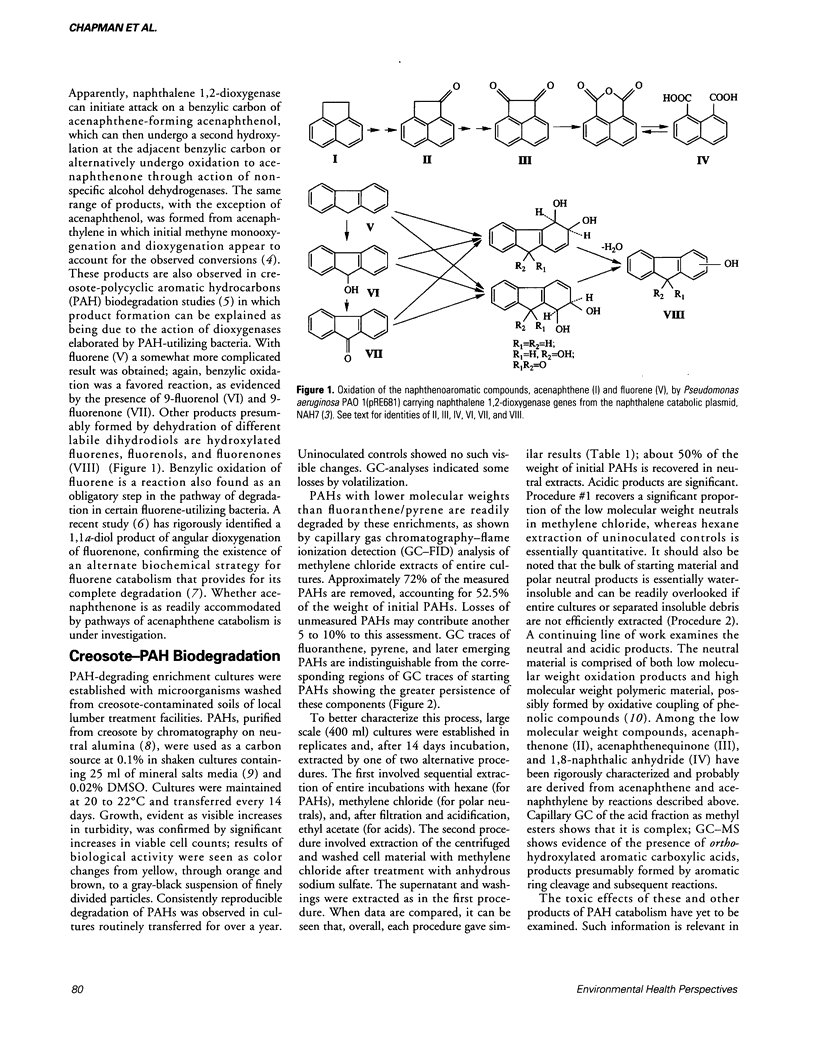
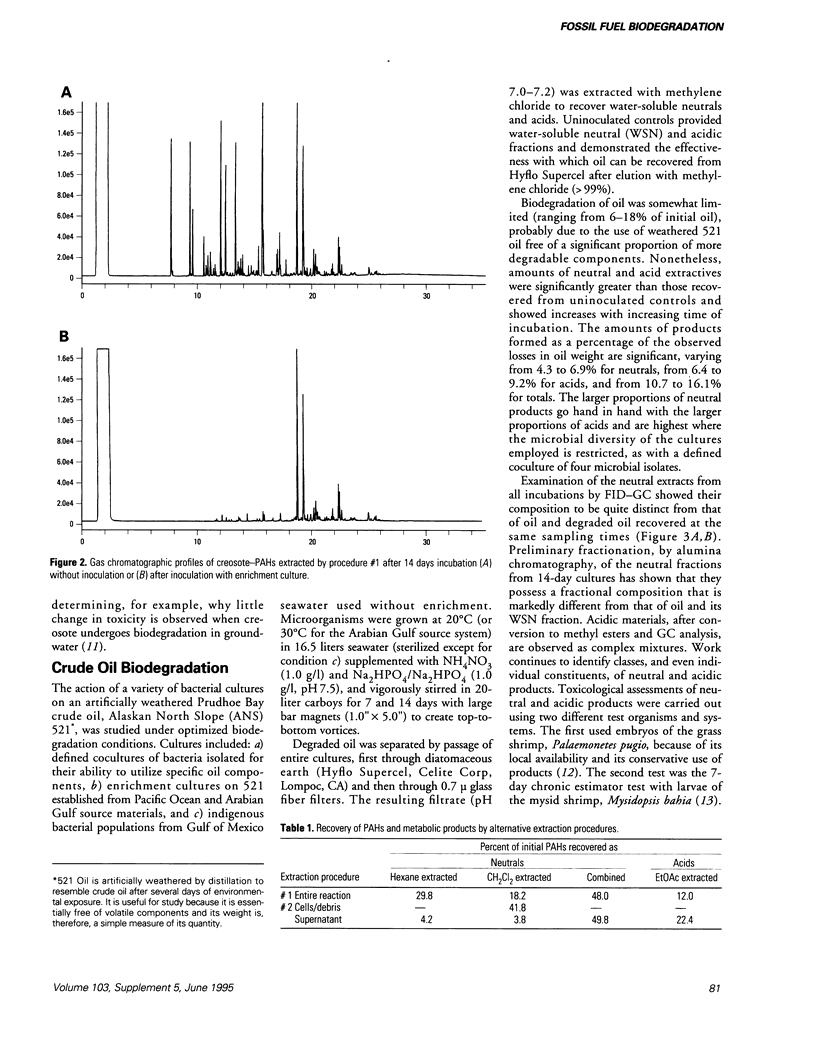
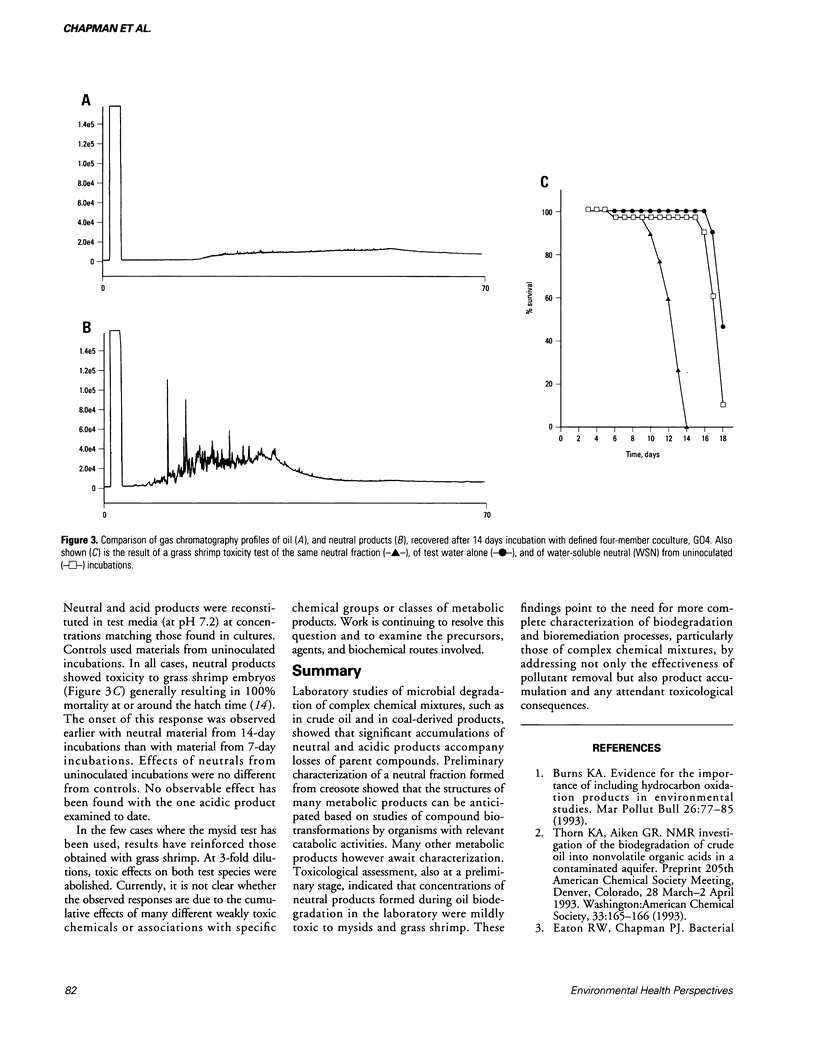
Abstract
Biodegradation of the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons of creosote by undefined bacterial cultures was shown to be accompanied by the accumulation of neutral and acidic oxidation products. Formation of a number of identified neutral products is accounted for by demonstration of anomalous actions of an arene dioxygenase on the benzylic methylene and methylene carbons of napthenoaromatic hydrocarbons. Both neutral and acidic water-soluble fractions are also formed when various mixed bacterial cultures degrade weathered crude oil. While constituents of these fractions are not yet identified, the neutral materials have been shown to be toxic to developing embryos of invertebrates. These observations are discussed in relation to chemical and toxicological assessments of biodegradation of the complex chemical mixtures of fossil fuels.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Eaton R. W., Chapman P. J. Bacterial metabolism of naphthalene: construction and use of recombinant bacteria to study ring cleavage of 1,2-dihydroxynaphthalene and subsequent reactions. J Bacteriol. 1992 Dec;174(23):7542–7554. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.23.7542-7554.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grifoll M., Selifonov S. A., Chapman P. J. Evidence for a novel pathway in the degradation of fluorene by Pseudomonas sp. strain F274. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1994 Jul;60(7):2438–2449. doi: 10.1128/aem.60.7.2438-2449.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hareland W. A., Crawford R. L., Chapman P. J., Dagley S. Metabolic function and properties of 4-hydroxyphenylacetic acid 1-hydroxylase from Pseudomonas acidovorans. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jan;121(1):272–285. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.1.272-285.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller J. G., Middaugh D. P., Lantz S. E., Chapman P. J. Biodegradation of creosote and pentachlorophenol in contaminated groundwater: chemical and biological assessment. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 May;57(5):1277–1285. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.5.1277-1285.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selifonov S. A., Grifoll M., Gurst J. E., Chapman P. J. Isolation and characterization of (+)-1,1a-dihydroxy-1-hydrofluoren-9-one formed by angular dioxygenation in the bacterial catabolism of fluorene. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 May 28;193(1):67–76. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.1591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


