Abstract
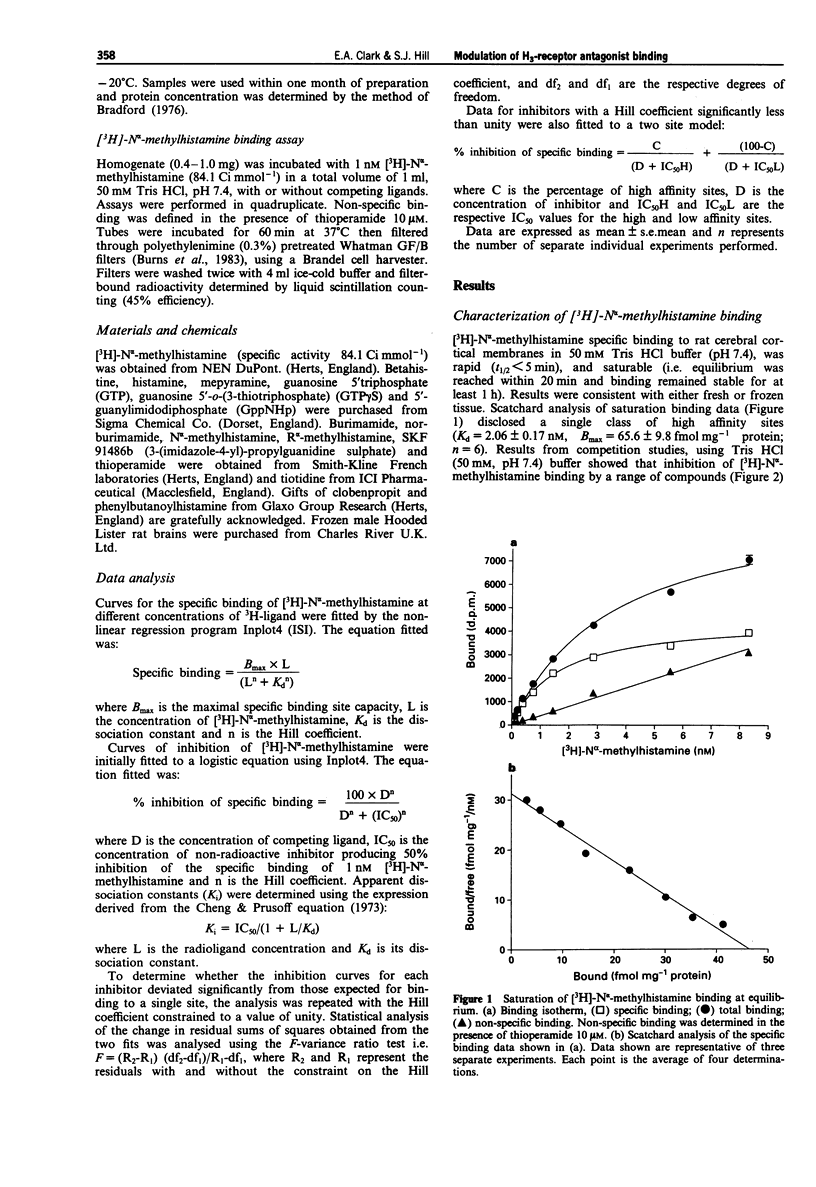
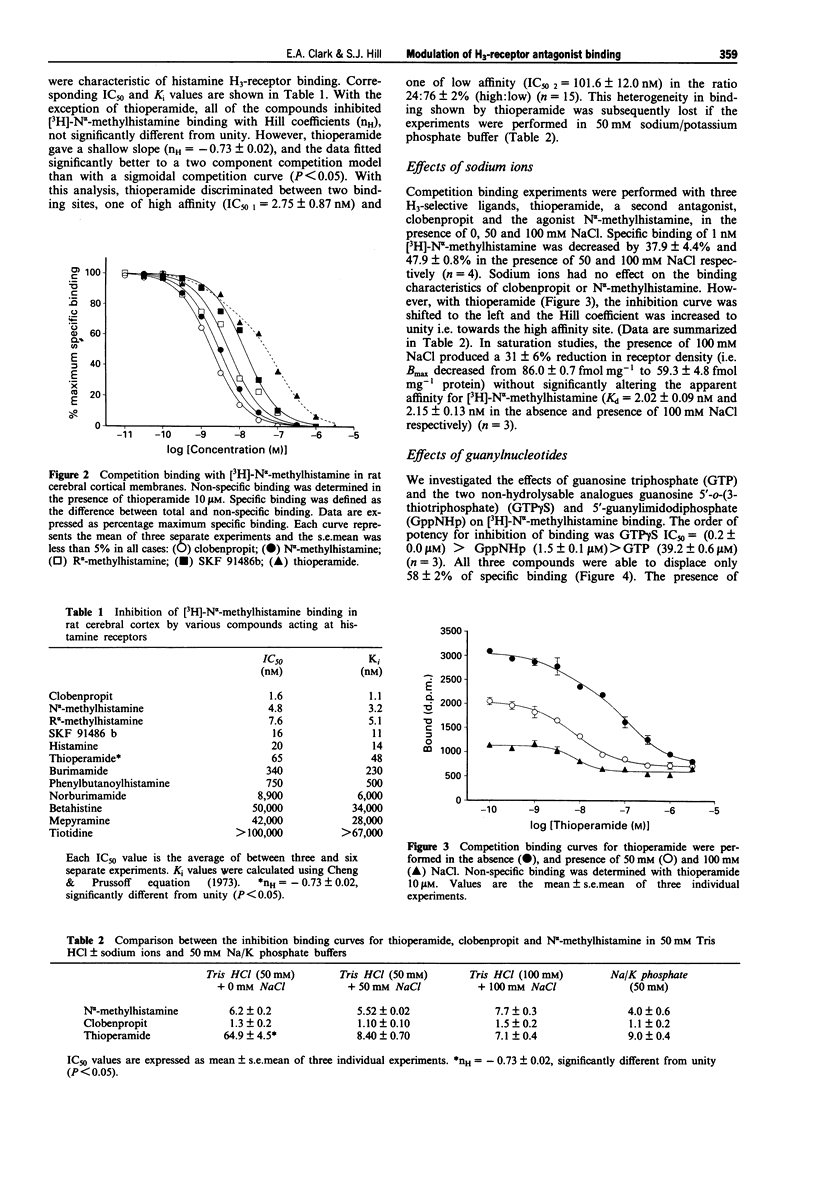
1. Conflicting reports in the literature over heterogeneity (West et al., 1990) or homogeneity (Arrange et al., 1990) of histamine H3-receptor binding sites may be attributed to the use of different incubation conditions. In the present study we have investigated the extent to which the binding of H3-receptor ligands to rat cerebral cortical membranes can be modified by both sodium ions and guanine nucleotides. 2. The H3-selective antagonist, thioperamide, discriminated between two specific binding sites for [3H]-N alpha-methylhistamine (IC50 1 = 2.75 +/- 0.87 nM, IC50 2 101.6 +/- 12.0 nM, % site 1 = 24 +/- 2%) in 50 mM Tris HCl buffer, but showed homogeneity of binding in 50 mM Na/K phosphate buffer. 3. Sodium ions markedly altered the binding characteristics of thioperamide (i.e. heterogeneity was lost and IC50 value shifted towards the high affinity site). The competition curves for a second H3-antagonist, clobenpropit and the H3-agonist N alpha-methylhistamine however, were unaltered in the presence of sodium ions. 4. Guanylnucleotides displaced only 60% of specific [3H]-N alpha- methylhistamine binding and modulated thioperamide binding in the same way as sodium ions. 5. These data suggest that the H3-receptor can exist in different conformations for which thioperamide, but not N alpha-methylhistamine and clobenpropit, show differential affinity. 6. The potential nature of these sites, and the implications of this apparent receptor heterogeneity for H3-receptor antagonism by thioperamide, are discussed.
Full text
PDF
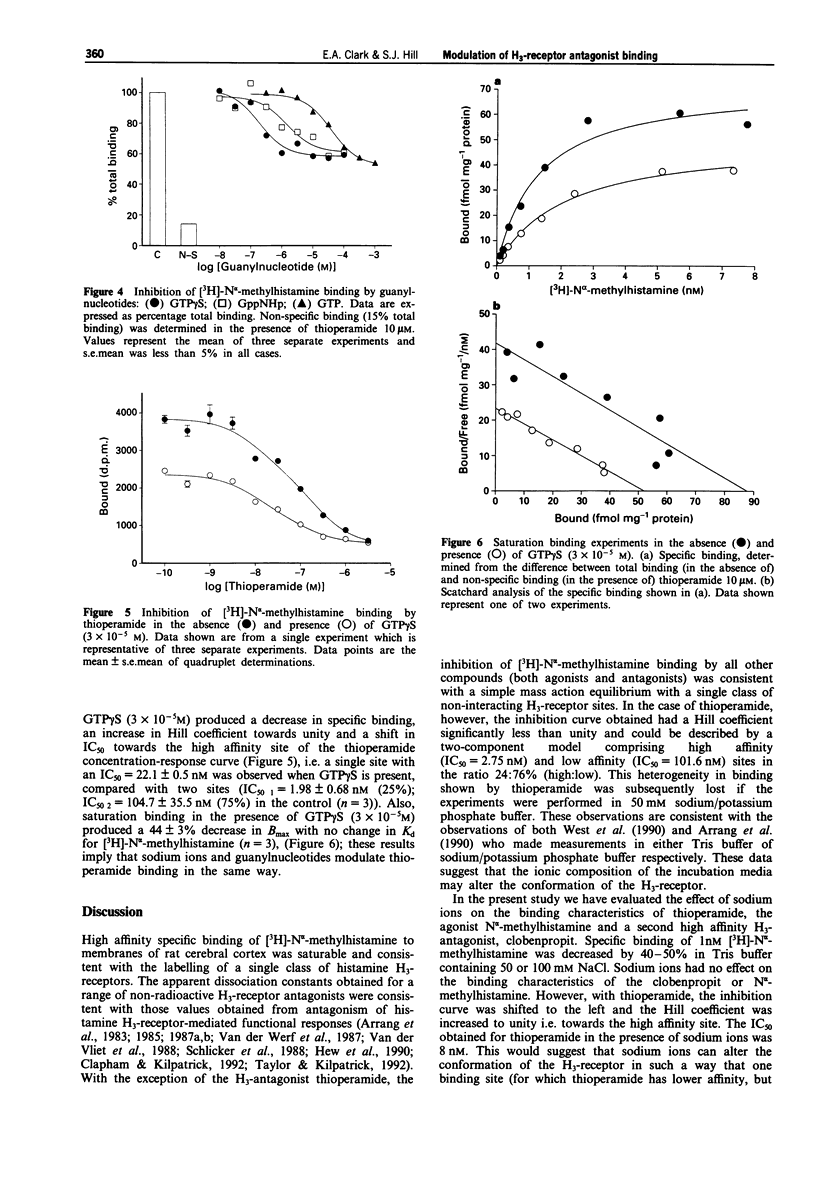


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arrang J. M., Garbarg M., Lancelot J. C., Lecomte J. M., Pollard H., Robba M., Schunack W., Schwartz J. C. Highly potent and selective ligands for histamine H3-receptors. Nature. 1987 May 14;327(6118):117–123. doi: 10.1038/327117a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arrang J. M., Garbarg M., Schwartz J. C. Auto-inhibition of brain histamine release mediated by a novel class (H3) of histamine receptor. Nature. 1983 Apr 28;302(5911):832–837. doi: 10.1038/302832a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arrang J. M., Garbarg M., Schwartz J. C. Autoinhibition of histamine synthesis mediated by presynaptic H3-receptors. Neuroscience. 1987 Oct;23(1):149–157. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(87)90279-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arrang J. M., Garbarg M., Schwartz J. C. Autoregulation of histamine release in brain by presynaptic H3-receptors. Neuroscience. 1985 Jun;15(2):553–562. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(85)90233-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arrang J. M., Roy J., Morgat J. L., Schunack W., Schwartz J. C. Histamine H3 receptor binding sites in rat brain membranes: modulations by guanine nucleotides and divalent cations. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Apr 25;188(4-5):219–227. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(90)90005-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruns R. F., Lawson-Wendling K., Pugsley T. A. A rapid filtration assay for soluble receptors using polyethylenimine-treated filters. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):74–81. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90427-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y., Prusoff W. H. Relationship between the inhibition constant (K1) and the concentration of inhibitor which causes 50 per cent inhibition (I50) of an enzymatic reaction. Biochem Pharmacol. 1973 Dec 1;22(23):3099–3108. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(73)90196-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chidiac P., Hebert T. E., Valiquette M., Dennis M., Bouvier M. Inverse agonist activity of beta-adrenergic antagonists. Mol Pharmacol. 1994 Mar;45(3):490–499. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clapham J., Kilpatrick G. J. Histamine H3 receptors modulate the release of [3H]-acetylcholine from slices of rat entorhinal cortex: evidence for the possible existence of H3 receptor subtypes. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Dec;107(4):919–923. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb13386.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa T., Lang J., Gless C., Herz A. Spontaneous association between opioid receptors and GTP-binding regulatory proteins in native membranes: specific regulation by antagonists and sodium ions. Mol Pharmacol. 1990 Mar;37(3):383–394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa T., Ogino Y., Munson P. J., Onaran H. O., Rodbard D. Drug efficacy at guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory protein-linked receptors: thermodynamic interpretation of negative antagonism and of receptor activity in the absence of ligand. Mol Pharmacol. 1992 Mar;41(3):549–560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hew R. W., Hodgkinson C. R., Hill S. J. Characterization of histamine H3-receptors in guinea-pig ileum with H3-selective ligands. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Nov;101(3):621–624. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14130.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill S. J. Distribution, properties, and functional characteristics of three classes of histamine receptor. Pharmacol Rev. 1990 Mar;42(1):45–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilpatrick G. J., Michel A. D. Characterisation of the binding of the histamine H3 receptor agonist [3H] (R)-alpha methyl histamine to homogenates of rat and guinea-pig cortex. Agents Actions Suppl. 1991;33:69–75. doi: 10.1007/978-3-0348-7309-3_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjelsberg M. A., Cotecchia S., Ostrowski J., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Constitutive activation of the alpha 1B-adrenergic receptor by all amino acid substitutions at a single site. Evidence for a region which constrains receptor activation. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 25;267(3):1430–1433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korte A., Myers J., Shih N. Y., Egan R. W., Clark M. A. Characterization and tissue distribution of H3 histamine receptors in guinea pigs by N alpha-methylhistamine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 May 16;168(3):979–986. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91125-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefkowitz R. J., Cotecchia S., Samama P., Costa T. Constitutive activity of receptors coupled to guanine nucleotide regulatory proteins. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1993 Aug;14(8):303–307. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(93)90048-O. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samama P., Cotecchia S., Costa T., Lefkowitz R. J. A mutation-induced activated state of the beta 2-adrenergic receptor. Extending the ternary complex model. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 5;268(7):4625–4636. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samama P., Pei G., Costa T., Cotecchia S., Lefkowitz R. J. Negative antagonists promote an inactive conformation of the beta 2-adrenergic receptor. Mol Pharmacol. 1994 Mar;45(3):390–394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlicker E., Betz R., Göthert M. Histamine H3 receptor-mediated inhibition of serotonin release in the rat brain cortex. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1988 May;337(5):588–590. doi: 10.1007/BF00182737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlicker E., Fink K., Hinterthaner M., Göthert M. Inhibition of noradrenaline release in the rat brain cortex via presynaptic H3 receptors. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1989 Dec;340(6):633–638. doi: 10.1007/BF00717738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. J., Kilpatrick G. J. Characterization of histamine-H3 receptors controlling non-adrenergic non-cholinergic contractions of the guinea-pig isolated ileum. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Mar;105(3):667–674. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb09036.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tian W. N., Duzic E., Lanier S. M., Deth R. C. Determinants of alpha 2-adrenergic receptor activation of G proteins: evidence for a precoupled receptor/G protein state. Mol Pharmacol. 1994 Mar;45(3):524–531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Vliet A., Van der Werf J. F., Bast A., Timmerman H. Frequency-dependent autoinhibition of histamine release from rat cortical slices: a possible role for H3 receptor reserve. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1988 Aug;40(8):577–579. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1988.tb05308.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Werf J. F., Bast A., Bijloo G. J., Van der Vliet A., Timmerman H. HA autoreceptor assay with superfused slices of rat brain cortex and electrical stimulation. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Jun 19;138(2):199–206. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90433-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West R. E., Jr, Zweig A., Shih N. Y., Siegel M. I., Egan R. W., Clark M. A. Identification of two H3-histamine receptor subtypes. Mol Pharmacol. 1990 Nov;38(5):610–613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zweig A., Siegel M. I., Egan R. W., Clark M. A., Shorr R. G., West R. E., Jr Characterization of a digitonin-solubilized bovine brain H3 histamine receptor coupled to a guanine nucleotide-binding protein. J Neurochem. 1992 Nov;59(5):1661–1666. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1992.tb10996.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


