Abstract
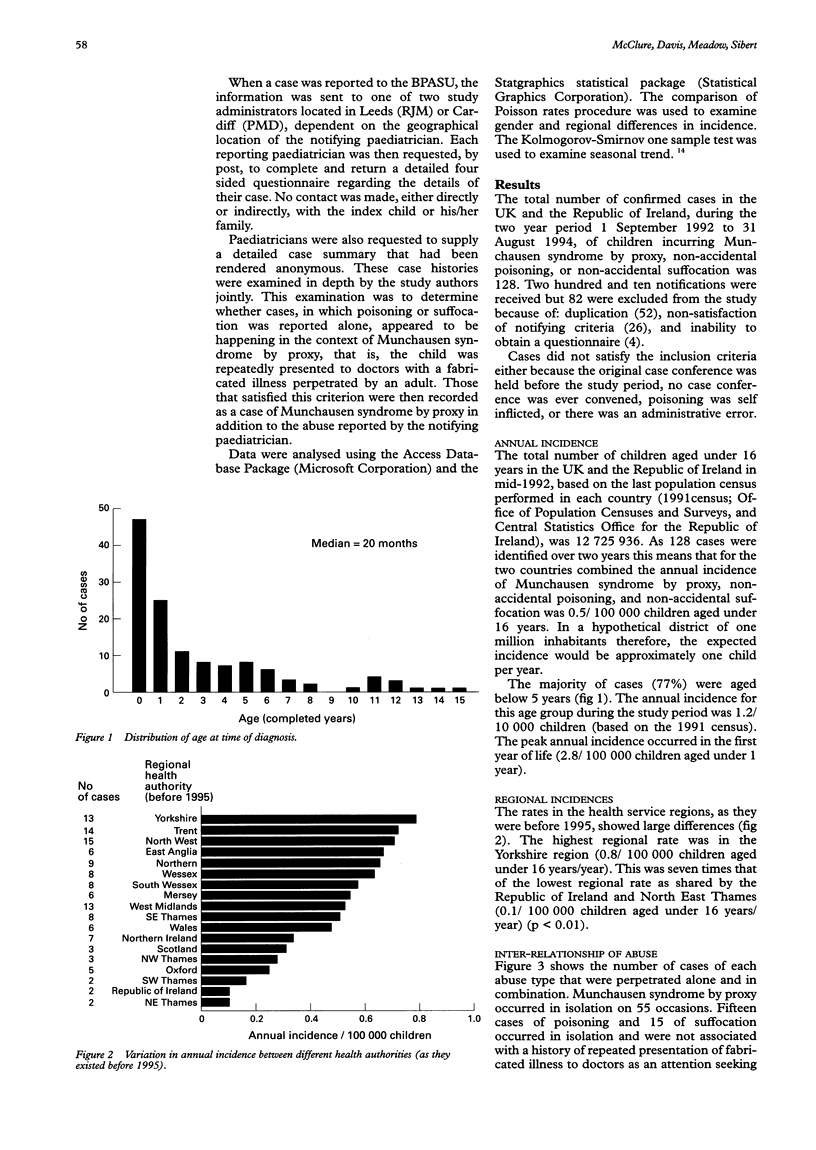
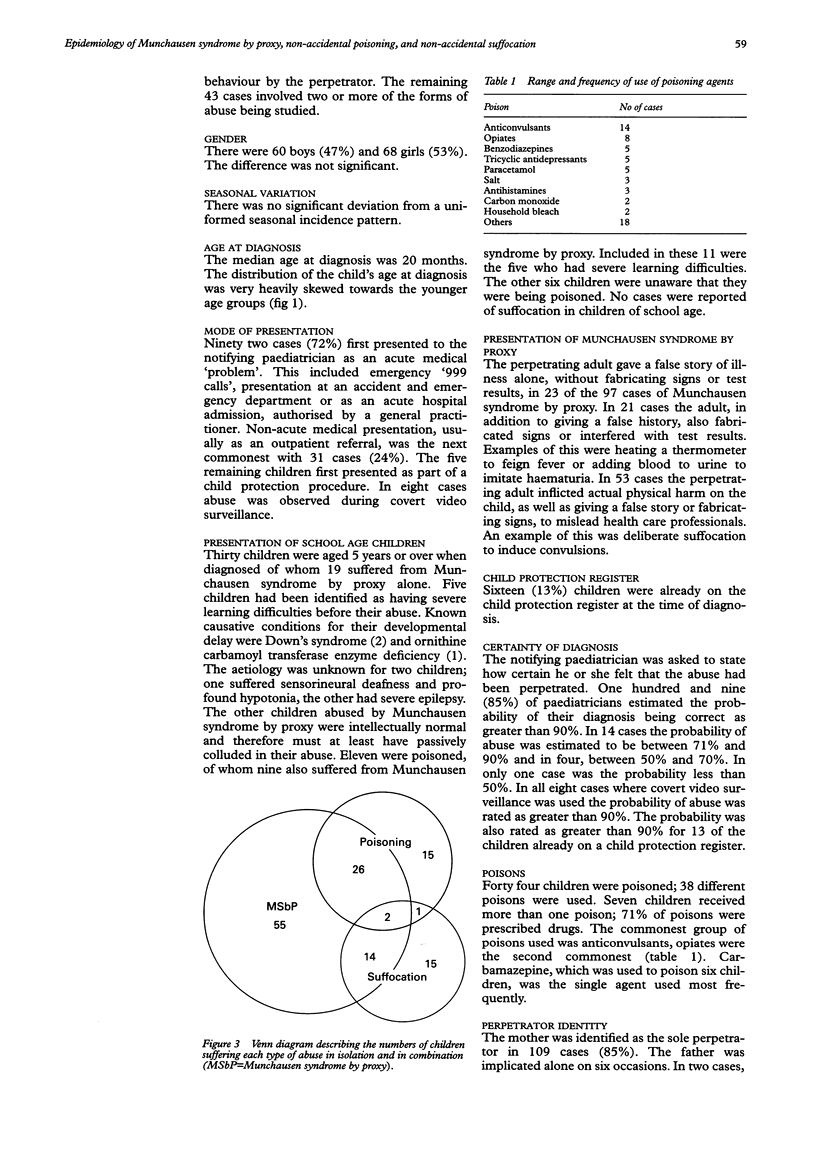
A two year prospective study was performed to determine the epidemiology of Munchausen syndrome by proxy, non-accidental poisoning, and non-accidental suffocation in the UK and the Republic of Ireland. Cases were notified to the British Paediatric Association Surveillance Unit from September 1992 to August 1994 if a formal case conference had been held for the first time during that period to discuss any of the above conditions. A total of 128 cases were identified: 55 suffered Munchausen syndrome by proxy alone, 15 poisoning, and 15 suffocation; 43 suffered more than one type of abuse. The majority of children were aged under 5 years, the median age being 20 months. On 85% of occasions the perpetrator was the child's mother. In 42% of families with more than one child, a sibling had previously suffered some form of abuse. Eighty five per cent of notifying paediatricians considered the probability of their diagnosis as virtually certain before a case conference was convened. The commonest drugs used to poison were anticonvulsants; opiates were the second commonest. Sixty eight children suffered severe illness of whom eight died. The combined annual incidence of these conditions in children aged under 16 years is at least 0.5/100,000, and for children aged under 1, at least 2.8/100,000.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ASHER R. Munchausen's syndrome. Lancet. 1951 Feb 10;1(6650):339–341. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(51)92313-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dine M. S., McGovern M. E. Intentional poisoning of children--an overlooked category of child abuse: report of seven cases and review of the literature. Pediatrics. 1982 Jul;70(1):32–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher G. C., Mitchell I. Is Munchausen syndrome by proxy really a syndrome? Arch Dis Child. 1995 Jun;72(6):530–534. doi: 10.1136/adc.72.6.530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall S. M., Glickman M. The British Paediatric Surveillance Unit. Arch Dis Child. 1988 Mar;63(3):344–346. doi: 10.1136/adc.63.3.344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp A., Sibert J. R. Drowning and near drowning in children in the United Kingdom: lessons for prevention. BMJ. 1992 May 2;304(6835):1143–1146. doi: 10.1136/bmj.304.6835.1143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meadow R. Fictitious epilepsy. Lancet. 1984 Jul 7;2(8393):25–28. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)92008-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meadow R. Munchausen syndrome by proxy. The hinterland of child abuse. Lancet. 1977 Aug 13;2(8033):343–345. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)91497-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meadow R. Munchausen syndrome by proxy. Arch Dis Child. 1982 Feb;57(2):92–98. doi: 10.1136/adc.57.2.92. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meadow R. Suffocation, recurrent apnea, and sudden infant death. J Pediatr. 1990 Sep;117(3):351–357. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)81072-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meadow R. What is, and what is not, 'Munchausen syndrome by proxy'? Arch Dis Child. 1995 Jun;72(6):534–538. doi: 10.1136/adc.72.6.534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morley C. J. Practical concerns about the diagnosis of Munchausen syndrome by proxy. Arch Dis Child. 1995 Jun;72(6):528–530. doi: 10.1136/adc.72.6.528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers D., Tripp J., Bentovim A., Robinson A., Berry D., Goulding R. Papers and originals. Br Med J. 1976 Apr 3;1(6013):793–796. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6013.793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen C. L., Frost J. D., Jr, Bricker T., Tarnow J. D., Gillette P. C., Dunlavy S. Two siblings with recurrent cardiorespiratory arrest: Munchausen syndrome by proxy or child abuse? Pediatrics. 1983 May;71(5):715–720. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg D. A. Web of deceit: a literature review of Munchausen syndrome by proxy. Child Abuse Negl. 1987;11(4):547–563. doi: 10.1016/0145-2134(87)90081-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuels M. P., McClaughlin W., Jacobson R. R., Poets C. F., Southall D. P. Fourteen cases of imposed upper airway obstruction. Arch Dis Child. 1992 Feb;67(2):162–170. doi: 10.1136/adc.67.2.162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


