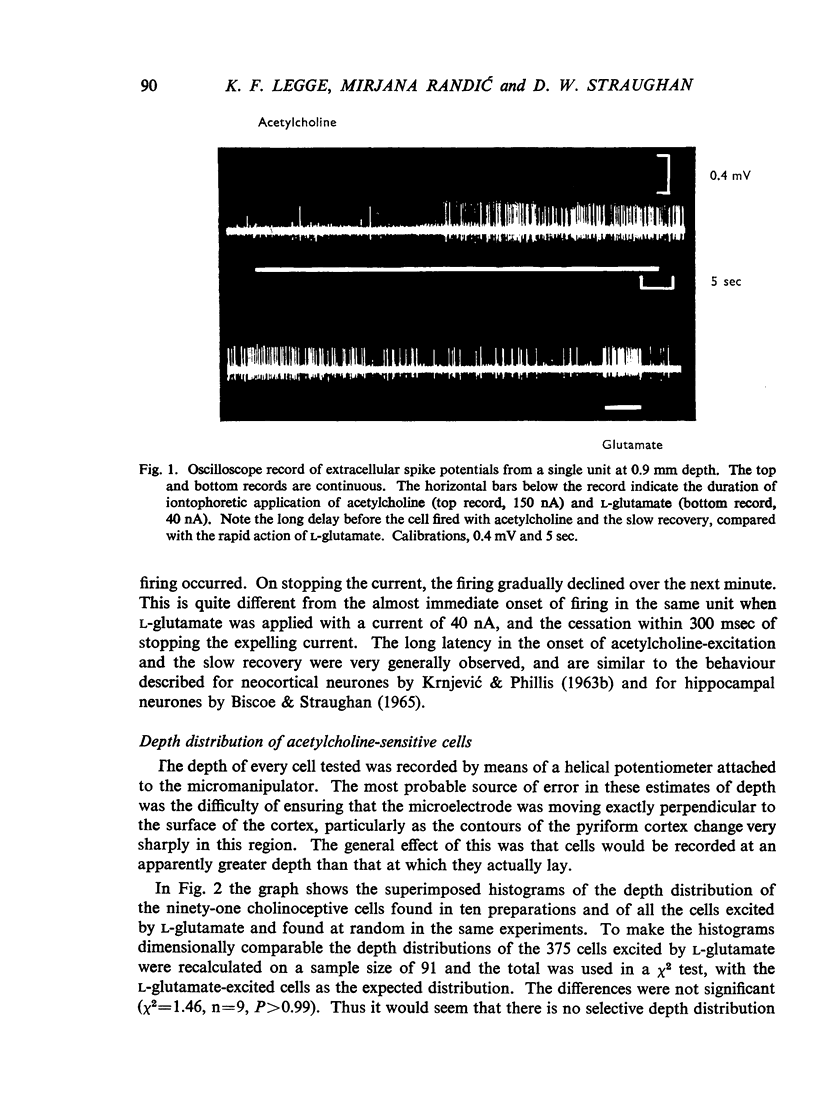
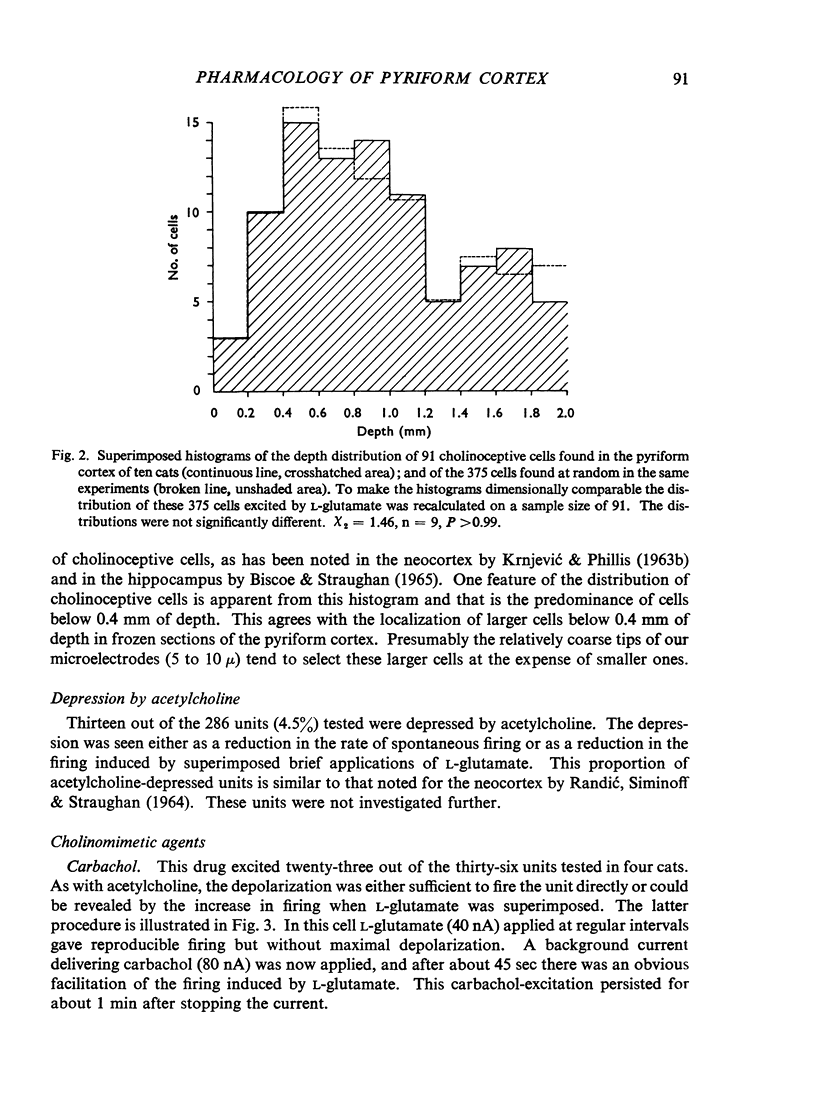
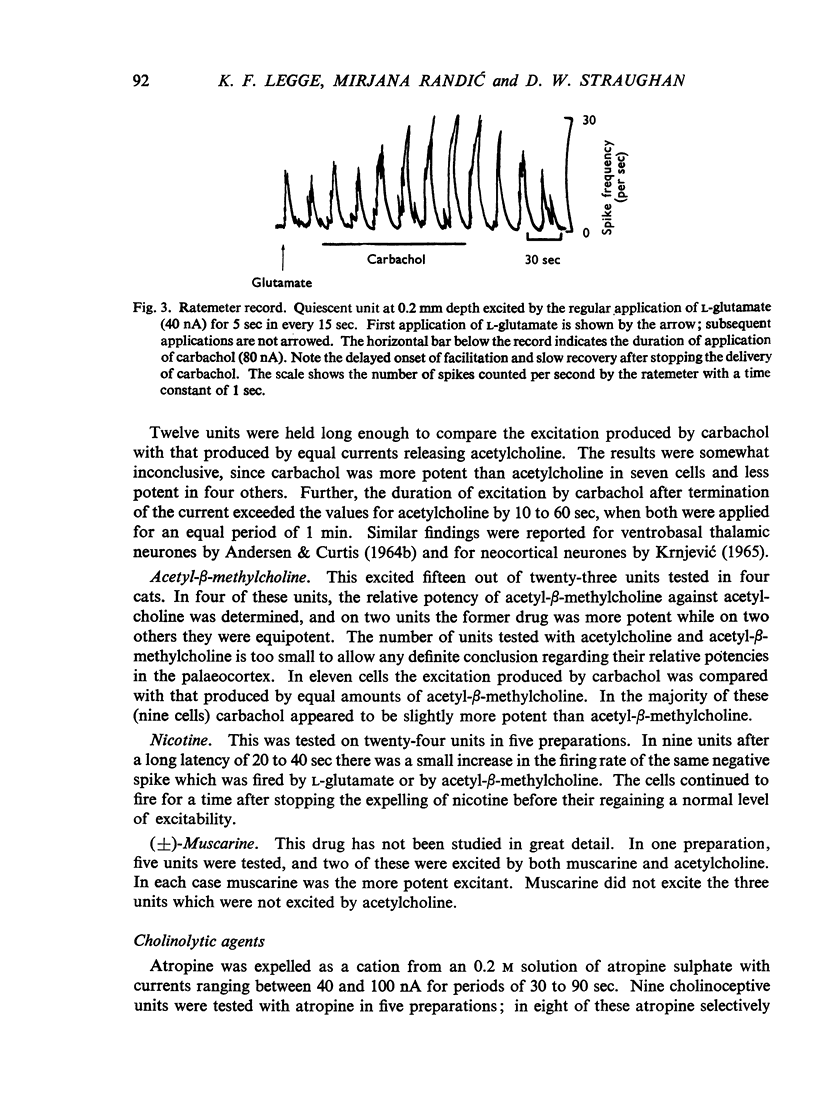
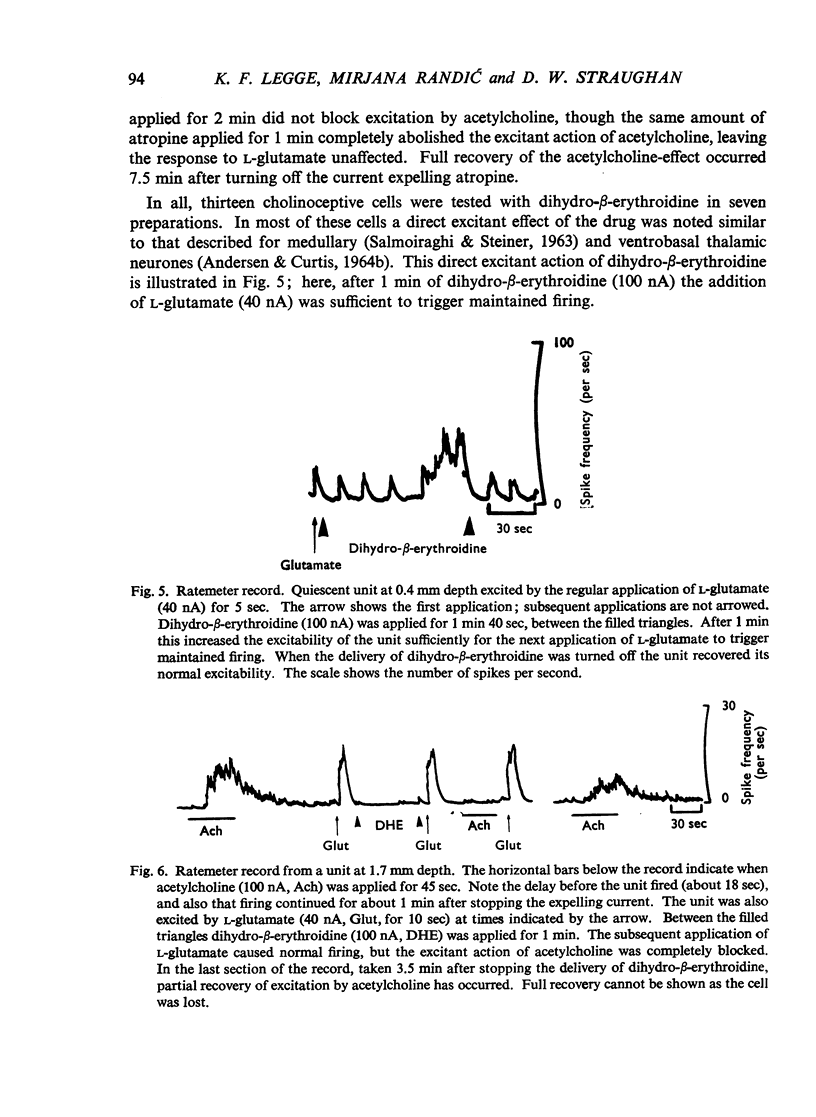
Full text
PDF












Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADRIAN E. D. The electrical activity of the mammalian olfactory bulb. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1950 Nov;2(4):377–388. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(50)90075-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AMIN A. H., CRAWFORD T. B., GADDUM J. H. The distribution of substance P and 5-hydroxytryptamine in the central nervous system of the dog. J Physiol. 1954 Dec 10;126(3):596–618. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ANDERSEN P., CURTIS D. R. THE EXCITATION OF THALAMIC NEURONES BY ACETYLCHOLINE. Acta Physiol Scand. 1964 May-Jun;61:85–99. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1964.tb02945.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ANDERSEN P., CURTIS D. R. THE PHARMACOLOGY OF THE SYNAPTIC AND ACETYLCHOLINE-INDUCED EXCITATION OF VENTROBASAL THALAMIC NEURONES. Acta Physiol Scand. 1964 May-Jun;61:100–120. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1964.tb02946.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian E. D. Olfactory reactions in the brain of the hedgehog. J Physiol. 1942 Mar 31;100(4):459–473. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1942.sp003955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BISCOE T. J., STRAUGHAN D. W. THE PHARMACOLOGY OF HIPPOCAMPAL NEURONES. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1965 Jan;17:60–61. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1965.tb07571.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLOOM F. E., COSTA E., SALMOIRAGHI G. C. ANALYSIS OF INDIVIDUAL RABBIT OLFACTORY BULB NEURON RESPONSES TO THE MICROELECTROPHORESIS OF ACETYLCHOLINE, NOREPINEPHRINE AND SEROTONIN SYNERGISTS AND ANTAGONISTS. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1964 Oct;146:16–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOGDANSKI D. F., WEISSBACH H., UDENFRIEND S. The distribution of serotonin, 5-hydroxytryptophan decarboxylase, and monoamine oxidase in brain. J Neurochem. 1957;1(3):272–278. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1957.tb12082.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRADLEY P. B., WOLSTENCROFT J. H. ACTIONS OF DRUGS ON SINGLE NEURONES IN THE BRAIN-STEM. Br Med Bull. 1965 Jan;21:15–18. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a070349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRADLEY P. B., WOLSTENCROFT J. H. Excitaion and inhibition of brain-stem neurones by noradrenaline and acetylcholine. Nature. 1962 Dec 1;196:840–passim. doi: 10.1038/196840a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURGEN A. S. V., CHIPMAN L. M. Cholinesterase and succinic dehydrogenase in the central nervous system of the dog. J Physiol. 1951 Jul;114(3):296–305. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1951.sp004621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARLSSON A., FALCK B., FUXE K., HILLARP N. A. CELLULAR LOCALIZATION OF MONOAMINES IN THE SPINAL CORD. Acta Physiol Scand. 1964 Jan-Feb;60:112–119. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1964.tb02874.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARLSSON A., FALCK B., HILLARP N. A., TORP A. Histochemical localization at the cellular level of hypothalamic noradrenaline. Acta Physiol Scand. 1962 Mar-Apr;54:385–386. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1962.tb02364.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRAWFORD J. M., CURTIS D. R. THE EXCITATION AND DEPRESSION OF MAMMALIAN CORTICAL NEURONES BY AMINO ACIDS. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1964 Oct;23:313–329. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1964.tb01589.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRAWFORD J. M., CURTIS D. R., VOORHOEVE P. E., WILSON V. J. EXCITATION OF CEREBELLAR NEURONES BY ACETYLCHOLINE. Nature. 1963 Nov 9;200:579–580. doi: 10.1038/200579b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CURTIS D. R., ANDERSEN P. Acetylcholine: a central transmitter? Nature. 1962 Sep 15;195:1105–1106. doi: 10.1038/1951105a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CURTIS D. R. Action of 3-hydroxytyramine and some tryptamine derivatives on spinal neurones. Nature. 1962 Apr 21;194:292–292. doi: 10.1038/194292a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CURTIS D. R., DAVIS R. Pharmacological studies upon neurones of the lateral geniculate nucleus of the cat. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1962 Apr;18:217–246. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1962.tb01404.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CURTIS D. R., DAVIS R. The excitation of lateral geniculate neurones by quaternary ammonium derivatives. J Physiol. 1963 Jan;165:62–82. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CURTIS D. R., KOIZUMI K. Chemical transmitter substances in brain stem of cat. J Neurophysiol. 1961 Jan;24:80–90. doi: 10.1152/jn.1961.24.1.80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CURTIS D. R., PHILLIS J. W. The action of procaine and atropine on spinal neurones. J Physiol. 1960 Aug;153:17–34. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CURTIS D. R., PHILLIS J. W., WATKINS J. C. Cholinergic and non-cholinergic transmission in the mammalian spinal cord. J Physiol. 1961 Sep;158:296–323. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CURTIS D. R., RYALL R. W. NICOTINIC AND MUSCARINIC RECEPTORS OF RENSHAW CELLS. Nature. 1964 Aug 8;203:652–653. doi: 10.1038/203652a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlström A., Fuxe K. Localization of monoamines in the lower brain stem. Experientia. 1964 Jul 15;20(7):398–399. doi: 10.1007/BF02147990. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldberg W., Vogt M. Acetylcholine synthesis in different regions of the central nervous system. J Physiol. 1948 Jun 25;107(3):372–381. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1948.sp004282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GADDUM J. H. Antagonism between lysergic acid diethylamide and 5-hydroxytryptamine. J Physiol. 1953 Jul;121(1):15P–15P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GADDUM J. H., HAMEED K. A. Drugs which antagonize 5-hydroxytryptamine. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1954 Jun;9(2):240–248. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1954.tb00848.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN J. D., CLEMENTE C. D., DE GROOT J. Rhinencephalic lesions and behavior in cats: an analysis of the Kluver-Bucy syndrome with particular reference to normal and abnormal sexual behavior. J Comp Neurol. 1957 Dec;108(3):505–545. doi: 10.1002/cne.901080308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN J. D., MANCIA M., von BAUMGARTEN Recurrent inhibition in the olfactory bulb. I. Effects of antidromic stimulation of the lateral olfactory tract. J Neurophysiol. 1962 Jul;25:467–488. doi: 10.1152/jn.1962.25.4.467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEBB C. O., SILVER A. Choline acetylase in the central nervous system of man and some other mammals. J Physiol. 1956 Dec 28;134(3):718–728. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOFMANN A. Psychotomimetic drugs; chemical and pharmacological aspects. Acta Physiol Pharmacol Neerl. 1959 Jun;8:240–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRNJEVIC K., LAVERTY R., SHARMAN D. F. Iontophoretic release of adrenaline, noradrenaline and 5-hydroxytryptamine from micropipettes. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1963 Jun;20:491–496. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1963.tb01485.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRNJEVIC K., PHILLIS J. W. Acetylcholine-sensitive cells in the cerebral cortex. J Physiol. 1963 Apr;166:296–327. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRNJEVIC K., PHILLIS J. W. Iontophoretic studies of neurones in the mammalian cerebral cortex. J Physiol. 1963 Feb;165:274–304. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUNTZMAN R., SHORE P. A., BOGDANSKI D., BRODIE B. B. Microanalytical procedures for fluorometric assay of brain DOPA-5HTP decarboxylase, norepinephrine and serotonin, and a detailed mapping of decarboxylase activity in brain. J Neurochem. 1961 Feb;6:226–232. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1961.tb13469.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krnjević K., Phillis J. W. Pharmacological properties of acetylcholine-sensitive cells in the cerebral cortex. J Physiol. 1963 May;166(2):328–350. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krnjević K., Silver A. A histochemical study of cholinergic fibres in the cerebral cortex. J Anat. 1965 Oct;99(Pt 4):711–759. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACLEAN P. D., DELGADO J. M. R. Electrical and chemical stimulation of frontotemporal portion of limbic system in the waking animal. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1953 Feb;5(1):91–100. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(53)90056-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACLEAN P. D., HORWITZ N. H., ROBINSON F. Olfactory-like responses in pyriform area to non-olfactory stimulation. Yale J Biol Med. 1952 Dec;25(3):159–172. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCance I., Phillis J. W. The action of acetylcholine on cells in cat cerebellar cortex. Experientia. 1964 Apr 15;20(4):217–218. doi: 10.1007/BF02135411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OLDS J. Self-stimulation of the brain; its use to study local effects of hunger, sex, and drugs. Science. 1958 Feb 14;127(3294):315–324. doi: 10.1126/science.127.3294.315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAASONEN M. K., MACLEAN P. D., GIARMAN N. J. 5-Hydroxytryptamine (serotonin, enteramine) content of structures of the limbic system. J Neurochem. 1957;1(4):326–333. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1957.tb12089.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PHILLIPS C. G., POWELL T. P., SHEPHERD G. M. RESPONSES OF MITRAL CELLS TO STIMULATION OF THE LATERAL OLFACTORY TRACT IN THE RABBIT. J Physiol. 1963 Aug;168:65–88. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PHILLIS J. W. CHOLINERGIC MECHANISMS IN THE CEREBELLUM. Br Med Bull. 1965 Jan;21:26–29. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a070351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RANDIC M., SIMINOFF R., STRAUGHAN D. W. ACETYLCHOLINE DEPRESSION OF CORTICAL NEURONS. Exp Neurol. 1964 Mar;9:236–242. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(64)90020-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SALMOIRAGHI G. C., STEINER F. A. Acetylcholine sensitivity of cat's medullary neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1963 Jul;26:581–597. doi: 10.1152/jn.1963.26.4.581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHREINER L., KLING A. Behavioral changes following rhinencephalic injury in cat. J Neurophysiol. 1953 Nov;16(6):643–659. doi: 10.1152/jn.1953.16.6.643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHUTE C. C., LEWIS P. R. CHOLINESTERASE-CONTAINING SYSTEMS OF THE BRAIN OF THE RAT. Nature. 1963 Sep 21;199:1160–1164. doi: 10.1038/1991160a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGT M., GUNN C. G., Jr, SAWYER C. H. Electroencephalographic effects of intraventricular 5-HT and LSD in the cat. Neurology. 1957 Aug;7(8):559–566. doi: 10.1212/wnl.7.8.559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGT M. The concentration of sympathin in different parts of the central nervous system under normal conditions and after the administration of drugs. J Physiol. 1954 Mar 29;123(3):451–481. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


