Abstract
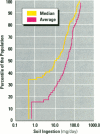
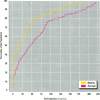
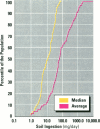
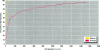
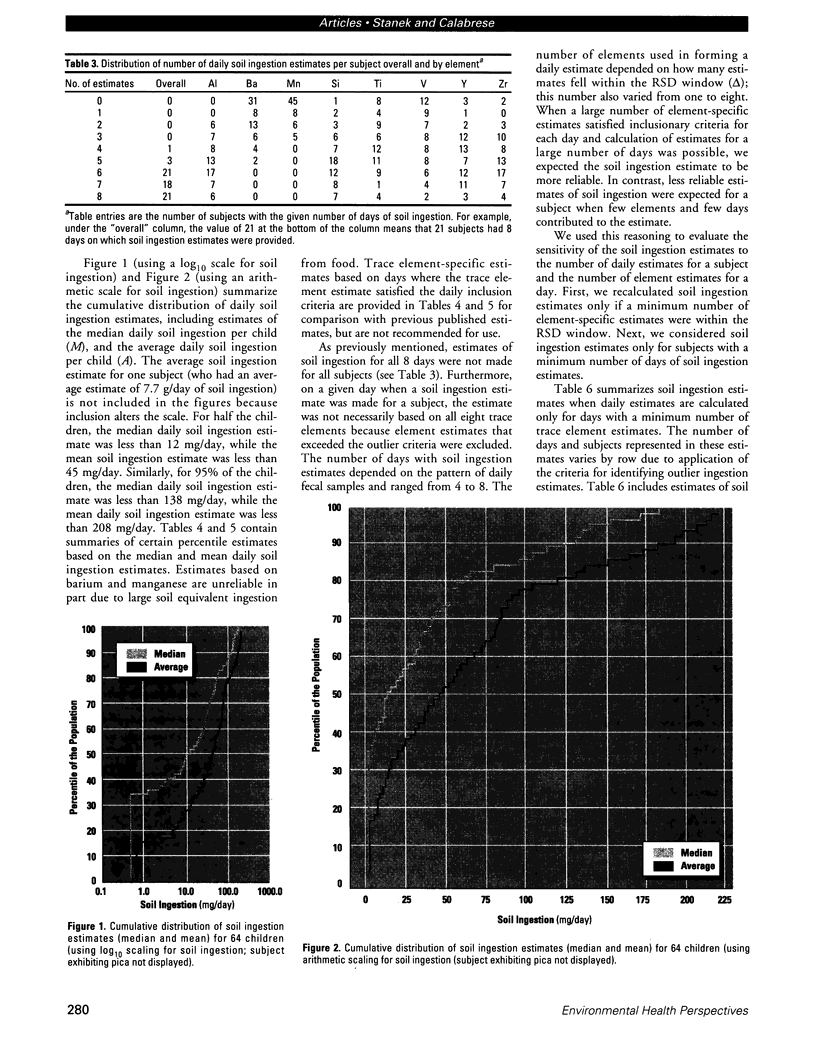
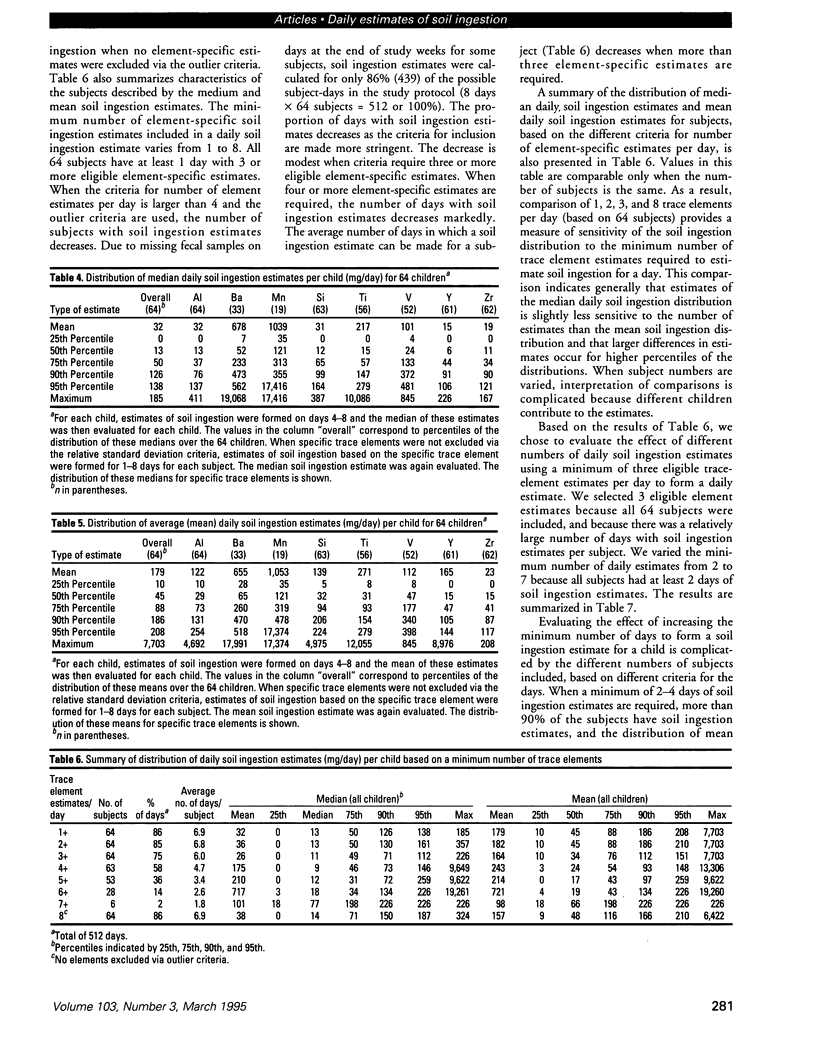
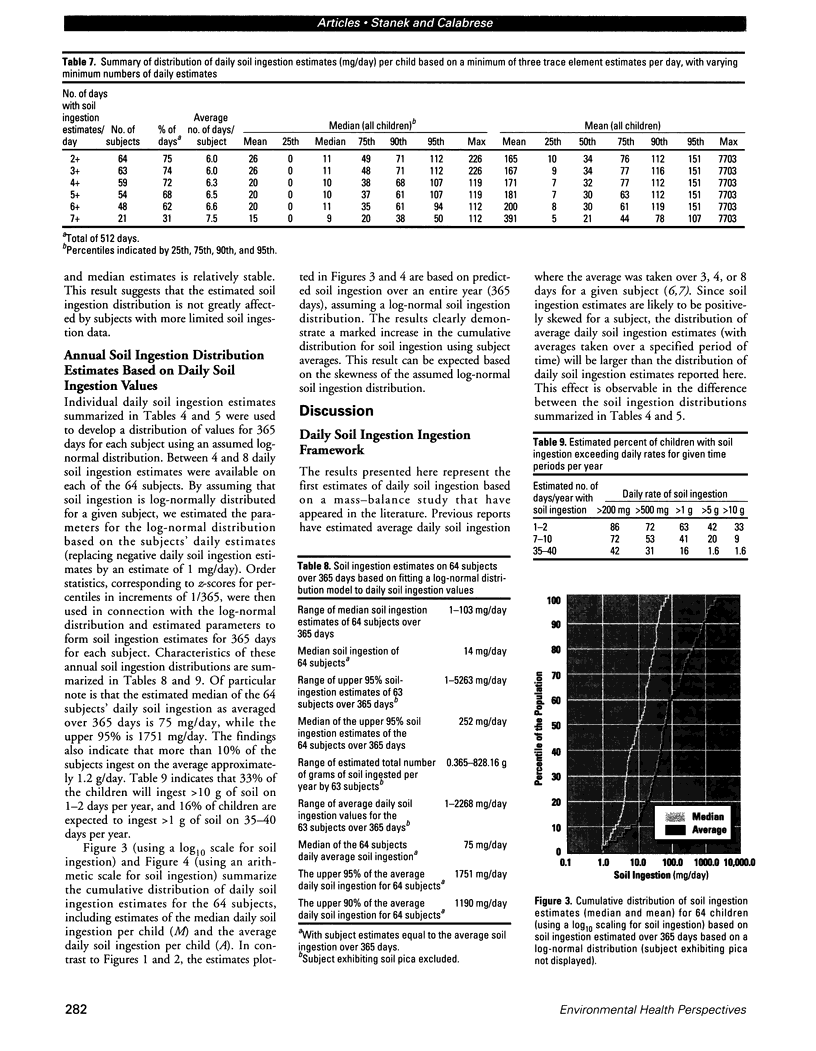
Soil ingestion estimates play an important role in risk assessment of contaminated sites, and estimates of soil ingestion in children are of special interest. Current estimates of soil ingestion are trace-element specific and vary widely among elements. Although expressed as daily estimates, the actual estimates have been constructed by averaging soil ingestion over a study period of several days. The wide variability has resulted in uncertainty as to which method of estimation of soil ingestion is best. We developed a methodology for calculating a single estimate of soil ingestion for each subject for each day. Because the daily soil ingestion estimate represents the median estimate of eligible daily trace-element-specific soil ingestion estimates for each child, this median estimate is not trace-element specific. Summary estimates for individuals and weeks are calculated using these daily estimates. Using this methodology, the median daily soil ingestion estimate for 64 children participating in the 1989 Amherst soil ingestion study is 13 mg/day or less for 50% of the children and 138 mg/day or less for 95% of the children. Mean soil ingestion estimates (for up to an 8-day period) were 45 mg/day or less for 50% of the children, whereas 95% of the children reported a mean soil ingestion of 208 mg/day or less. Daily soil ingestion estimates were used subsequently to estimate the mean and variance in soil ingestion for each child and to extrapolate a soil ingestion distribution over a year, assuming that soil ingestion followed a log-normal distribution.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Binder S., Sokal D., Maughan D. Estimating soil ingestion: the use of tracer elements in estimating the amount of soil ingested by young children. Arch Environ Health. 1986 Nov-Dec;41(6):341–345. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1986.9935776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calabrese E. J., Barnes R., Stanek E. J., 3rd, Pastides H., Gilbert C. E., Veneman P., Wang X. R., Lasztity A., Kostecki P. T. How much soil do young children ingest: an epidemiologic study. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 1989 Oct;10(2):123–137. doi: 10.1016/0273-2300(89)90019-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calabrese E. J., Stanek E. J., 3rd A guide to interpreting soil ingestion studies. II. Qualitative and quantitative evidence of soil ingestion. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 1991 Jun;13(3):278–292. doi: 10.1016/0273-2300(91)90068-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calabrese E. J., Stanek E. S. Distinguishing outdoor soil ingestion from indoor dust ingestion in a soil pica child. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 1992 Feb;15(1):83–85. doi: 10.1016/0273-2300(92)90086-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clausing P., Brunekreef B., van Wijnen J. H. A method for estimating soil ingestion by children. Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 1987;59(1):73–82. doi: 10.1007/BF00377681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis S., Waller P., Buschbom R., Ballou J., White P. Quantitative estimates of soil ingestion in normal children between the ages of 2 and 7 years: population-based estimates using aluminum, silicon, and titanium as soil tracer elements. Arch Environ Health. 1990 Mar-Apr;45(2):112–122. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1990.9935935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finley B. L., Scott P., Paustenbach D. J. Evaluating the adequacy of maximum contaminant levels as health-protective cleanup goals: an analysis based on Monte Carlo techniques. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 1993 Dec;18(3):438–455. doi: 10.1006/rtph.1993.1069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanek E. J., 3rd, Calabrese E. J. A guide to interpreting soil ingestion studies. I. Development of a model to estimate the soil ingestion detection level of soil ingestion studies. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 1991 Jun;13(3):263–277. doi: 10.1016/0273-2300(91)90067-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Wijnen J. H., Clausing P., Brunekreef B. Estimated soil ingestion by children. Environ Res. 1990 Apr;51(2):147–162. doi: 10.1016/s0013-9351(05)80085-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]