Abstract
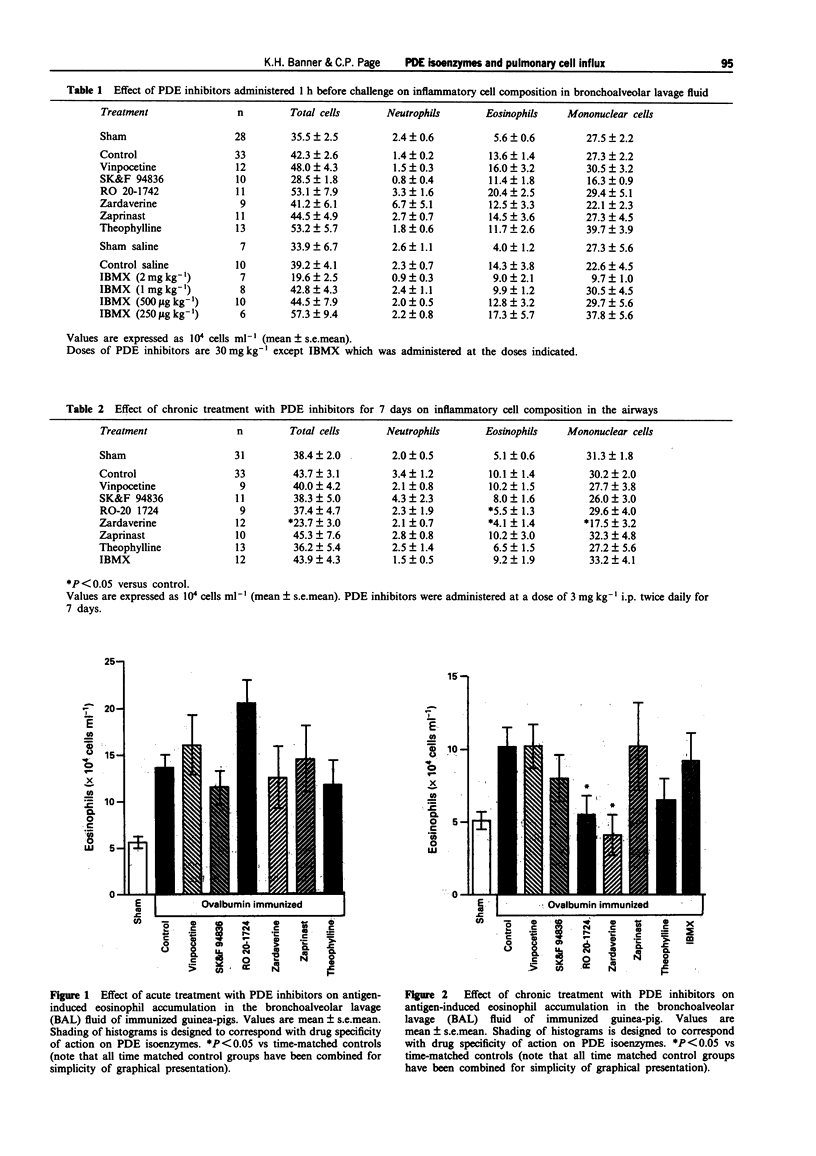
1. The aims of this study were to determine which phosphodiesterase (PDE) isoenzymes are involved in the control of eosinophil accumulation in the airways of ovalbumin (OVA)-immunized guinea-pigs by the use of isoenzyme selective inhibitors and to compare the effects of acute versus chronic administration of PDE isozyme inhibitors on pulmonary cell influx in ovalbumin-immunized guinea-pigs. 2. Guinea-pigs were sensitized and subsequently challenged with aerosolized OVA. Twenty four hours later bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) was performed to permit assessment of inflammatory cell accumulation. A significant increase in the number of eosinophils was observed in the lavage fluid from OVA-immunized (13.6 +/- 1.4 x 10(4) ml-1 in acute experiments and 10.1 +/- 1.4 x 10(4) ml-1 in chronic experiments) animals compared with sham-treated controls (5.6 +/- 0.6 x 10(4) ml-1 in acute experiments and 5.1 +/- 0.6 x 10(4) ml-1 in chronic experiments). There was no difference in neutrophil, mononuclear cell or total cell numbers between the two groups. 3. Acute administration of a high dose of selective and non-selective PDE inhibitors by the i.p. route had no significant effect on eosinophil accumulation in the airways. 4. Chronic administration of a low dose (3 mg kg-1, i.p., twice daily for 7 days) of the type IV PDE inhibitor, RO 20-1724, and the PDE III/IV inhibitor, zardaverine, produced a significant inhibition of eosinophil accumulation (46% and 59% respectively).(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dent G., Giembycz M. A., Rabe K. F., Barnes P. J. Inhibition of eosinophil cyclic nucleotide PDE activity and opsonised zymosan-stimulated respiratory burst by 'type IV'-selective PDE inhibitors. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Jun;103(2):1339–1346. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb09790.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frigas E., Gleich G. J. The eosinophil and the pathophysiology of asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1986 Apr;77(4):527–537. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(86)90341-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giembycz M. A. Could isoenzyme-selective phosphodiesterase inhibitors render bronchodilator therapy redundant in the treatment of bronchial asthma? Biochem Pharmacol. 1992 May 28;43(10):2041–2051. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(92)90160-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giembycz M. A., Dent G. Prospects for selective cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase inhibitors in the treatment of bronchial asthma. Clin Exp Allergy. 1992 Mar;22(3):337–344. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1992.tb03095.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gristwood R. W., Llupiá J., Fernández A. G., Berga P. Effects of theophylline compared with prednisolone on late phase airway leukocyte infiltration in guinea pigs. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1991;94(1-4):293–294. doi: 10.1159/000235388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn B. R., Robin E. D., Theodore J., Van Kessel A. Total eosinophil counts in the management of bronchial asthma. N Engl J Med. 1975 May 29;292(22):1152–1155. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197505292922204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lappin D., Riches D. W., Damerau B., Whaley K. Cyclic nucleotides and their relationship to complement-component-C2 synthesis by human monocytes. Biochem J. 1984 Sep 1;222(2):477–486. doi: 10.1042/bj2220477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugnier C., Schini V. B. Characterization of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases from cultured bovine aortic endothelial cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 1990 Jan 1;39(1):75–84. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(90)90650-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manzini S., Perretti F., Abelli L., Evangelista S., Seeds E. A., Page C. P. Isbufylline, a new xanthine derivative, inhibits airway hyperresponsiveness and airway inflammation in guinea pigs. Eur J Pharmacol. 1993 Nov 16;249(3):251–257. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(93)90519-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson C. D., Challiss R. A., Shahid M. Differential modulation of tissue function and therapeutic potential of selective inhibitors of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase isoenzymes. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1991 Jan;12(1):19–27. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(91)90484-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson C. D., Shahid M. Inhibitors of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase isoenzymes--their potential utility in the therapy of asthma. Pulm Pharmacol. 1994 Feb;7(1):1–17. doi: 10.1006/pulp.1994.1001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauwels R. The effects of theophylline on airway inflammation. Chest. 1987 Jul;92(1 Suppl):32S–37S. doi: 10.1378/chest.92.1_supplement.32s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson C. G. Overview of effects of theophylline. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1986 Oct;78(4 Pt 2):780–787. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(86)90061-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robicsek S. A., Blanchard D. K., Djeu J. Y., Krzanowski J. J., Szentivanyi A., Polson J. B. Multiple high-affinity cAMP-phosphodiesterases in human T-lymphocytes. Biochem Pharmacol. 1991 Jul 25;42(4):869–877. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(91)90047-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schudt C., Winder S., Eltze M., Kilian U., Beume R. Zardaverine: a cyclic AMP specific PDE III/IV inhibitor. Agents Actions Suppl. 1991;34:379–402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seibert A. F., Thompson W. J., Taylor A., Wilborn W. H., Barnard J., Haynes J. Reversal of increased microvascular permeability associated with ischemia-reperfusion: role of cAMP. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1992 Jan;72(1):389–395. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1992.72.1.389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Souness J. E., Carter C. M., Diocee B. K., Hassall G. A., Wood L. J., Turner N. C. Characterization of guinea-pig eosinophil phosphodiesterase activity. Assessment of its involvement in regulating superoxide generation. Biochem Pharmacol. 1991 Jul 25;42(4):937–945. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(91)90056-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan P., Bekir S., Jaffar Z., Page C., Jeffery P., Costello J. Anti-inflammatory effects of low-dose oral theophylline in atopic asthma. Lancet. 1994 Apr 23;343(8904):1006–1008. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)90127-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suttorp N., Weber U., Welsch T., Schudt C. Role of phosphodiesterases in the regulation of endothelial permeability in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1993 Apr;91(4):1421–1428. doi: 10.1172/JCI116346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teixeira M. M., Rossi A. G., Williams T. J., Hellewell P. G. Effects of phosphodiesterase isoenzyme inhibitors on cutaneous inflammation in the guinea-pig. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 May;112(1):332–340. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb13073.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson W. J., Ross C. P., Pledger W. J., Strada S. J., Banner R. L., Hersh E. M. Cyclic adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate phosphodiesterase. Distinct forms in human lymphocytes and monocytes. J Biol Chem. 1976 Aug 25;251(16):4922–4929. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torphy T. J., Undem B. J. Phosphodiesterase inhibitors: new opportunities for the treatment of asthma. Thorax. 1991 Jul;46(7):512–523. doi: 10.1136/thx.46.7.512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner C. R., Andresen C. J., Smith W. B., Watson J. W. Effects of rolipram on responses to acute and chronic antigen exposure in monkeys. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1994 May;149(5):1153–1159. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.149.5.8173755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Underwood D. C., Osborn R. R., Novak L. B., Matthews J. K., Newsholme S. J., Undem B. J., Hand J. M., Torphy T. J. Inhibition of antigen-induced bronchoconstriction and eosinophil infiltration in the guinea pig by the cyclic AMP-specific phosphodiesterase inhibitor, rolipram. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993 Jul;266(1):306–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward A. J., McKenniff M., Evans J. M., Page C. P., Costello J. F. Theophylline--an immunomodulatory role in asthma? Am Rev Respir Dis. 1993 Mar;147(3):518–523. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/147.3.518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wardlaw A. J., Kay A. B. The role of the eosinophil in the pathogenesis of asthma. Allergy. 1987 Jul;42(5):321–335. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.1987.tb02218.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberger M., Hendeles L., Ahrens R. Pharmacologic management of reversible obstructive airways disease. Med Clin North Am. 1981 May;65(3):579–613. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(16)31515-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellicome S. M., Thornhill M. H., Pitzalis C., Thomas D. S., Lanchbury J. S., Panayi G. S., Haskard D. O. A monoclonal antibody that detects a novel antigen on endothelial cells that is induced by tumor necrosis factor, IL-1, or lipopolysaccharide. J Immunol. 1990 Apr 1;144(7):2558–2565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yukawa T., Kroegel C., Chanez P., Dent G., Ukena D., Chung K. F., Barnes P. J. Effect of theophylline and adenosine on eosinophil function. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 Aug;140(2):327–333. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/140.2.327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


