Abstract
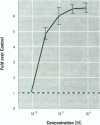
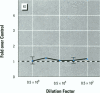
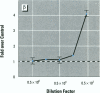
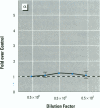
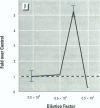
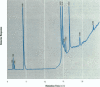
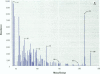
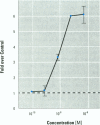
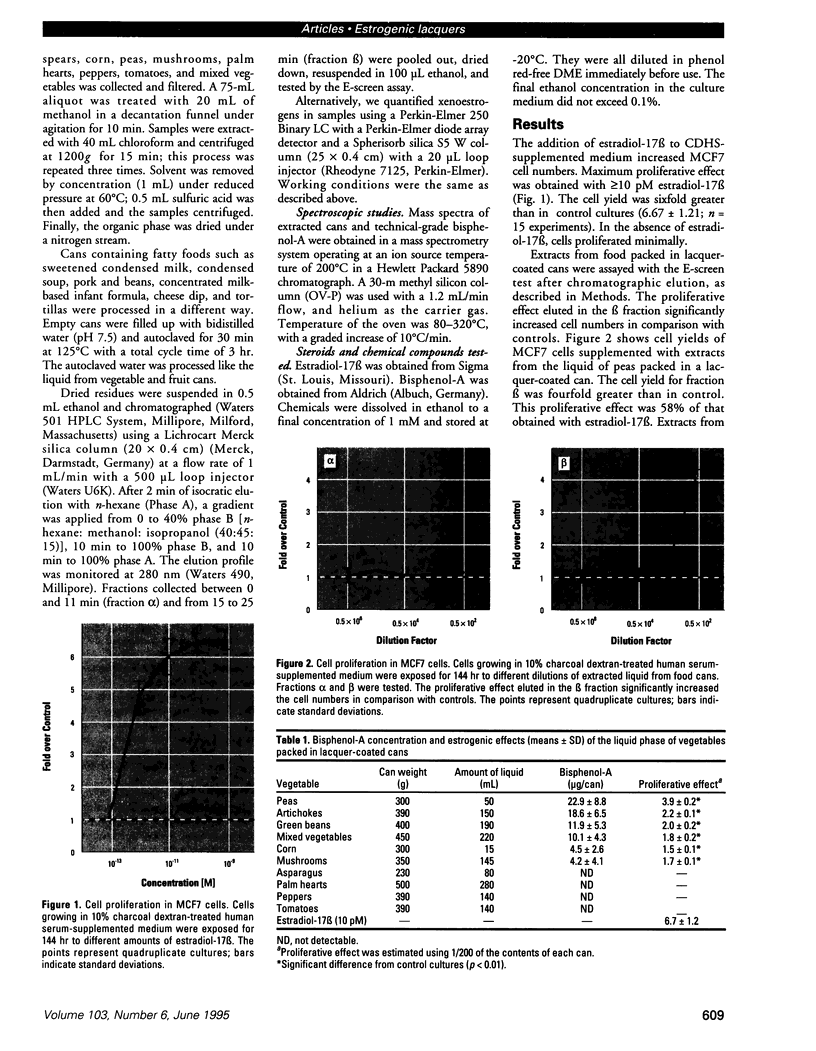
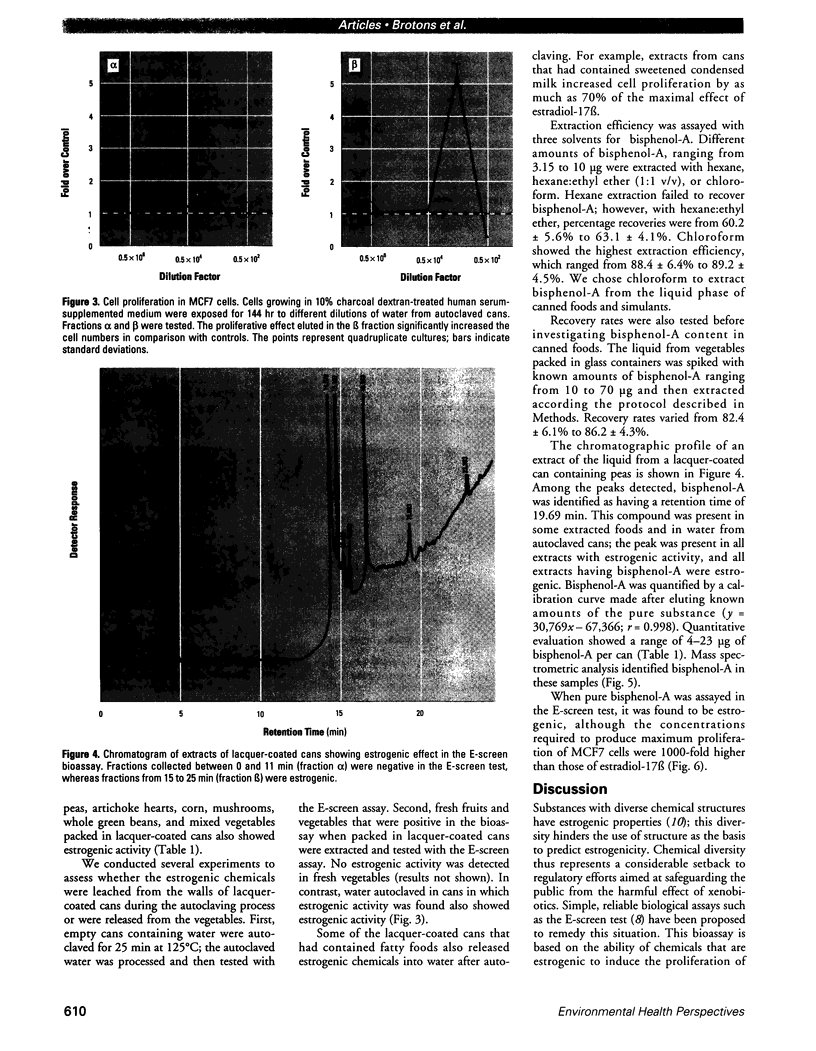
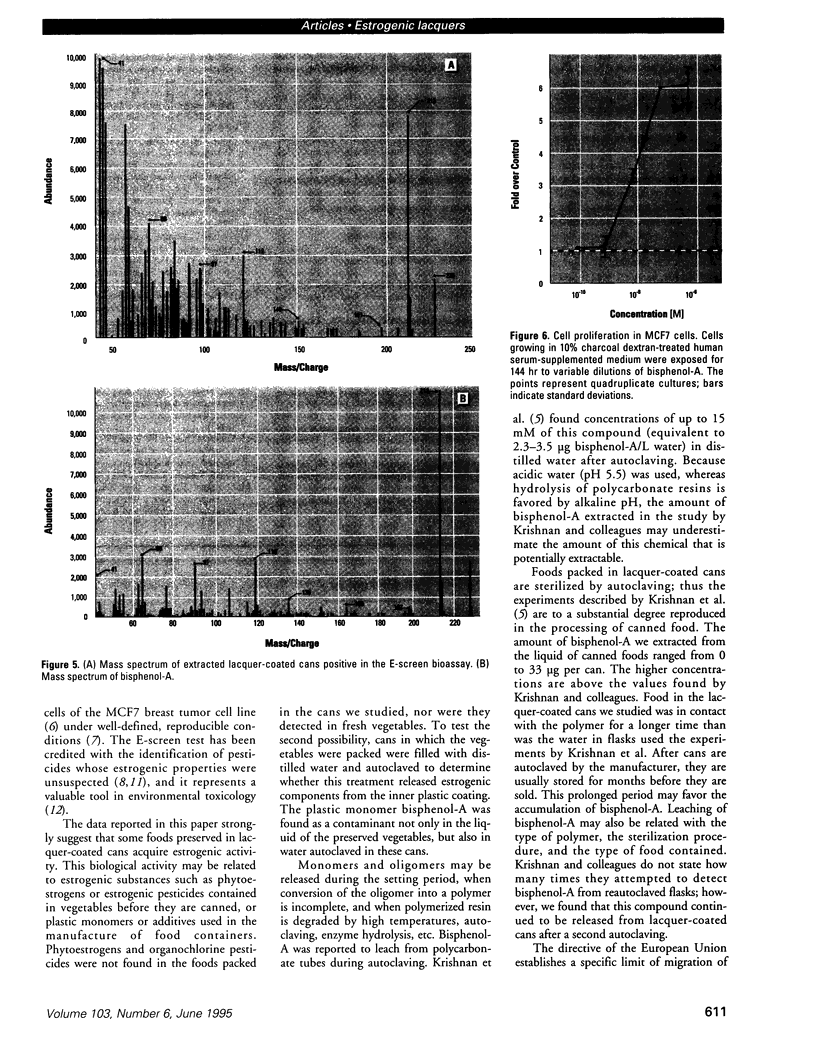
We present data showing that some foods preserved in lacquer-coated cans and the liquid in them may acquire estrogenic activity. Hormonal activity was measured using the E-screen bioassay. The biological activity of vegetables packed in cans was a result of plastic monomers used in manufacturing the containers. The plastic monomer bisphenol-A, identified by mass spectrometry, was found as a contaminant not only in the liquid of the preserved vegetables but also in water autoclaved in the cans. The amount of bisphenol-A in the extracts accounted for all the hormonal activity measured. Although the presence of other xenoestrogens cannot be ruled out, it is apparent that all estrogenic activity in these cans was due to bisphenol-A leached from the lacquer coating. The use of plastic in food-packaging materials may require closer scrutiny to determine whether epoxy resins and polycarbonates contribute to human exposure to xenoestrogens.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Colborn T., vom Saal F. S., Soto A. M. Developmental effects of endocrine-disrupting chemicals in wildlife and humans. Environ Health Perspect. 1993 Oct;101(5):378–384. doi: 10.1289/ehp.93101378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks C. T., Strawn S. E., Wataha J. C., Craig R. G. Cytotoxic effects of resin components on cultured mammalian fibroblasts. J Dent Res. 1991 Nov;70(11):1450–1455. doi: 10.1177/00220345910700111201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishnan A. V., Stathis P., Permuth S. F., Tokes L., Feldman D. Bisphenol-A: an estrogenic substance is released from polycarbonate flasks during autoclaving. Endocrinology. 1993 Jun;132(6):2279–2286. doi: 10.1210/endo.132.6.8504731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLachlan J. A. Functional toxicology: a new approach to detect biologically active xenobiotics. Environ Health Perspect. 1993 Oct;101(5):386–387. doi: 10.1289/ehp.93101386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skehan P., Storeng R., Scudiero D., Monks A., McMahon J., Vistica D., Warren J. T., Bokesch H., Kenney S., Boyd M. R. New colorimetric cytotoxicity assay for anticancer-drug screening. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1990 Jul 4;82(13):1107–1112. doi: 10.1093/jnci/82.13.1107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soto A. M., Chung K. L., Sonnenschein C. The pesticides endosulfan, toxaphene, and dieldrin have estrogenic effects on human estrogen-sensitive cells. Environ Health Perspect. 1994 Apr;102(4):380–383. doi: 10.1289/ehp.94102380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soto A. M., Justicia H., Wray J. W., Sonnenschein C. p-Nonyl-phenol: an estrogenic xenobiotic released from "modified" polystyrene. Environ Health Perspect. 1991 May;92:167–173. doi: 10.1289/ehp.9192167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soto A. M., Sonnenschein C. The role of estrogens on the proliferation of human breast tumor cells (MCF-7). J Steroid Biochem. 1985 Jul;23(1):87–94. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(85)90265-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soule H. D., Vazguez J., Long A., Albert S., Brennan M. A human cell line from a pleural effusion derived from a breast carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1973 Nov;51(5):1409–1416. doi: 10.1093/jnci/51.5.1409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]