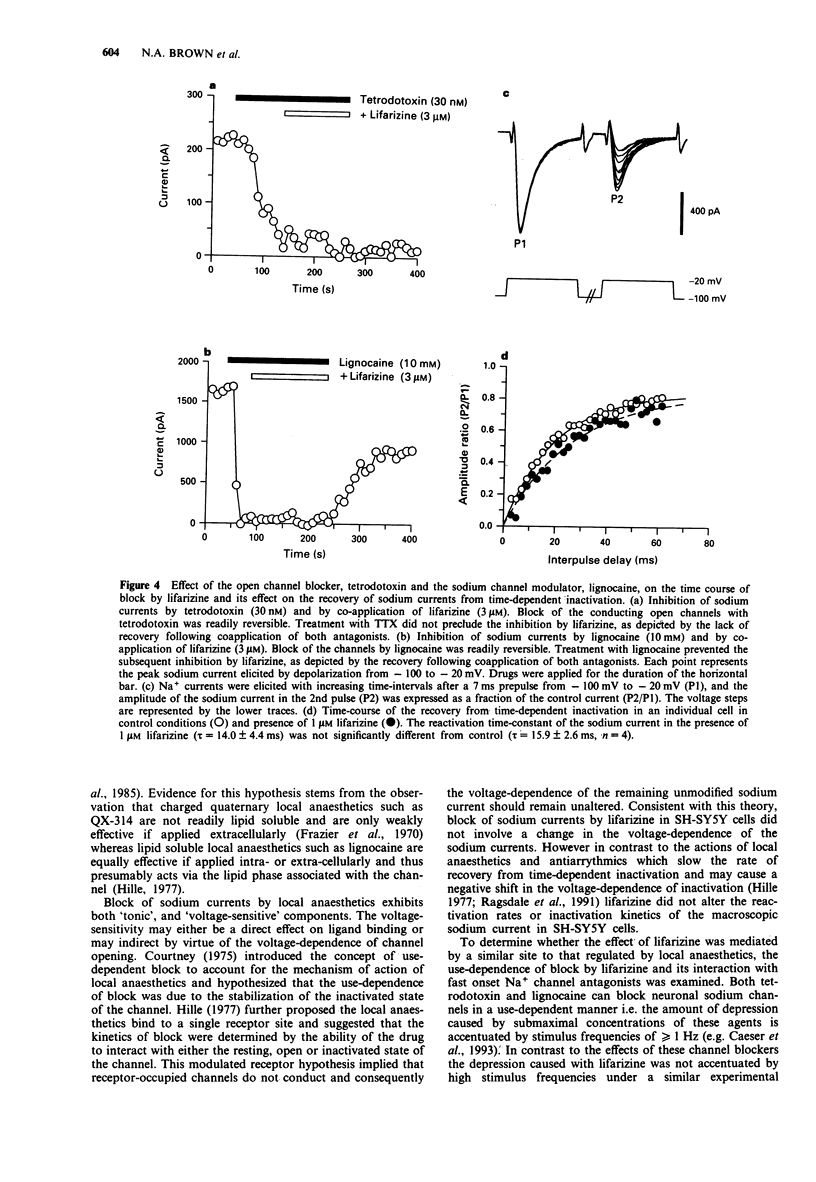


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmed C. M., Ware D. H., Lee S. C., Patten C. D., Ferrer-Montiel A. V., Schinder A. F., McPherson J. D., Wagner-McPherson C. B., Wasmuth J. J., Evans G. A. Primary structure, chromosomal localization, and functional expression of a voltage-gated sodium channel from human brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 1;89(17):8220–8224. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.17.8220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alps B. J. Drugs acting on calcium channels: potential treatment for ischaemic stroke. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1992 Sep;34(3):199–206. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1992.tb04125.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biedler J. L., Helson L., Spengler B. A. Morphology and growth, tumorigenicity, and cytogenetics of human neuroblastoma cells in continuous culture. Cancer Res. 1973 Nov;33(11):2643–2652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caeser M., Seabrook G. R., Kemp J. A. Block of voltage-dependent sodium currents by the substance P receptor antagonist (+/-)-CP-96,345 in neurones cultured from rat cortex. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Aug;109(4):918–924. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13708.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall W. A. Cellular and molecular biology of voltage-gated sodium channels. Physiol Rev. 1992 Oct;72(4 Suppl):S15–S48. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1992.72.suppl_4.S15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtney K. R. Mechanism of frequency-dependent inhibition of sodium currents in frog myelinated nerve by the lidocaine derivative GEA. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1975 Nov;195(2):225–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsythe I. D., Lambert D. G., Nahorski S. R., Lindsdell P. Elevation of cytosolic calcium by cholinoceptor agonists in SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells: estimation of the contribution of voltage-dependent currents. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Sep;107(1):207–214. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14488.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frazier D. T., Narahashi T., Yamada M. The site of action and active form of local anesthetics. II. Experiments with quaternary compounds. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1970 Jan;171(1):45–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellens M. E., George A. L., Jr, Chen L. Q., Chahine M., Horn R., Barchi R. L., Kallen R. G. Primary structure and functional expression of the human cardiac tetrodotoxin-insensitive voltage-dependent sodium channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 15;89(2):554–558. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.2.554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George A. L., Jr, Knittle T. J., Tamkun M. M. Molecular cloning of an atypical voltage-gated sodium channel expressed in human heart and uterus: evidence for a distinct gene family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 1;89(11):4893–4897. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.11.4893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George A. L., Jr, Komisarof J., Kallen R. G., Barchi R. L. Primary structure of the adult human skeletal muscle voltage-dependent sodium channel. Ann Neurol. 1992 Feb;31(2):131–137. doi: 10.1002/ana.410310203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsborg B. L., Martin R. J., Patmore L. On the sodium and potassium currents of a human neuroblastoma cell line. J Physiol. 1991 Mar;434:121–149. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goa K. L., Ross S. R., Chrisp P. Lamotrigine. A review of its pharmacological properties and clinical efficacy in epilepsy. Drugs. 1993 Jul;46(1):152–176. doi: 10.2165/00003495-199346010-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant A. O. Models of drug interaction with the sodium channel. Clin Invest Med. 1991 Oct;14(5):447–457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. Currents carried by sodium and potassium ions through the membrane of the giant axon of Loligo. J Physiol. 1952 Apr;116(4):449–472. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B. The pH-dependent rate of action of local anesthetics on the node of Ranvier. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Apr;69(4):475–496. doi: 10.1085/jgp.69.4.475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isom L. L., De Jongh K. S., Patton D. E., Reber B. F., Offord J., Charbonneau H., Walsh K., Goldin A. L., Catterall W. A. Primary structure and functional expression of the beta 1 subunit of the rat brain sodium channel. Science. 1992 May 8;256(5058):839–842. doi: 10.1126/science.1375395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kayano T., Noda M., Flockerzi V., Takahashi H., Numa S. Primary structure of rat brain sodium channel III deduced from the cDNA sequence. FEBS Lett. 1988 Feb 8;228(1):187–194. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80614-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kucharczyk J., Mintorovitch J., Moseley M. E., Asgari H. S., Sevick R. J., Derugin N., Norman D. Ischemic brain damage: reduction by sodium-calcium ion channel modulator RS-87476. Radiology. 1991 Apr;179(1):221–227. doi: 10.1148/radiology.179.1.2006281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuki N., Quandt F. N., Ten Eick R. E., Yeh J. Z. Characterization of the block of sodium channels by phenytoin in mouse neuroblastoma cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1984 Feb;228(2):523–530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean M. J., Macdonald R. L. Carbamazepine and 10,11-epoxycarbamazepine produce use- and voltage-dependent limitation of rapidly firing action potentials of mouse central neurons in cell culture. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986 Aug;238(2):727–738. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeal E. T., Lewandowski G. A., Daly J. W., Creveling C. R. [3H]Batrachotoxinin A 20 alpha-benzoate binding to voltage-sensitive sodium channels: a rapid and quantitative assay for local anesthetic activity in a variety of drugs. J Med Chem. 1985 Mar;28(3):381–388. doi: 10.1021/jm00381a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meldrum B. S., Swan J. H., Leach M. J., Millan M. H., Gwinn R., Kadota K., Graham S. H., Chen J., Simon R. P. Reduction of glutamate release and protection against ischemic brain damage by BW 1003C87. Brain Res. 1992 Oct 9;593(1):1–6. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(92)91254-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto J., Hisatome I., Matsuoka S., Kosaka H., Kurata Y., Tanaka Y., Nawada T., Kotake H., Mashiba H., Sato R. The effect of TYB-3823, a new antiarrhythmic drug, on sodium current in isolated cardiac cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Sep;104(1):25–30. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12379.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton A. J., Hammond C., Mason W. T., Henderson G. Characterisation of the L- and N-type calcium channels in differentiated SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells: calcium imaging and single channel recording. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1992 Mar;13(1-2):53–61. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(92)90044-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Ikeda T., Suzuki H., Takeshima H., Takahashi T., Kuno M., Numa S. Expression of functional sodium channels from cloned cDNA. 1986 Aug 28-Sep 3Nature. 322(6082):826–828. doi: 10.1038/322826a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Påhlman S., Ruusala A. I., Abrahamsson L., Mattsson M. E., Esscher T. Retinoic acid-induced differentiation of cultured human neuroblastoma cells: a comparison with phorbolester-induced differentiation. Cell Differ. 1984 Jun;14(2):135–144. doi: 10.1016/0045-6039(84)90038-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ragsdale D. S., Numann R., Catterall W. A., Scheuer T. Inhibition of Na+ channels by the novel blocker PD85,639. Mol Pharmacol. 1993 Jun;43(6):949–954. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ragsdale D. S., Scheuer T., Catterall W. A. Frequency and voltage-dependent inhibition of type IIA Na+ channels, expressed in a mammalian cell line, by local anesthetic, antiarrhythmic, and anticonvulsant drugs. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Nov;40(5):756–765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R. A., Spengler B. A., Biedler J. L. Coordinate morphological and biochemical interconversion of human neuroblastoma cells. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1983 Oct;71(4):741–747. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seward E. P., Henderson G. Characterization of two components of the N-like, high-threshold-activated calcium channel current in differentiated SH-SY5Y cells. Pflugers Arch. 1990 Oct;417(2):223–230. doi: 10.1007/BF00370703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanguy J., Yeh J. Z. Batrachotoxin uncouples gating charge immobilization from fast Na inactivation in squid giant axons. Biophys J. 1988 Oct;54(4):719–730. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)83007-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toselli M., Masetto S., Rossi P., Taglietti V. Characterization of a Voltage-dependent Calcium Current in the Human Neuroblastoma Cell Line SH-SY5Y During Differentiation. Eur J Neurosci. 1991 Jun;3(6):514–522. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1991.tb00838.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


