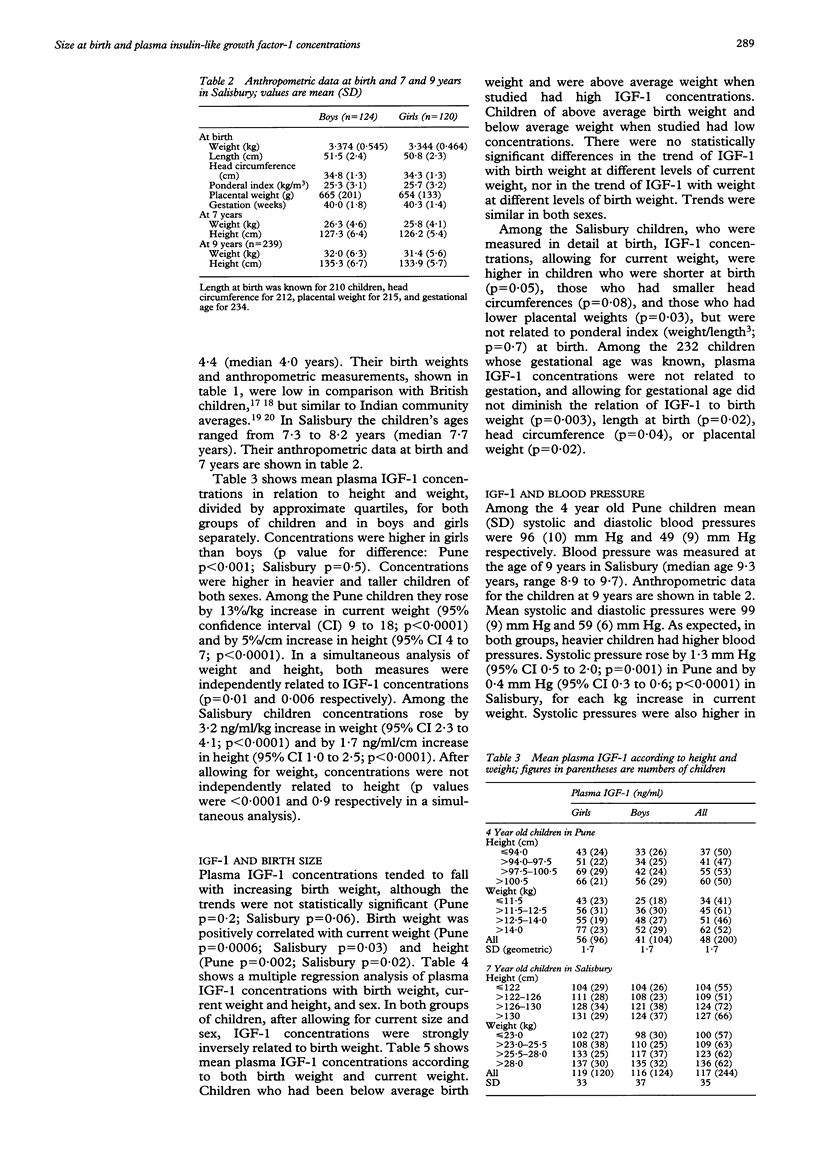
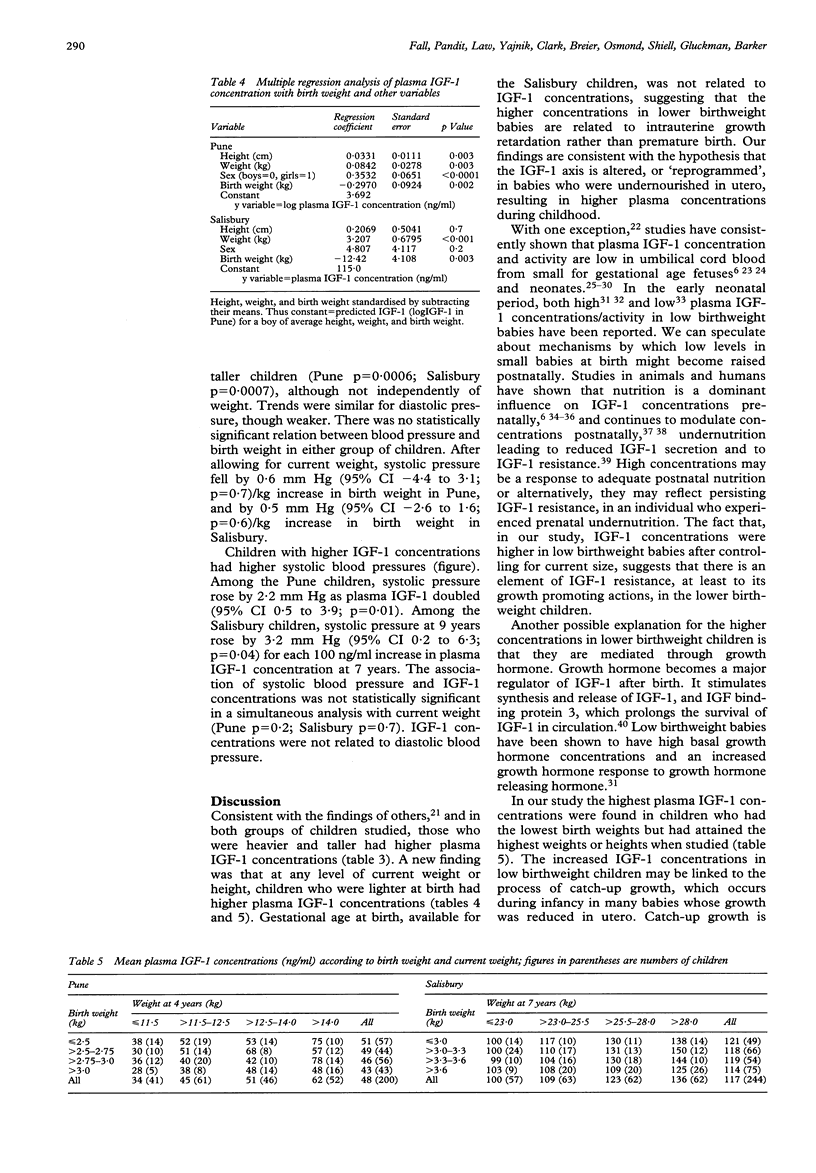
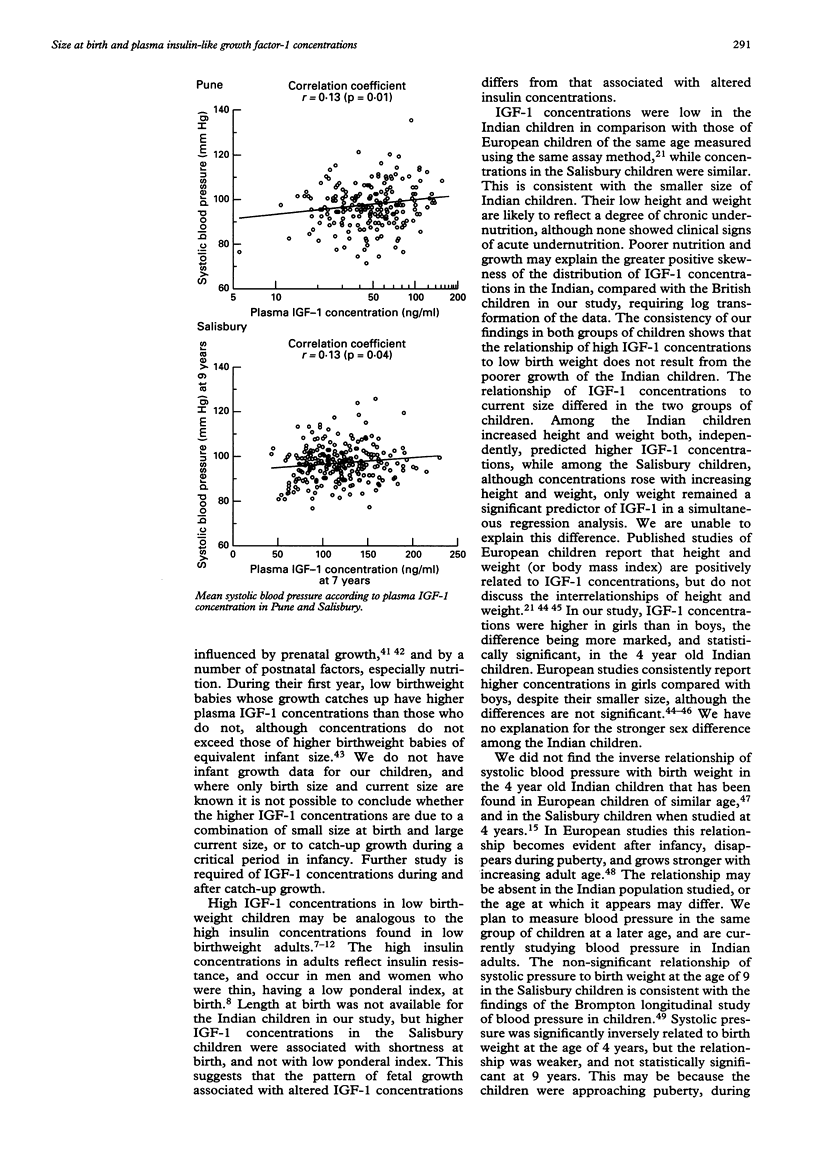
Abstract
OBJECTIVE--To test the hypothesis that reduced fetal growth leads to altered plasma insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) concentrations in childhood. DESIGN--A follow up study of 4 year old children whose birth weights were recorded, and of 7 year old children whose weight, length, head circumference, and placental weight were measured at birth. SETTING--Pune, India, and Salisbury, England. SUBJECTS--200 children born during October 1987 to April 1989 in the King Edward Memorial Hospital, Pune, weighing over 2.0 kg at birth and not requiring special care, and 244 children born during July 1984 to February 1985 in the Salisbury Health District and still living there. MAIN OUTCOME MEASURE--Plasma IGF-1 concentrations. RESULTS--In both groups of children, and consistent with findings in other studies, plasma IGF-1 concentrations were higher in taller and heavier children, and higher in girls than boys. Allowing for sex and current size, concentrations were inversely related to birth weight (Pune p = 0.002; Salisbury p = 0.003). Thus at any level of weight or height, children of lower birth weight had higher IGF-1 concentrations. The highest concentrations were in children who were below average birth weight and above average weight or height when studied. Systolic blood pressures were higher in children with higher IGF-1 concentrations (Pune p = 0.01; Salisbury p = 0.04). CONCLUSIONS--Children of lower birth weight develop higher circulating concentrations of IGF-1 than expected for their height and weight. This is consistent with the hypothesis that under-nutrition in utero leads to reprogramming of the IGF-1 axis. The increase of plasma IGF-1 concentrations in low birthweight children may also be linked to postnatal catch-up growth. High IGF-1 concentrations may be one of the mechanisms linking reduced fetal growth and high blood pressure in later life.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Argente J., Barrios V., Pozo J., Muñoz M. T., Hervás F., Stene M., Hernández M. Normative data for insulin-like growth factors (IGFs), IGF-binding proteins, and growth hormone-binding protein in a healthy Spanish pediatric population: age- and sex-related changes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1993 Dec;77(6):1522–1528. doi: 10.1210/jcem.77.6.7505288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashton I. K., Vesey J. Somatomedin activity in human cord plasma and relationship to birth size, insulin, growth hormone, and prolactin. Early Hum Dev. 1978 Jul;2(2):115–122. doi: 10.1016/0378-3782(78)90003-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashton I. K., Zapf J., Einschenk I., MacKenzie I. Z. Insulin-like growth factors (IGF) 1 and 2 in human foetal plasma and relationship to gestational age and foetal size during midpregnancy. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1985 Dec;110(4):558–563. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.1100558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bala R. M., Lopatka J., Leung A., McCoy E., McArthur R. G. Serum immunoreactive somatomedin levels in normal adults, pregnant women at term, children at various ages, and children with constitutionally delayed growth. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1981 Mar;52(3):508–512. doi: 10.1210/jcem-52-3-508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker D. J., Bull A. R., Osmond C., Simmonds S. J. Fetal and placental size and risk of hypertension in adult life. BMJ. 1990 Aug 4;301(6746):259–262. doi: 10.1136/bmj.301.6746.259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker D. J., Gluckman P. D., Godfrey K. M., Harding J. E., Owens J. A., Robinson J. S. Fetal nutrition and cardiovascular disease in adult life. Lancet. 1993 Apr 10;341(8850):938–941. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)91224-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker D. J., Hales C. N., Fall C. H., Osmond C., Phipps K., Clark P. M. Type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus, hypertension and hyperlipidaemia (syndrome X): relation to reduced fetal growth. Diabetologia. 1993 Jan;36(1):62–67. doi: 10.1007/BF00399095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker D. J., Osmond C., Simmonds S. J., Wield G. A. The relation of small head circumference and thinness at birth to death from cardiovascular disease in adult life. BMJ. 1993 Feb 13;306(6875):422–426. doi: 10.1136/bmj.306.6875.422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett A., Wilson D. M., Liu F., Nagashima R., Rosenfeld R. G., Hintz R. L. Levels of insulin-like growth factors I and II in human cord blood. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1983 Sep;57(3):609–612. doi: 10.1210/jcem-57-3-609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blum W. F., Albertsson-Wikland K., Rosberg S., Ranke M. B. Serum levels of insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) and IGF binding protein 3 reflect spontaneous growth hormone secretion. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1993 Jun;76(6):1610–1616. doi: 10.1210/jcem.76.6.7684744. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breier B. H., Milsom S. R., Blum W. F., Schwander J., Gallaher B. W., Gluckman P. D. Insulin-like growth factors and their binding proteins in plasma and milk after growth hormone-stimulated galactopoiesis in normally lactating women. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1993 Nov;129(5):427–435. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.1290427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemmons D. R., Underwood L. E. Nutritional regulation of IGF-I and IGF binding proteins. Annu Rev Nutr. 1991;11:393–412. doi: 10.1146/annurev.nu.11.070191.002141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deiber M., Chatelain P., Naville D., Putet G., Salle B. Functional hypersomatotropism in small for gestational age (SGA) newborn infants. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1989 Jan;68(1):232–234. doi: 10.1210/jcem-68-1-232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fall C. H., Osmond C., Barker D. J., Clark P. M., Hales C. N., Stirling Y., Meade T. W. Fetal and infant growth and cardiovascular risk factors in women. BMJ. 1995 Feb 18;310(6977):428–432. doi: 10.1136/bmj.310.6977.428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferns G. A., Motani A. S., Anggård E. E. The insulin-like growth factors: their putative role in atherogenesis. Artery. 1991;18(4):197–225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foley T. P., Jr, DePhilip R., Perricelli A., Miller A. Low somatomedin activity in cord serum from infants with intrauterine growth retardation. J Pediatr. 1980 Mar;96(3 Pt 2):605–610. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(80)80874-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluckman P. D., Brinsmead M. W. Somatomedin in cord blood: relationship to gestational age and birth size. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1976 Dec;43(6):1378–1381. doi: 10.1210/jcem-43-6-1378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluckman P. D. Fetal growth: an endocrine perspective. Acta Paediatr Scand Suppl. 1989;349:21–26. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1989.tb17162.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hales C. N., Barker D. J., Clark P. M., Cox L. J., Fall C., Osmond C., Winter P. D. Fetal and infant growth and impaired glucose tolerance at age 64. BMJ. 1991 Oct 26;303(6809):1019–1022. doi: 10.1136/bmj.303.6809.1019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes G. E., Miller H. C., Hassanein K., Lansky S. B., Goggin J. E. Postnatal somatic growth in infants with atypical fetal growth patterns. Am J Dis Child. 1977 Oct;131(10):1078–1083. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1977.02120230024003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juul A., Bang P., Hertel N. T., Main K., Dalgaard P., Jørgensen K., Müller J., Hall K., Skakkebaek N. E. Serum insulin-like growth factor-I in 1030 healthy children, adolescents, and adults: relation to age, sex, stage of puberty, testicular size, and body mass index. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1994 Mar;78(3):744–752. doi: 10.1210/jcem.78.3.8126152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King G. L., Goodman A. D., Buzney S., Moses A., Kahn C. R. Receptors and growth-promoting effects of insulin and insulinlike growth factors on cells from bovine retinal capillaries and aorta. J Clin Invest. 1985 Mar;75(3):1028–1036. doi: 10.1172/JCI111764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langford K. S., Miell J. P. The insulin-like growth factor-I/binding protein axis: physiology, pathophysiology and therapeutic manipulation. Eur J Clin Invest. 1993 Sep;23(9):503–516. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1993.tb00958.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langford K., Blum W., Nicolaides K., Jones J., McGregor A., Miell J. The pathophysiology of the insulin-like growth factor axis in fetal growth failure: a basis for programming by undernutrition? Eur J Clin Invest. 1994 Dec;24(12):851–856. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1994.tb02030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassarre C., Hardouin S., Daffos F., Forestier F., Frankenne F., Binoux M. Serum insulin-like growth factors and insulin-like growth factor binding proteins in the human fetus. Relationships with growth in normal subjects and in subjects with intrauterine growth retardation. Pediatr Res. 1991 Mar;29(3):219–225. doi: 10.1203/00006450-199103000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law C. M., Barker D. J., Bull A. R., Osmond C. Maternal and fetal influences on blood pressure. Arch Dis Child. 1991 Nov;66(11):1291–1295. doi: 10.1136/adc.66.11.1291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law C. M., Barker D. J. Fetal influences on blood pressure. J Hypertens. 1994 Dec;12(12):1329–1332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law C. M., Gordon G. S., Shiell A. W., Barker D. J., Hales C. N. Thinness at birth and glucose tolerance in seven-year-old children. Diabet Med. 1995 Jan;12(1):24–29. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-5491.1995.tb02057.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law C. M., de Swiet M., Osmond C., Fayers P. M., Barker D. J., Cruddas A. M., Fall C. H. Initiation of hypertension in utero and its amplification throughout life. BMJ. 1993 Jan 2;306(6869):24–27. doi: 10.1136/bmj.306.6869.24. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lever A. F., Harrap S. B. Essential hypertension: a disorder of growth with origins in childhood? J Hypertens. 1992 Feb;10(2):101–120. doi: 10.1097/00004872-199202000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohan M., Prasad S. R., Chellani H. K., Kapani V. Intrauterine growth curves in north Indian babies: weight, length, head circumference and ponderal index. Indian Pediatr. 1990 Jan;27(1):43–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakao-Hayashi J., Ito H., Kanayasu T., Morita I., Murota S. Stimulatory effects of insulin and insulin-like growth factor I on migration and tube formation by vascular endothelial cells. Atherosclerosis. 1992 Feb;92(2-3):141–149. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(92)90273-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver M. H., Harding J. E., Breier B. H., Evans P. C., Gluckman P. D. Glucose but not a mixed amino acid infusion regulates plasma insulin-like growth factor-I concentrations in fetal sheep. Pediatr Res. 1993 Jul;34(1):62–65. doi: 10.1203/00006450-199307000-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osmond C., Barker D. J., Winter P. D., Fall C. H., Simmonds S. J. Early growth and death from cardiovascular disease in women. BMJ. 1993 Dec 11;307(6918):1519–1524. doi: 10.1136/bmj.307.6918.1519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips D. I., Barker D. J., Hales C. N., Hirst S., Osmond C. Thinness at birth and insulin resistance in adult life. Diabetologia. 1994 Feb;37(2):150–154. doi: 10.1007/s001250050086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straus D. S. Nutritional regulation of hormones and growth factors that control mammalian growth. FASEB J. 1994 Jan;8(1):6–12. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.8.1.8299891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straus D. S., Ooi G. T., Orlowski C. C., Rechler M. M. Expression of the genes for insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I), IGF-II, and IGF-binding proteins-1 and -2 in fetal rat under conditions of intrauterine growth retardation caused by maternal fasting. Endocrinology. 1991 Jan;128(1):518–525. doi: 10.1210/endo-128-1-518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanner J. M., Whitehouse R. H., Takaishi M. Standards from birth to maturity for height, weight, height velocity, and weight velocity: British children, 1965. II. Arch Dis Child. 1966 Dec;41(220):613–635. doi: 10.1136/adc.41.220.613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatò L., Dal Moro A., Piemonte G., Vigi V., Pizzo P., Volpato S., Gaburro D. A longitudinal study on plasma somatomedin activity in full-term, preterm and small-for-gestational age newborns. Biol Neonate. 1981;39(3-4):160–164. doi: 10.1159/000241421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thieriot-Prevost G., Boccara J. F., Francoual C., Badoual J., Job J. C. Serum insulin-like growth factor 1 and serum growth-promoting activity during the first postnatal year in infants with intrauterine growth retardation. Pediatr Res. 1988 Sep;24(3):380–383. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198809000-00020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thissen J. P., Underwood L. E., Maiter D., Maes M., Clemmons D. R., Ketelslegers J. M. Failure of insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) infusion to promote growth in protein-restricted rats despite normalization of serum IGF-I concentrations. Endocrinology. 1991 Feb;128(2):885–890. doi: 10.1210/endo-128-2-885. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiériot-Prévost G., Daffos F., Forestier F. Serum somatomedin-C and bioassayable growth-promoting activity (thymidine activity) in appropriate and small-for-gestational-age human newborns. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1985 Sep;110(1):32–35. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.1100032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valdez R., Athens M. A., Thompson G. H., Bradshaw B. S., Stern M. P. Birthweight and adult health outcomes in a biethnic population in the USA. Diabetologia. 1994 Jun;37(6):624–631. doi: 10.1007/BF00403383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verhaeghe J., Van Bree R., Van Herck E., Laureys J., Bouillon R., Van Assche F. A. C-peptide, insulin-like growth factors I and II, and insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 in umbilical cord serum: correlations with birth weight. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1993 Jul;169(1):89–97. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(93)90137-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villar J., Smeriglio V., Martorell R., Brown C. H., Klein R. E. Heterogeneous growth and mental development of intrauterine growth-retarded infants during the first 3 years of life. Pediatrics. 1984 Nov;74(5):783–791. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang H. S., Lim J., English J., Irvine L., Chard T. The concentration of insulin-like growth factor-I and insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-1 in human umbilical cord serum at delivery: relation to fetal weight. J Endocrinol. 1991 Jun;129(3):459–464. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1290459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whincup P. H., Cook D. G., Shaper A. G. Early influences on blood pressure: a study of children aged 5-7 years. BMJ. 1989 Sep 2;299(6699):587–591. doi: 10.1136/bmj.299.6699.587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigglesworth J. S. Lesions in the neonatal brain. Arch Dis Child. 1985 Dec;60(12):1202–1203. doi: 10.1136/adc.60.12.1202-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yajnik C. S., Fall C. H., Vaidya U., Pandit A. N., Bavdekar A., Bhat D. S., Osmond C., Hales C. N., Barker D. J. Fetal growth and glucose and insulin metabolism in four-year-old Indian children. Diabet Med. 1995 Apr;12(4):330–336. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-5491.1995.tb00487.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


