Abstract
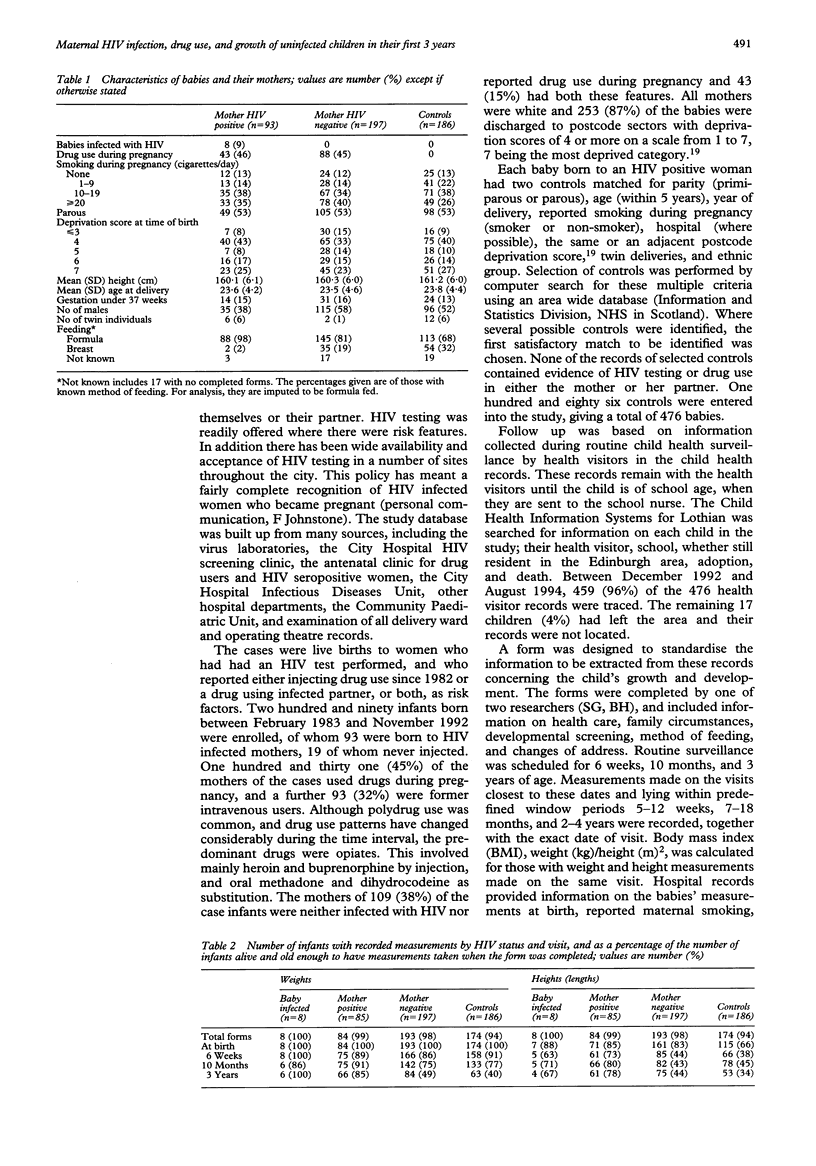
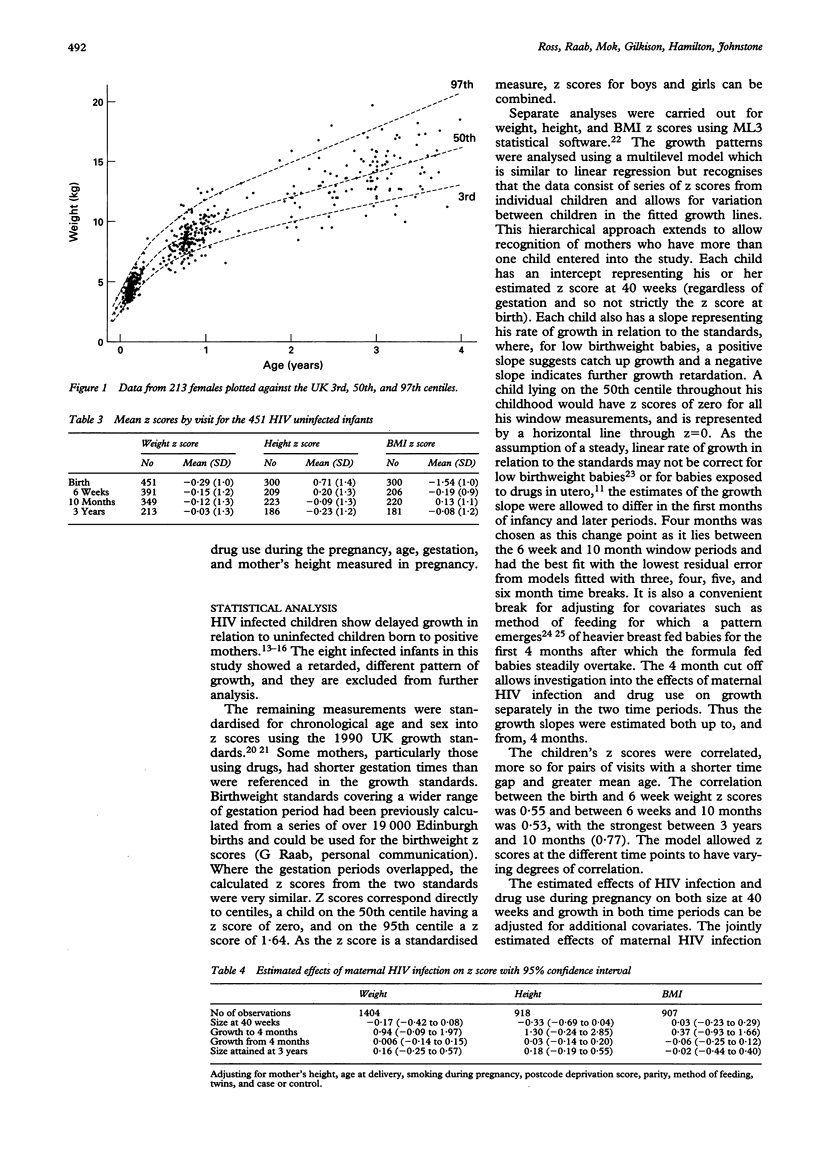
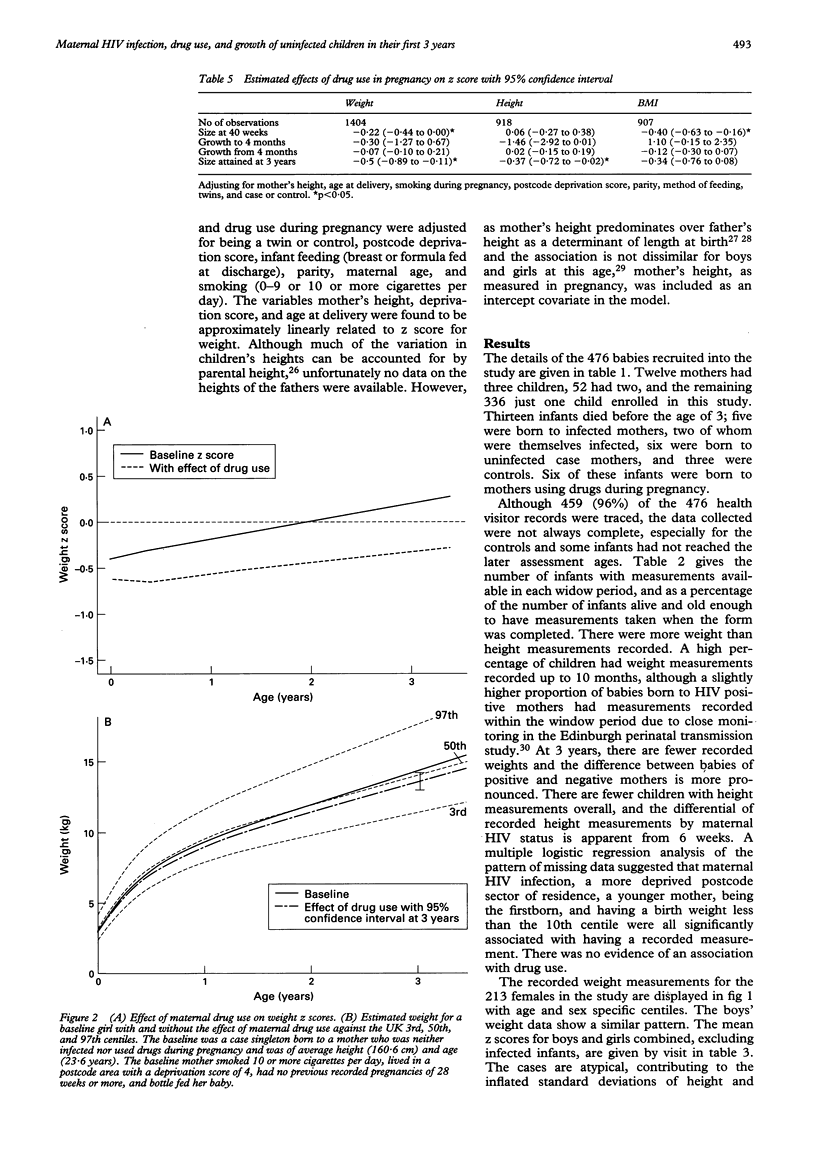
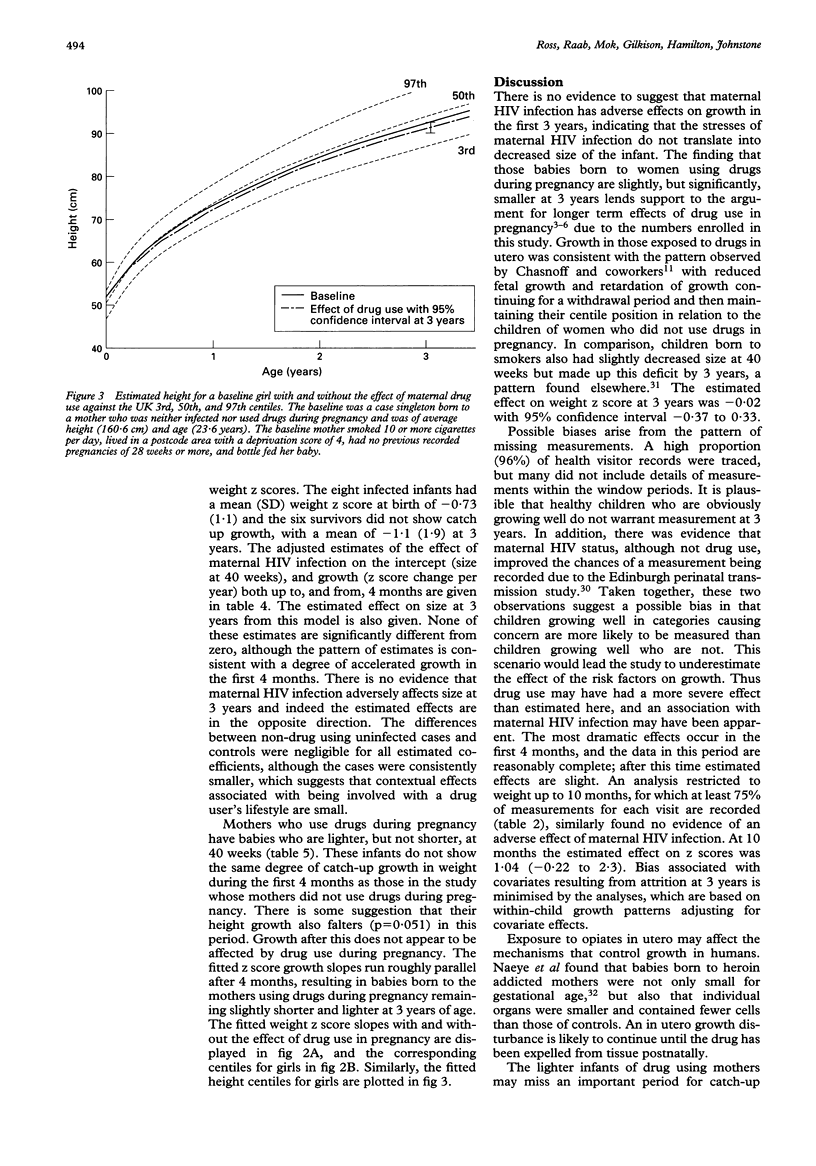
OBJECTIVE--To determine the separate effects of maternal HIV infection and drug use during pregnancy on growth of uninfected children in their first 3 years. DESIGN--Retrospective analysis of measurements from health visitor records made during routine child health surveillance at 6 weeks, 10 months, and 3 years of age. Multilevel analysis allowed for between-infant variation in fitted growth lines, and adjustment for other factors. Growth was described in terms of an intercept (z score at term) and growth slopes (change in z score per year) up to, and from, 4 months. SUBJECTS--290 case babies delivered in Edinburgh hospitals to women who reported injection drug use by either themselves or their HIV infected partner, and 186 community controls. A total of 131 (45%) of the case babies were born to women who used drugs, predominantly opiates, during pregnancy and 93 (32%) to HIV infected women. The eight infected children were excluded from analysis. MAIN OUTCOME MEASURES--Age and sex standardised z scores for height, weight, and body mass index. RESULTS--459 (96%) of the 476 records for cases and controls were traced, yielding 1432 weight and 939 height measurements. Maternal HIV infection was not found to affect growth; at 3 years the estimated effect on weight z score was 0.16 with 95% confidence interval (-0.25 to 0.57) and for height 0.18 (-0.19 to 0.55). Drug use during pregnancy was associated with lighter babies at 40 weeks followed by depressed growth in the first four months, these infants remaining just slightly smaller at 3 years with an estimated effect on z scores of -0.5 for weight with 95% confidence interval (-0.89 to -0.11) and -0.37 (-0.72 to -0.02) for height. CONCLUSIONS--Maternal HIV infection does not adversely affect growth in uninfected infants, and the effect of drug use during pregnancy is limited to small decrease in size at 3 years.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brettle R. P., Bisset K., Burns S., Davidson J., Davidson S. J., Gray J. M., Inglis J. M., Lees J. S., Mok J. Human immunodeficiency virus and drug misuse: the Edinburgh experience. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1987 Aug 15;295(6595):421–424. doi: 10.1136/bmj.295.6595.421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carstairs V., Morris R. Deprivation and health in Scotland. Health Bull (Edinb) 1990 Jul;48(4):162–175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chasnoff I. J., Hatcher R., Burns W. J. Early growth patterns of methadone-addicted infants. Am J Dis Child. 1980 Nov;134(11):1049–1051. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1980.02130230029009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole T. J., Freeman J. V., Preece M. A. Body mass index reference curves for the UK, 1990. Arch Dis Child. 1995 Jul;73(1):25–29. doi: 10.1136/adc.73.1.25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conter V., Cortinovis I., Rogari P., Riva L. Weight growth in infants born to mothers who smoked during pregnancy. BMJ. 1995 Mar 25;310(6982):768–771. doi: 10.1136/bmj.310.6982.768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dewey K. G., Heinig M. J., Nommsen L. A., Peerson J. M., Lönnerdal B. Growth of breast-fed and formula-fed infants from 0 to 18 months: the DARLING Study. Pediatrics. 1992 Jun;89(6 Pt 1):1035–1041. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzhardinge P. M., Steven E. M. The small-for-date infant. I. Later growth patterns. Pediatrics. 1972 May;49(5):671–681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman J. V., Cole T. J., Chinn S., Jones P. R., White E. M., Preece M. A. Cross sectional stature and weight reference curves for the UK, 1990. Arch Dis Child. 1995 Jul;73(1):17–24. doi: 10.1136/adc.73.1.17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein H. Factors influencing the height of seven year old children--results from the National Child Development Study. Hum Biol. 1971 Feb;43(1):92–111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hans S. L. Developmental consequences of prenatal exposure to methadone. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1989;562:195–207. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1989.tb21018.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lifschitz M. H., Wilson G. S., Smith E. O., Desmond M. M. Fetal and postnatal growth of children born to narcotic-dependent women. J Pediatr. 1983 May;102(5):686–691. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(83)80234-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lifschltz M. H., Wilson G. S. Patterns of growth and development in narcotic-exposed children. NIDA Res Monogr. 1991;114:323–339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKinney R. E., Jr, Robertson J. W. Effect of human immunodeficiency virus infection on the growth of young children. Duke Pediatric AIDS Clinical Trials Unit. J Pediatr. 1993 Oct;123(4):579–582. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)80955-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller T. L., Evans S. J., Orav E. J., Morris V., McIntosh K., Winter H. S. Growth and body composition in children infected with the human immunodeficiency virus-1. Am J Clin Nutr. 1993 Apr;57(4):588–592. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/57.4.588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mok J. Y., Hague R. A., Yap P. L., Hargreaves F. D., Inglis J. M., Whitelaw J. M., Steel C. M., Eden O. B., Rebus S., Peutherer J. F. Vertical transmission of HIV: a prospective study. Arch Dis Child. 1989 Aug;64(8):1140–1145. doi: 10.1136/adc.64.8.1140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naeye R. L., Blanc W., Leblanc W., Khatamee M. A. Fetal complications of maternal heroin addiction: abnormal growth, infections, and episodes of stress. J Pediatr. 1973 Dec;83(6):1055–1061. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(73)80550-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pizzo P. A., Wilfert C. M. Markers and determinants of disease progression in children with HIV infection. The Pediatric AIDS Siena Workshop II. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr Hum Retrovirol. 1995 Jan 1;8(1):30–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raye J. R., Dubin J. W., Blechner J. N. Fetal growth retardation following maternal morphine administration: nutritional or drug effect? Biol Neonate. 1977;32(3-4):222–228. doi: 10.1159/000241021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson J. R., Bucknall A. B., Welsby P. D., Roberts J. J., Inglis J. M., Peutherer J. F., Brettle R. P. Epidemic of AIDS related virus (HTLV-III/LAV) infection among intravenous drug abusers. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1986 Feb 22;292(6519):527–529. doi: 10.1136/bmj.292.6519.527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen T. S., Johnson H. L. Children of methadone-maintained mothers: follow-up to 18 months of age. J Pediatr. 1982 Aug;101(2):192–196. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(82)80115-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sardemann H., Madsen K. S., Friis-Hansen B. Follow-up of children of drug-addicted mothers. Arch Dis Child. 1976 Feb;51(2):131–134. doi: 10.1136/adc.51.2.131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. W., Truog W., Rogers J. E., Greitzer L. J., Skinner A. L., McCann J. J., Harvey M. A. Shifting linear growth during infancy: illustration of genetic factors in growth from fetal life through infancy. J Pediatr. 1976 Aug;89(2):225–230. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(76)80453-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanner J. M. Catch-up growth in man. Br Med Bull. 1981 Sep;37(3):233–238. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson G. S., Desmond M. M., Verniaud W. M. Early development of infants of heroin-addicted mothers. Am J Dis Child. 1973 Oct;126(4):457–462. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1973.02110190381004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson G. S., McCreary R., Kean J., Baxter J. C. The development of preschool children of heroin-addicted mothers: a controlled study. Pediatrics. 1979 Jan;63(1):135–141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wingerd J., Schoen E. J. Factors influencing length at birth and height at five years. Pediatrics. 1974 May;53(5):737–741. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


