Abstract
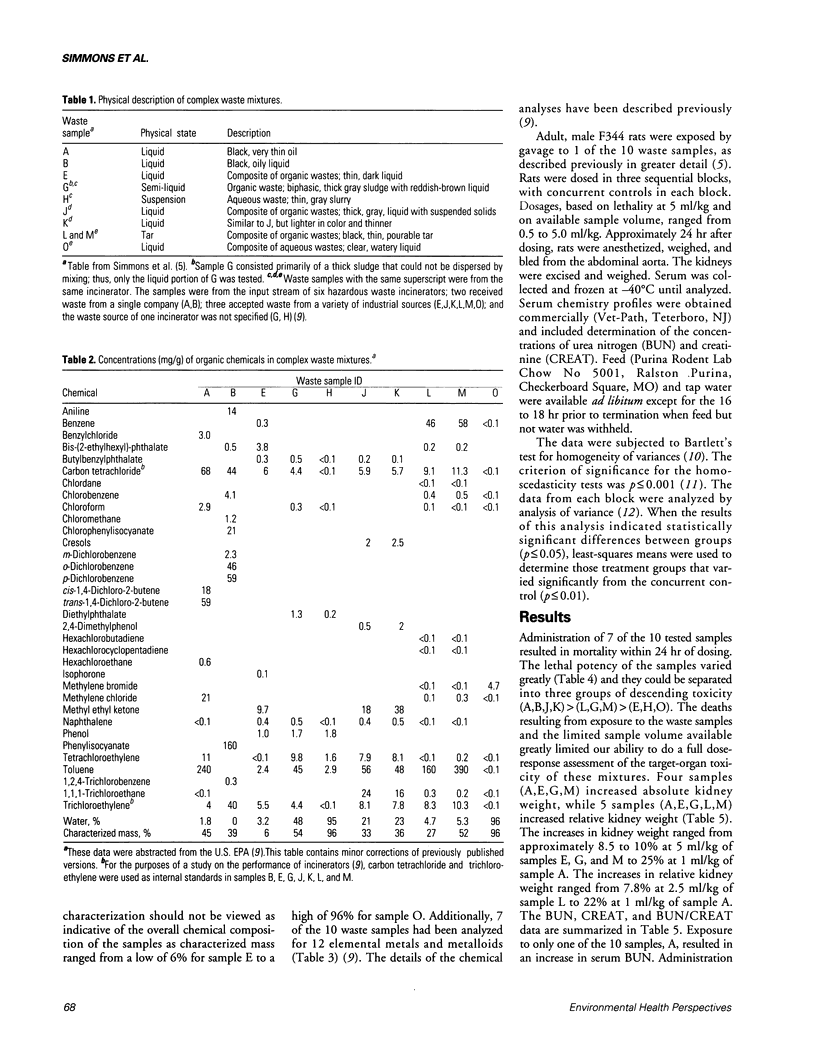
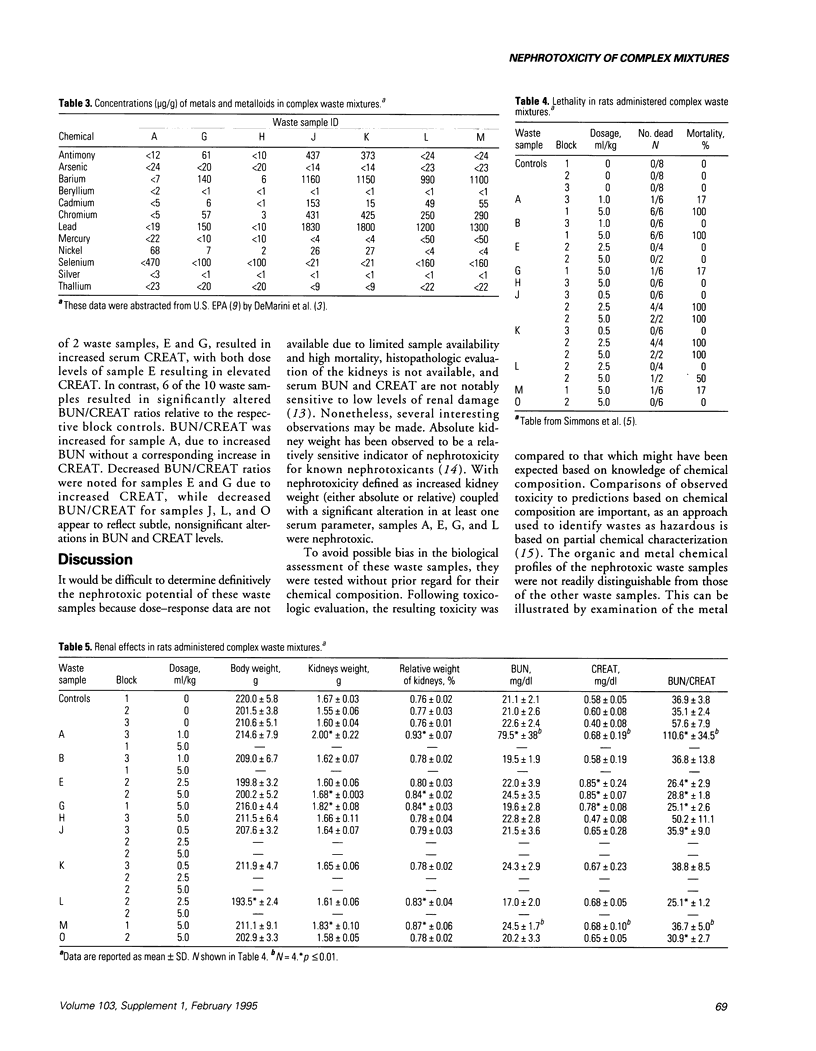
As part of a multidisciplinary health effects study, the nephrotoxicity of complex industrial waste mixtures was assessed. Adult, male Fischer 344 rats were gavaged with samples of complex industrial waste and nephrotoxicity evaluated 24 hr later. Of the 10 tested samples, 4 produced increased absolute or relative kidney weight, or both, coupled with a statistically significant alteration in at least one of the measured serum parameters (urea nitrogen (BUN), creatinine (CREAT), and BUN/CREAT ratio). Although the waste samples had been analyzed for a number of organic chemicals and 7 of the 10 samples were analyzed also for 12 elemental metals and metalloids, their nephrotoxicity was not readily predicted from the partial chemical characterization data. Because the chemical form or speciation of the metals was unknown, it was not possible to estimate their contribution to the observed biological response. Various experimental approaches, including use of real-world complex mixtures, chemically defined synthetic mixtures, and simple mixtures, will be necessary to adequately determine the potential human health risk from exposure to complex chemical mixtures.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Davis M. E. Dichloroacetic acid and trichloroacetic acid increase chloroform toxicity. J Toxicol Environ Health. 1992 Sep;37(1):139–148. doi: 10.1080/15287399209531661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMarini D. M., Gallagher J. E., Houk V. S., Simmons J. E. Toxicological evaluation of complex industrial wastes: implications for exposure assessment. Toxicol Lett. 1989 Dec;49(2-3):199–214. doi: 10.1016/0378-4274(89)90033-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMarini D. M., Inmon J. P., Simmons J. E., Berman E., Pasley T. C., Warren S. H., Williams R. W. Mutagenicity in salmonella of hazardous wastes and urine from rats fed these wastes. Mutat Res. 1987 Nov;189(3):205–216. doi: 10.1016/0165-1218(87)90054-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eyster M. E., Spero J. A., Catalano P. M., Gill F. M., Lusch C. J., Kajani M. K., Barron L. E., DeGreen H. P., Shapiro S. S., Lewis J. H. Inhibitor treatment using unactivated prothrombin complex concentrates: the Pennsylvania experience--1978-1982. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1984;150:309–322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goyer R. A. Introduction and overview. Environ Health Perspect. 1983 Feb;48:1–2. doi: 10.1289/ehp.48-1569055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hook J. B., Ishmael J., Lock E. A. Nephrotoxicity of Hexachloro-1:3-butadiene in the rat: the effect of age, sex, and strain. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1983 Jan;67(1):122–131. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(83)90251-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houk V. S., DeMarini D. M. Use of the microscreen phage-induction assay to assess the genotoxicity of 14 hazardous industrial wastes. Environ Mol Mutagen. 1988;11(1):13–29. doi: 10.1002/em.2850110104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kluwe W. M. Renal function tests as indicators of kidney injury in subacute toxicity studies. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1981 Mar 15;57(3):414–424. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(81)90239-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo C. H., Hook J. B. Effects of age and sex on hexachloro-1,3-butadiene toxicity in the Fischer 344 rat. Life Sci. 1983 Aug 8;33(6):517–523. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(83)90125-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons J. E., Berman E. Toxicity of complex waste mixtures: a comparison of observed and predicted lethality. J Toxicol Environ Health. 1989;27(3):275–286. doi: 10.1080/15287398909531299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons J. E., DeMarini D. M., Berman E. Lethality and hepatotoxicity of complex waste mixtures. Environ Res. 1988 Jun;46(1):74–85. doi: 10.1016/s0013-9351(88)80060-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


