Abstract
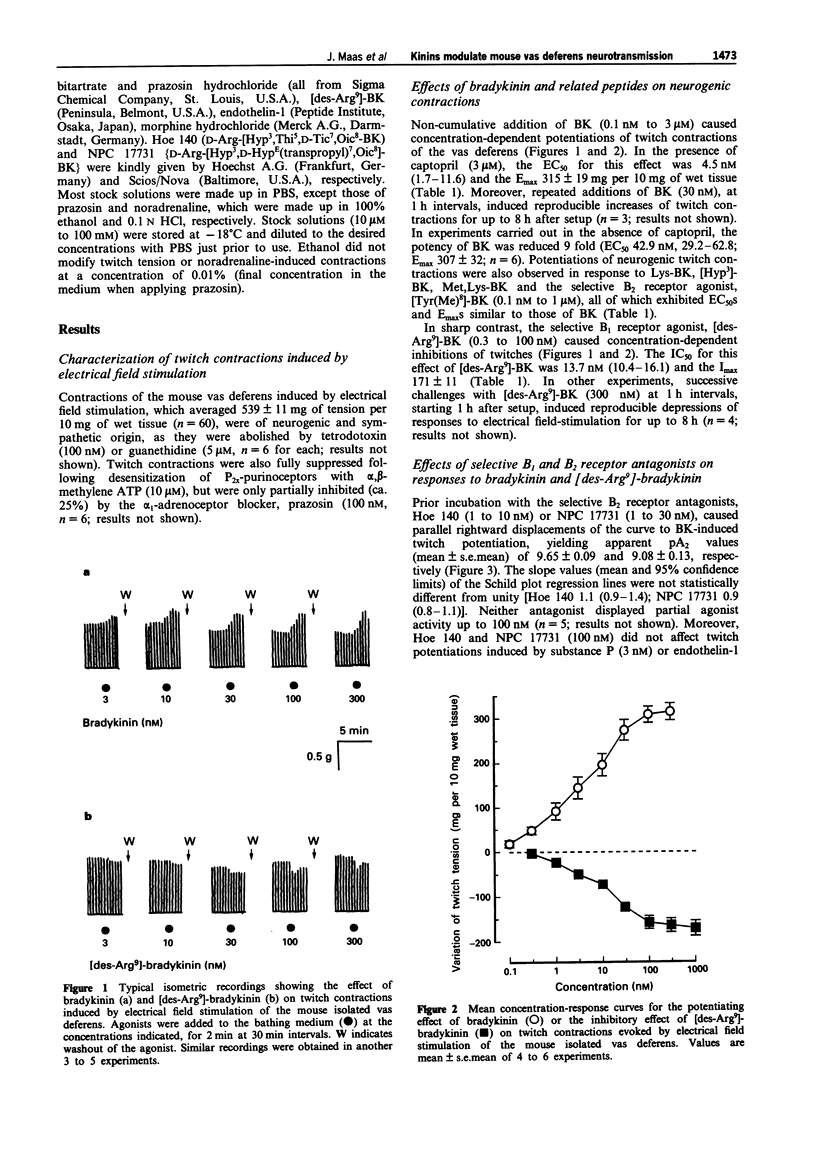
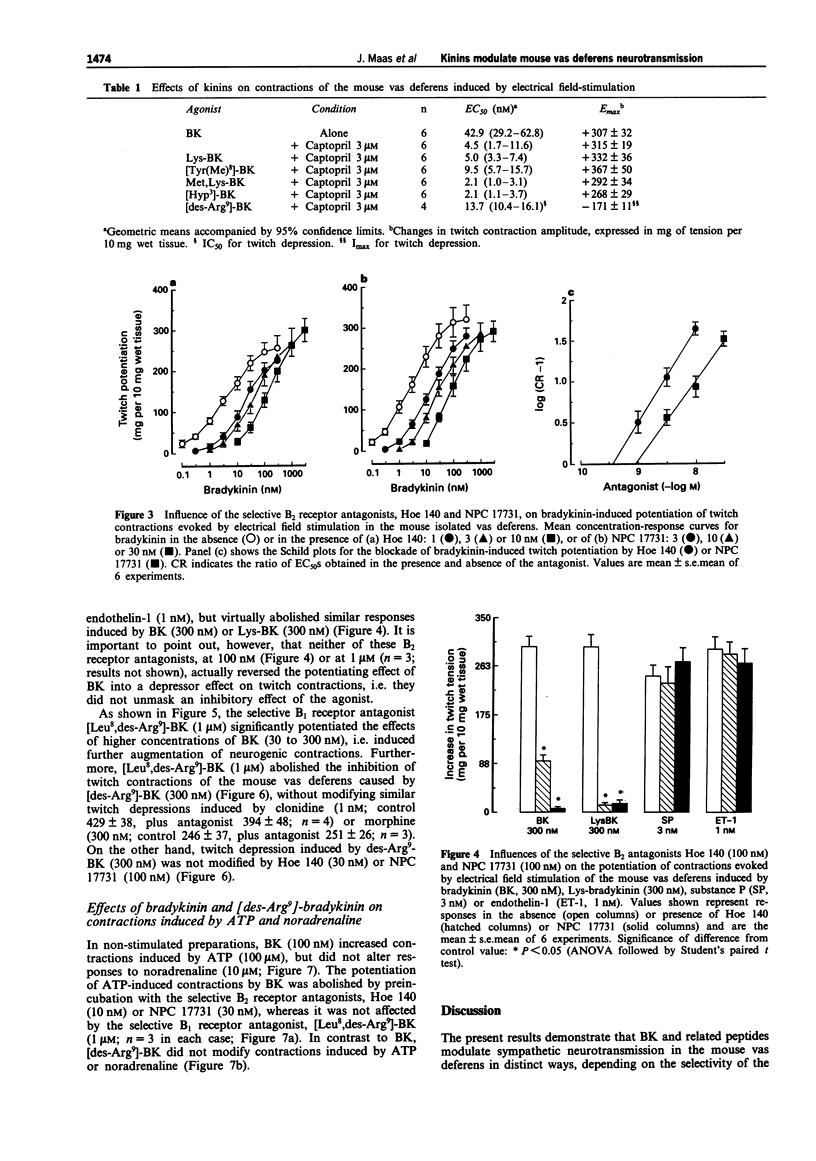
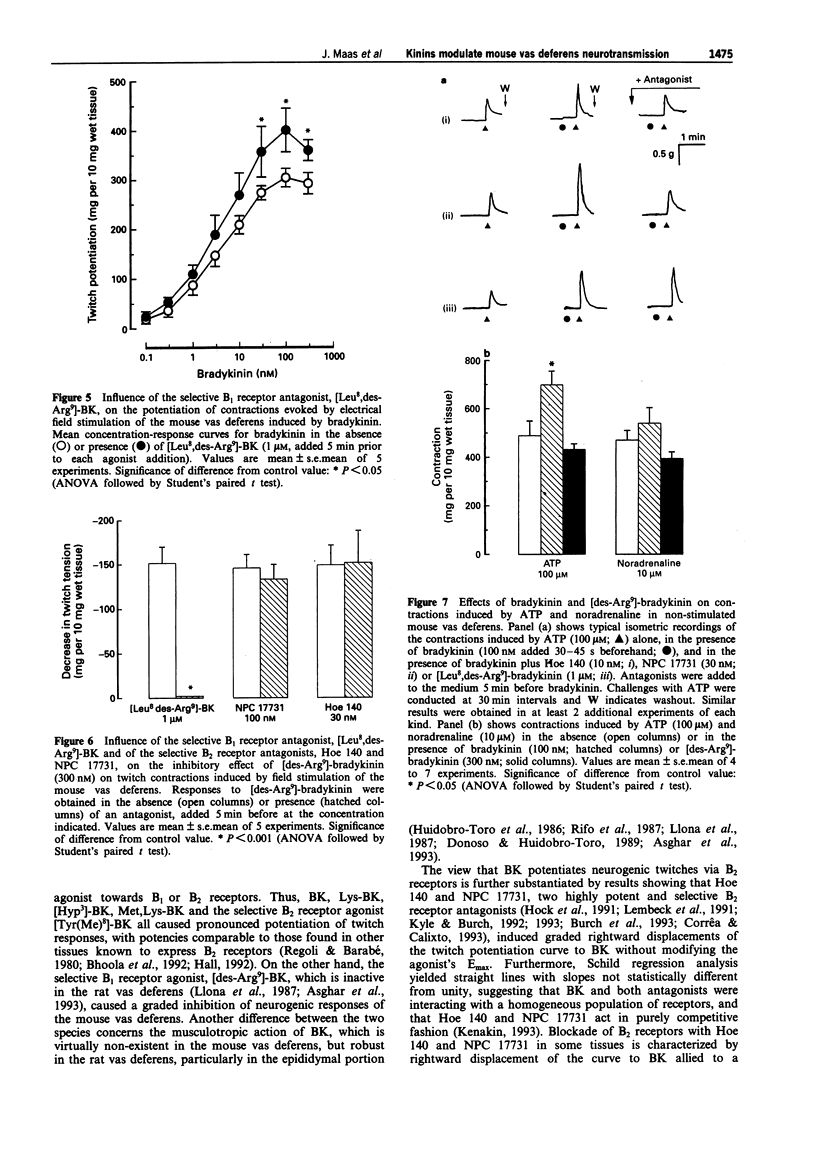
1. This study analyses the receptors mediating the effects of bradykinin (BK) and analogues on neurogenic twitch contractions of the mouse isolated vas deferens evoked, in the presence of captopril (3 microM), by electrical field stimulation with trains of 4 rectangular 0.5 ms pulses of supramaximal strength, delivered at a frequency of 10 Hz every 20 s. 2. BK (0.1-300 nM) induced a graded potentiation of twitches, with an EC50 (geometric mean and 95% confidence limits) of 4.5 nM (1.7-11.6) and an Emax of 315 +/- 19 mg per 10 mg of wet tissue (n = 6). Similar results were obtained in tissues challenged with Lys-BK, [Hyp3]-BK, Met,Lys-BK and the selective B2 receptor agonist [Tyr(Me)8]-BK (0.1-300 nM). 3. The selective B2 receptor antagonists, Hoe 140 (1-10 nM) and NPC 17731 (3-30 nM), caused graded rightward shifts of the curve to BK-induced twitch potentiation, yielding apparent pA2 values of 9.65 +/- 0.09 and 9.08 +/- 0.13, respectively, and Schild plot slopes not different from 1. Both antagonists (100 nM) failed to modify similar twitch potentiations induced by substance P (3 nM) or endothelin-1 (1 nM). Preincubation with the selective B1 receptor antagonist, [Leu8,des-Arg9]-BK (1 microM), increased the potentiating effect of BK on twitches at 30-300 nM. 4. In contrast to BK, the selective B1 receptor agonist, [des-Arg9]-BK (0.3-1000 nM) reduced the amplitude of twitches in a graded fashion, with an IC50 of 13.7 nM (10.4-16.1) and an Imax of 175 +/- 11 mg (n = 4).(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARUNLAKSHANA O., SCHILD H. O. Some quantitative uses of drug antagonists. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1959 Mar;14(1):48–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1959.tb00928.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Acevedo C. G., Lewin J., Contreras E., Huidobro-Toro J. P. Bradykinin facilitates the purinergic motor component of the rat bladder neurotransmission. Neurosci Lett. 1990 May 31;113(2):227–232. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(90)90308-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhoola K. D., Figueroa C. D., Worthy K. Bioregulation of kinins: kallikreins, kininogens, and kininases. Pharmacol Rev. 1992 Mar;44(1):1–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boschcov P., Paiva A. C., Paiva T. B., Shimuta S. I. Further evidence for the existence of two receptor sites for bradykinin responsible for the diphasic effect in the rat isolated duodenum. Br J Pharmacol. 1984 Oct;83(2):591–600. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1984.tb16523.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campos A. H., Calixto J. B. Mechanisms involved in the contractile responses of kinins in rat portal vein rings: mediation by B1 and B2 receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1994 Feb;268(2):902–909. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corrêa C. R., Calixto J. B. Evidence for participation of B1 and B2 kinin receptors in formalin-induced nociceptive response in the mouse. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Sep;110(1):193–198. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13791.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donoso M. V., Huidobro-Toro J. P. Involvement of postjunctional purinergic mechanisms in the facilitatory action of bradykinin in neurotransmission in the rat vas deferens. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Jan 31;160(2):263–273. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90499-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drake M. E., Petersen S. A. ATP overflow from the mouse isolated vas deferens. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Apr;105(4):825–830. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb09064.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field J. L., Hall J. M., Morton I. K. Bradykinin receptors in the guinea-pig taenia caeci are similar to proposed BK3 receptors in the guinea-pig trachea, and are blocked by HOE 140. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Feb;105(2):293–296. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14248.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming W. W., Westfall D. P., De la Lande I. S., Jellett L. B. Log-normal distribution of equiefective doses of norepinephrine and acetylcholine in several tissues. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1972 May;181(2):339–345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griesbacher T., Lembeck F. Analysis of the antagonistic actions of HOE 140 and other novel bradykinin analogues on the guinea-pig ileum. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Feb 18;211(3):393–398. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90397-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J. M. Bradykinin receptors: pharmacological properties and biological roles. Pharmacol Ther. 1992 Nov;56(2):131–190. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(92)90016-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J. M., Caulfield M. P., Watson S. P., Guard S. Receptor subtypes or species homologues: relevance to drug discovery. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1993 Oct;14(10):376–383. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(93)90096-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess J. F., Borkowski J. A., Macneil T., Stonesifer G. Y., Fraher J., Strader C. D., Ransom R. W. Differential pharmacology of cloned human and mouse B2 bradykinin receptors. Mol Pharmacol. 1994 Jan;45(1):1–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hock F. J., Wirth K., Albus U., Linz W., Gerhards H. J., Wiemer G., Henke S., Breipohl G., König W., Knolle J. Hoe 140 a new potent and long acting bradykinin-antagonist: in vitro studies. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Mar;102(3):769–773. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12248.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huidobro-Toro J. P., Herreros R., Pinto-Corrado A. Pre- and postsynaptic bradykinin responses in the rat vas deferens: asymmetric distribution of the postsynaptic effect. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 Mar 4;121(3):305–311. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90250-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Illes P., Starke K. An electrophysiological study of presynaptic alpha-adrenoceptors in the vas deferens of the mouse. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Feb;78(2):365–373. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb09402.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurz K., von Kügelgen I., Starke K. Prejunctional modulation of noradrenaline release in mouse and rat vas deferens: contribution of P1- and P2-purinoceptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Dec;110(4):1465–1472. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13986.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lembeck F., Griesbacher T., Eckhardt M., Henke S., Breipohl G., Knolle J. New, long-acting, potent bradykinin antagonists. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Feb;102(2):297–304. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12169.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llona I., Galleguillos X., Belmar J., Huidobro-Toro J. P. Bradykinin modulates the release of noradrenaline from vas deferens nerve terminals. Life Sci. 1991;48(26):2585–2592. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(91)90616-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llona I., Vavrek R., Stewart J., Huidobro-Toro J. P. Identification of pre- and postsynaptic bradykinin receptor sites in the vas deferens: evidence for different structural prerequisites. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 May;241(2):608–614. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lord J. A., Waterfield A. A., Hughes J., Kosterlitz H. W. Endogenous opioid peptides: multiple agonists and receptors. Nature. 1977 Jun 9;267(5611):495–499. doi: 10.1038/267495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medeiros Y. S., Calixto J. B. Analysis of the mechanisms underlying the biphasic responses to bradykinin in circular muscle from guinea pig ileum. Eur J Pharmacol. 1993 Sep 14;241(2-3):157–163. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(93)90197-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rae G. A., Calixto J. B. Effects of endothelins on nerve-mediated contractions of the mouse vas deferens. Life Sci. 1990;47(17):PL83–PL89. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(90)90191-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regoli D., Barabé J. Pharmacology of bradykinin and related kinins. Pharmacol Rev. 1980 Mar;32(1):1–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhaleb N. E., Rouissi N., Jukic D., Regoli D., Henke S., Breipohl G., Knolle J. Pharmacological characterization of a new highly potent B2 receptor antagonist (HOE 140: D-Arg-[Hyp3,Thi5,D-Tic7,Qic8]bradykinin). Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Jan 14;210(2):115–120. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90661-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rifo J., Pourrat M., Vavrek R. J., Stewart J. M., Huidobro-Toro J. P. Bradykinin receptor antagonists used to characterize the heterogeneity of bradykinin-induced responses in rat vas deferens. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Oct 13;142(2):305–312. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90120-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stjärne L., Lundberg J. M., Astrand P. Neuropeptide Y--a cotransmitter with noradrenaline and adenosine 5'-triphosphate in the sympathetic nerves of the mouse vas deferens? A biochemical, physiological and electropharmacological study. Neuroscience. 1986 May;18(1):151–166. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(86)90184-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tousignant C., Dion S., Drapeau G., Regoli D. Characterization of pre- and postjunctional receptors for neurokinins and kinins in the rat vas deferens. Neuropeptides. 1987 May-Jun;9(4):333–343. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(87)90007-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trifilieff A., Amrani Y., Landry Y., Gies J. P. Comparative action of new highly potent bradykinin receptor antagonists in the guinea-pig trachea. Eur J Pharmacol. 1993 Aug 3;239(1-3):227–229. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(93)91000-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zetler G., Kampmann E. An attempt to differentiate the effects of angiotensin II, substance P and bradykinin on the field-stimulated guinea-pig vas deferens. Eur J Pharmacol. 1979 Jun;56(1-2):21–29. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(79)90428-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Kügelgen I., Bültmann R., Starke K. Effects of suramin and alpha, beta-methylene ATP indicate noradrenaline-ATP co-transmission in the response of the mouse vas deferens to single and low frequency pulses. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1989 Dec;340(6 Pt 2):760–763. doi: 10.1007/BF00169686. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


