Abstract
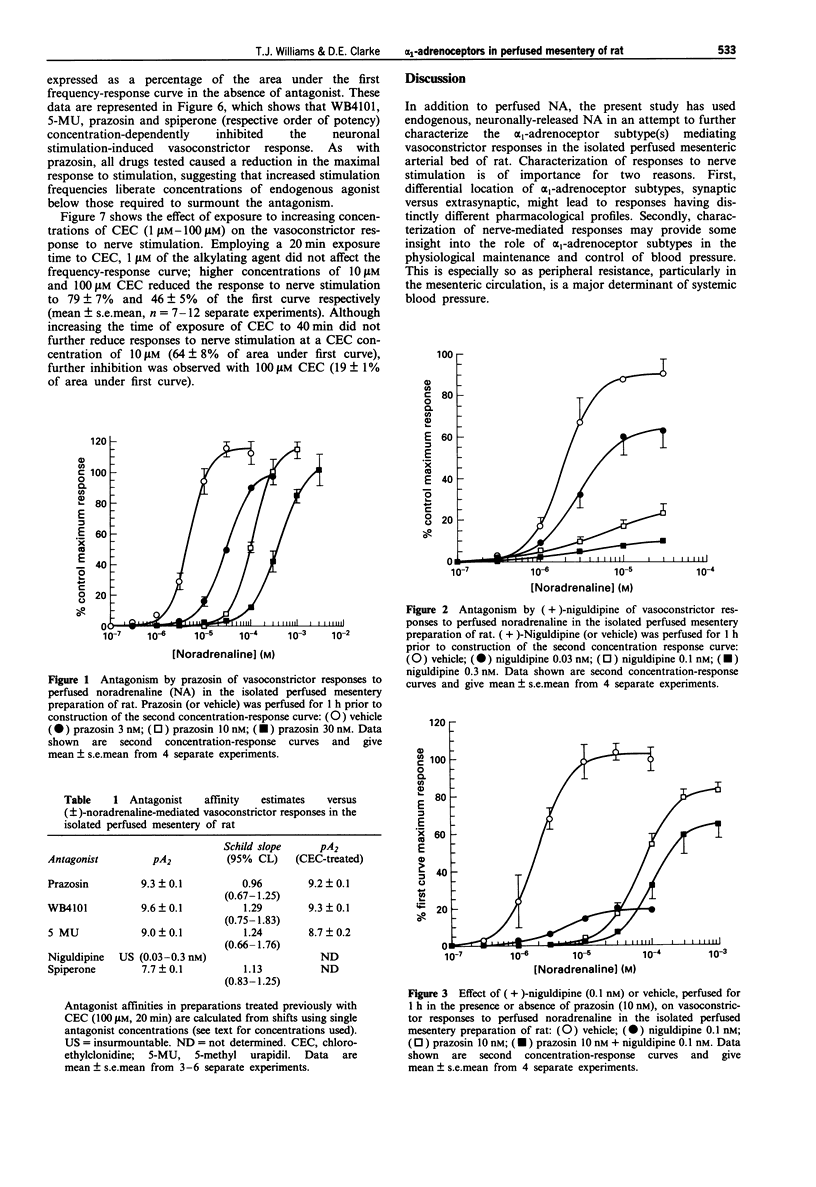
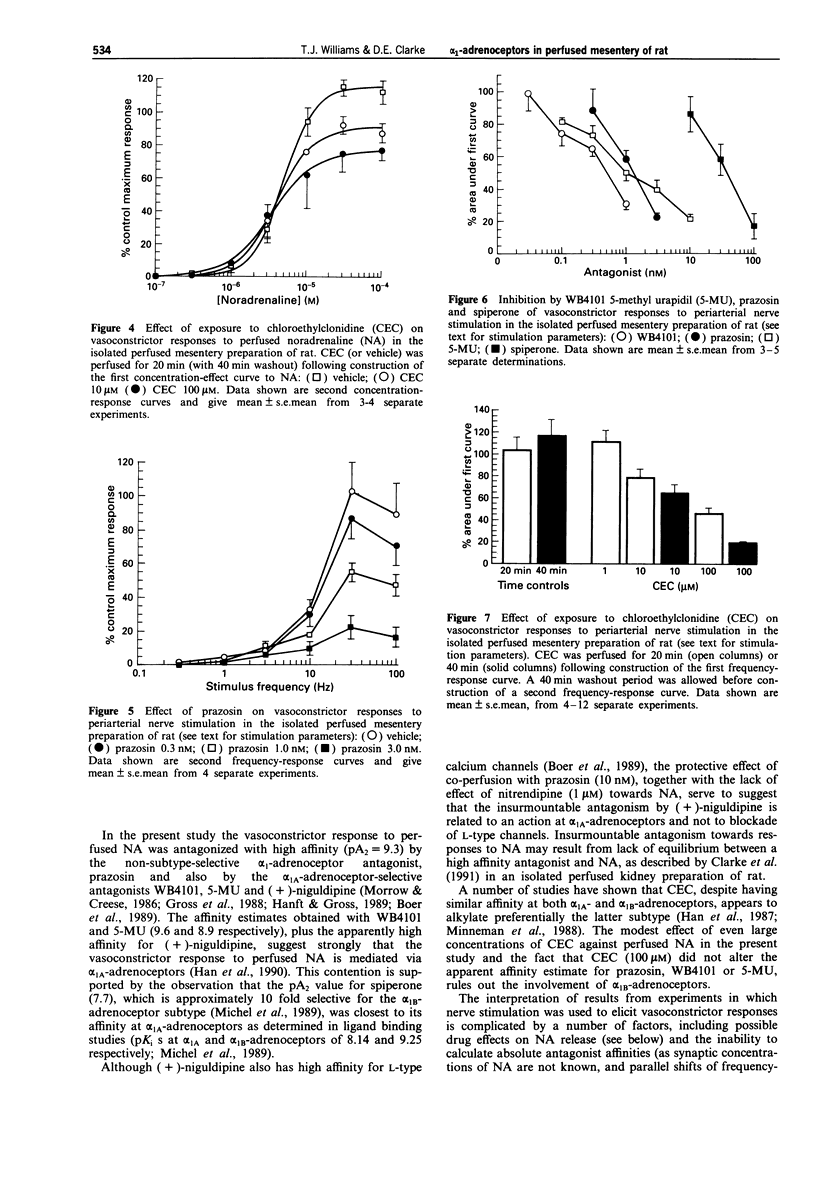
1. The objective of this study was to investigate the alpha 1-adrenoceptor subtype(s) mediating vasoconstrictor responses to perfused and neuronally-released noradrenaline (NA) in the isolated perfused mesentery preparation of rat. 2. Isolated mesenteric preparations (with gut attached) from male Sprague Dawley rats (250-300g) were perfused via the superior mesenteric artery with oxygenated Krebs solution at approximately 6 ml min-1. The effects of antagonists on vasoconstrictor responses to either perfused (+/-)-NA or periarterial nerve stimulation (70 V, 2 ms pulse width, 10 s train) were determined. 3. Vasoconstrictor responses to perfused NA were antagonized by prazosin (pA2 = 9.3 +/- 0.1), WB4101 (pA2 = 9.6 +/- 0.1), 5-methyl urapidil (5-MU: pA2 = 9.0 +/- 0.1), (+)-niguldipine (insurmountable) and spiperone (pA2 = 7.7 +/- 0.1). The insurmountable nature of the antagonism by (+)-niguldipine (0.1 nM) was greatly reduced by co-perfusion with prazosin (10 nM). Chloroethylclonidine (CEC: 100 microM for 20 min, followed by 40 min washout) caused an approximate twofold increase in the EC50 for (+/-)-NA and reduced the maximum response by approximately 25%. Pre-treatment of tissues with CEC (100 microM as above) did not significantly alter affinity estimates for prazosin (pA2 = 9.2 +/- 0.1), WB4101 (pA2 = 9.3 +/- 0.1) or 5-MU (pA2 = 8.7 +/- 0.2). Vasoconstrictor responses to periarterial nerve stimulation were antagonized by WB4101 > 5-MU > prazosin >> spiperone. CEC (100 microM as above) reduced nerve-stimulated responses by approximately 50%.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARUNLAKSHANA O., SCHILD H. O. Some quantitative uses of drug antagonists. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1959 Mar;14(1):48–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1959.tb00928.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boer R., Grassegger A., Schudt C., Glossmann H. (+)-Niguldipine binds with very high affinity to Ca2+ channels and to a subtype of alpha 1-adrenoceptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 May 11;172(2):131–145. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(89)90004-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bültmann R., Starke K. Chloroethylclonidine: an irreversible agonist at prejunctional alpha 2-adrenoceptors in rat vas deferens. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Feb;108(2):336–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb12806.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotecchia S., Schwinn D. A., Randall R. R., Lefkowitz R. J., Caron M. G., Kobilka B. K. Molecular cloning and expression of the cDNA for the hamster alpha 1-adrenergic receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7159–7163. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford A. P., Williams T. J., Blue D. R., Clarke D. E. Alpha 1-adrenoceptor classification: sharpening Occam's razor. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1994 Jun;15(6):167–170. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(94)90136-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross G., Hanft G., Rugevics C. 5-Methyl-urapidil discriminates between subtypes of the alpha 1-adrenoceptor. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Jul 7;151(2):333–335. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90819-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han C., Abel P. W., Minneman K. P. Heterogeneity of alpha 1-adrenergic receptors revealed by chlorethylclonidine. Mol Pharmacol. 1987 Oct;32(4):505–510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han C., Li J., Minneman K. P. Subtypes of alpha 1-adrenoceptors in rat blood vessels. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Nov 6;190(1-2):97–104. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)94116-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanft G., Gross G. Subclassification of alpha 1-adrenoceptor recognition sites by urapidil derivatives and other selective antagonists. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Jul;97(3):691–700. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb12005.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasakov L., Burnstock G. The use of the slowly degradable analog, alpha, beta-methylene ATP, to produce desensitisation of the P2-purinoceptor: effect on non-adrenergic, non-cholinergic responses of the guinea-pig urinary bladder. Eur J Pharmacol. 1982 Dec 24;86(2):291–294. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(82)90330-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kong J. Q., Taylor D. A., Fleming W. W. Functional distribution and role of alpha-1 adrenoceptor subtypes in the mesenteric vasculature of the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1994 Mar;268(3):1153–1159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomasney J. W., Cotecchia S., Lorenz W., Leung W. Y., Schwinn D. A., Yang-Feng T. L., Brownstein M., Lefkowitz R. J., Caron M. G. Molecular cloning and expression of the cDNA for the alpha 1A-adrenergic receptor. The gene for which is located on human chromosome 5. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 5;266(10):6365–6369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel A. D., Loury D. N., Whiting R. L. Identification of a single alpha 1-adrenoceptor corresponding to the alpha 1A-subtype in rat submaxillary gland. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Nov;98(3):883–889. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb14617.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minneman K. P., Han C., Abel P. W. Comparison of alpha 1-adrenergic receptor subtypes distinguished by chlorethylclonidine and WB 4101. Mol Pharmacol. 1988 May;33(5):509–514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow A. L., Creese I. Characterization of alpha 1-adrenergic receptor subtypes in rat brain: a reevaluation of [3H]WB4104 and [3H]prazosin binding. Mol Pharmacol. 1986 Apr;29(4):321–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oriowo M. A., Ruffolo R. R., Jr Heterogeneity of postjunctional alpha 1-adrenoceptors in mammalian aortae: subclassification based on chlorethylclonidine, WB 4101 and nifedipine. J Vasc Res. 1992 Jan-Feb;29(1):33–40. doi: 10.1159/000158929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez D. M., Piascik M. T., Graham R. M. Solution-phase library screening for the identification of rare clones: isolation of an alpha 1D-adrenergic receptor cDNA. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Dec;40(6):876–883. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rokosh D. G., Bailey B. A., Stewart A. F., Karns L. R., Long C. S., Simpson P. C. Distribution of alpha 1C-adrenergic receptor mRNA in adult rat tissues by RNase protection assay and comparison with alpha 1B and alpha 1D. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 May 16;200(3):1177–1184. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.1575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwinn D. A., Lomasney J. W., Lorenz W., Szklut P. J., Fremeau R. T., Jr, Yang-Feng T. L., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J., Cotecchia S. Molecular cloning and expression of the cDNA for a novel alpha 1-adrenergic receptor subtype. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 15;265(14):8183–8189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwinn D. A., Page S. O., Middleton J. P., Lorenz W., Liggett S. B., Yamamoto K., Lapetina E. G., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J., Cotecchia S. The alpha 1C-adrenergic receptor: characterization of signal transduction pathways and mammalian tissue heterogeneity. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Nov;40(5):619–626. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleight A. J., Koek W., Bigg D. C. Binding of antipsychotic drugs at alpha 1A- and alpha 1B-adrenoceptors: risperidone is selective for the alpha 1B-adrenoceptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1993 Jul 20;238(2-3):407–410. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(93)90876-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tian W. N., Gupta S., Deth R. C. Species differences in chlorethylclonidine antagonism at vascular alpha-1 adrenergic receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 May;253(2):877–883. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner T. D., Allcock G. H., Vane J. R. Reversal of established responses to endothelin-1 in vivo and in vitro by the endothelin receptor antagonists, BQ-123 and PD 145065. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 May;112(1):207–213. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb13053.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


