Abstract
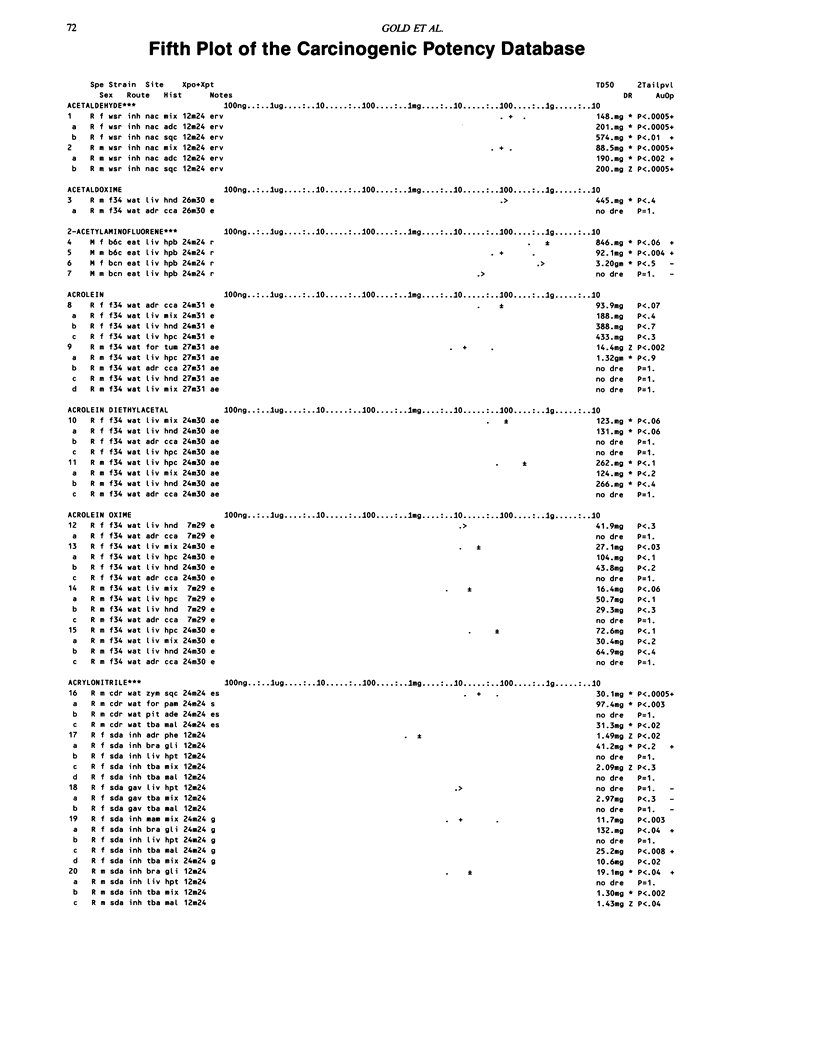
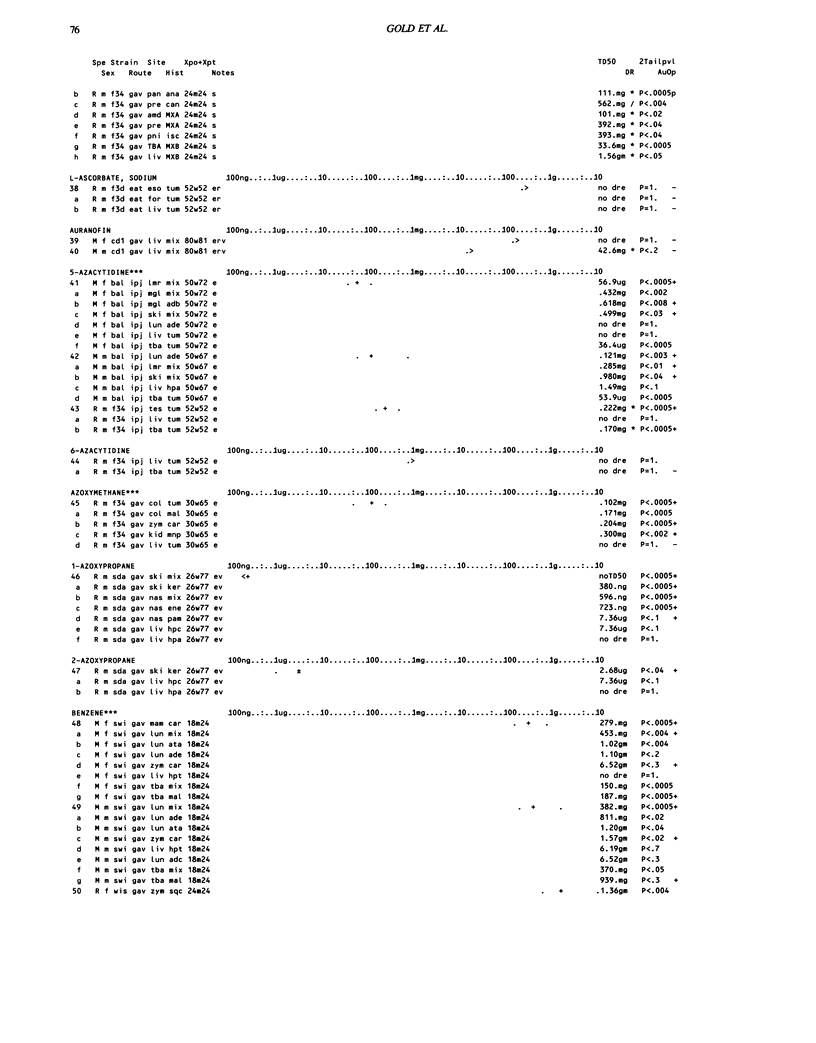
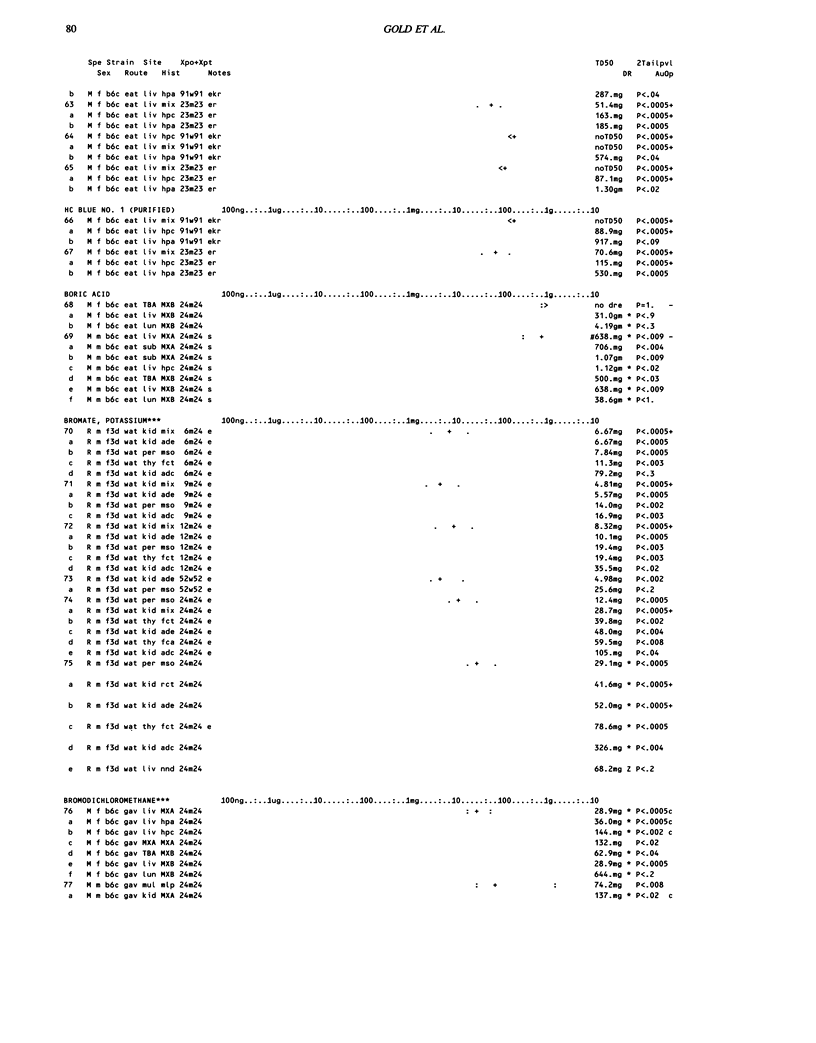
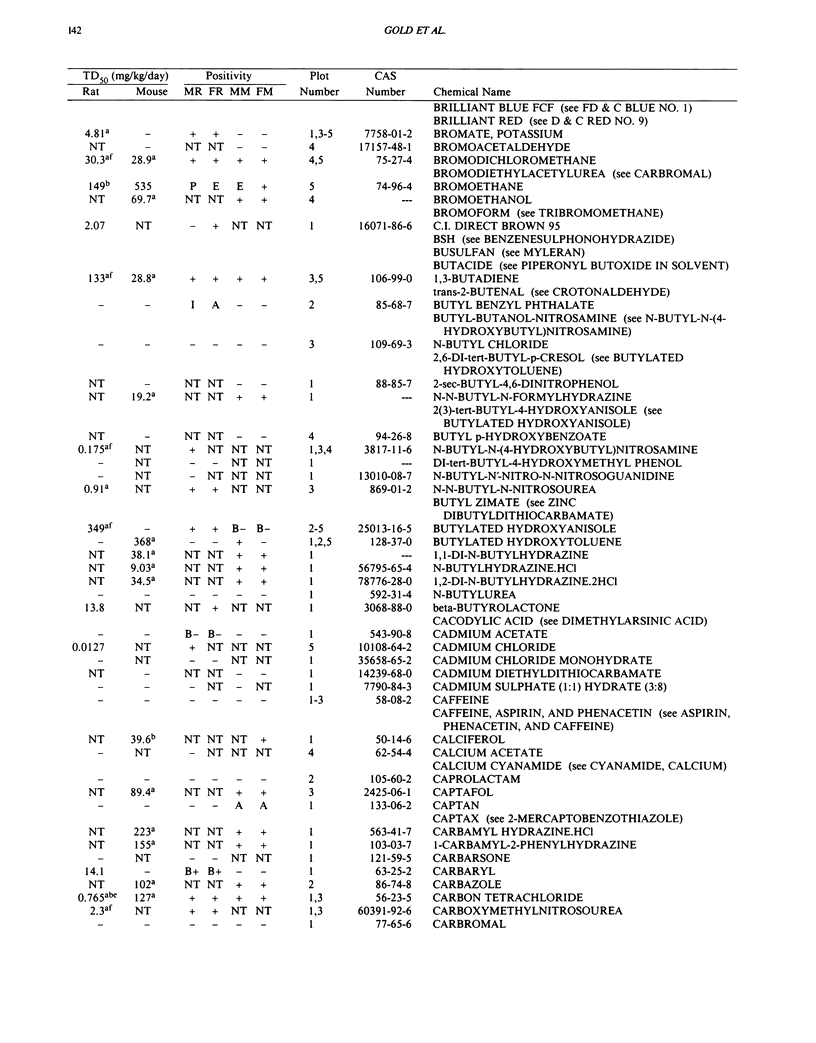
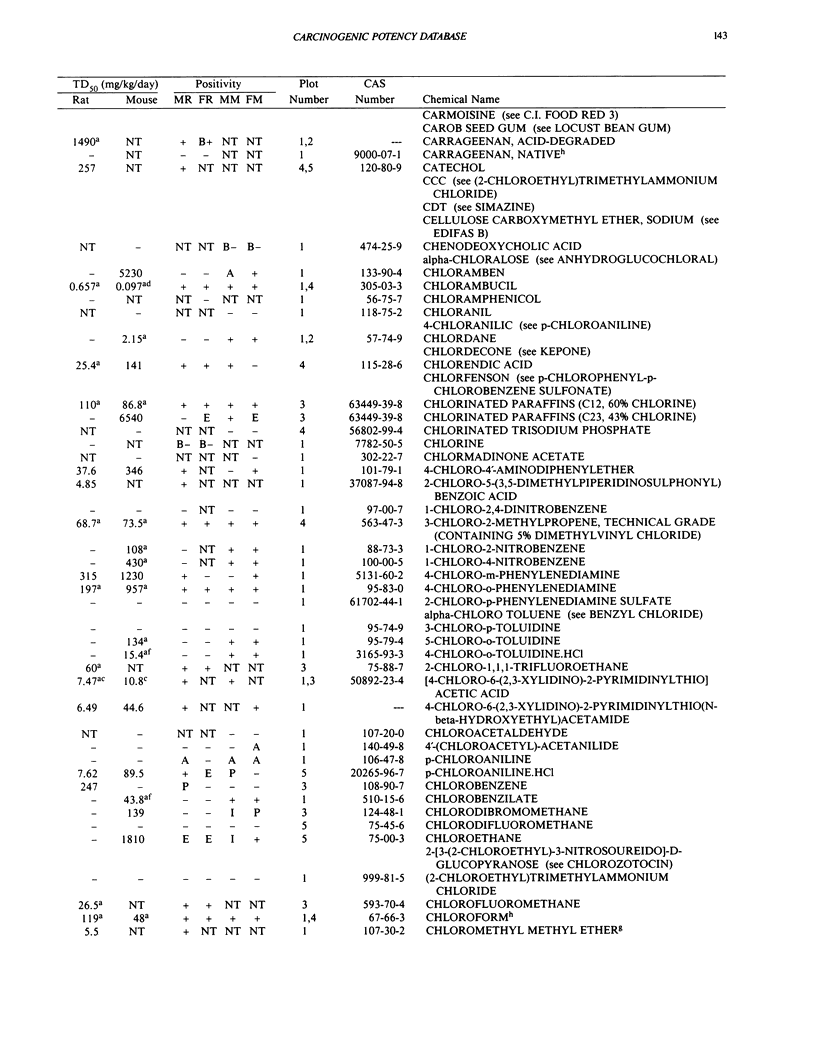
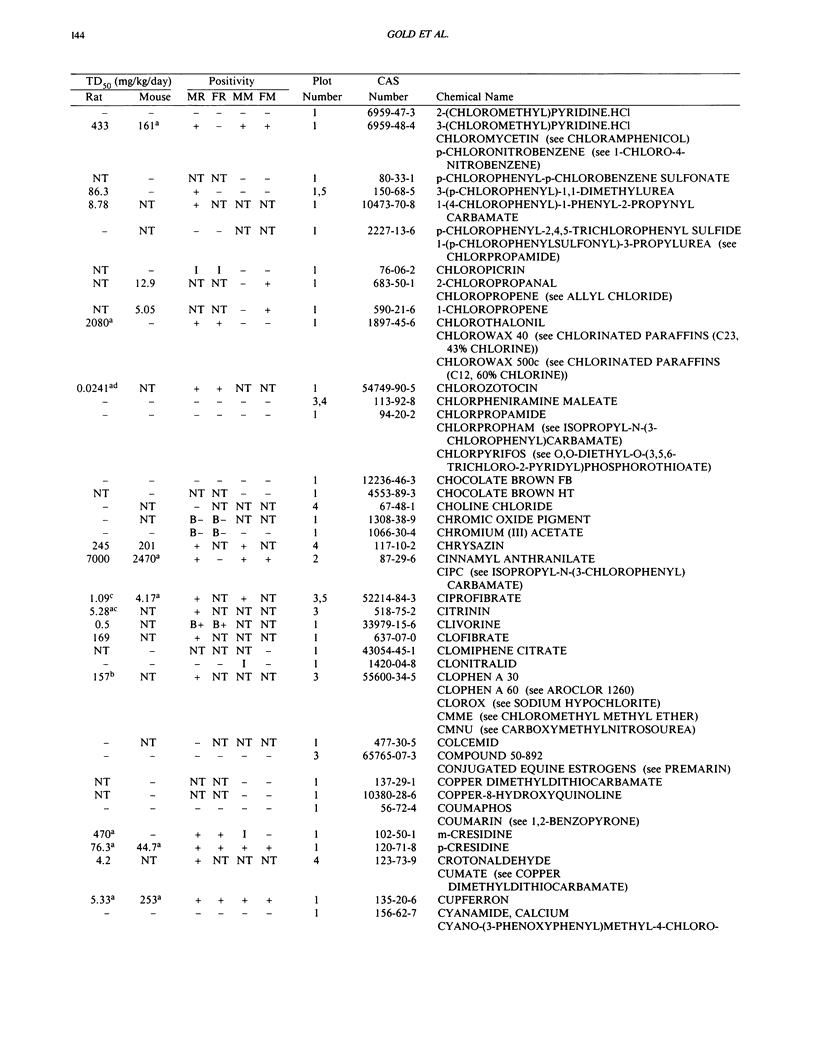
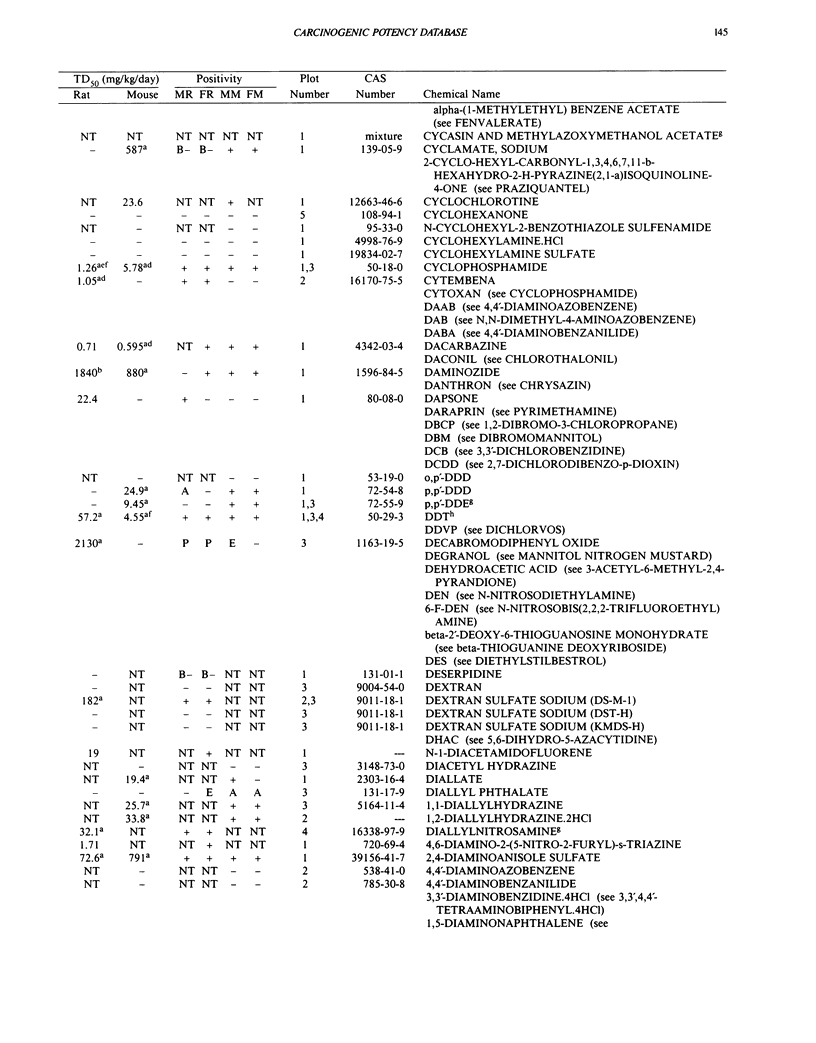
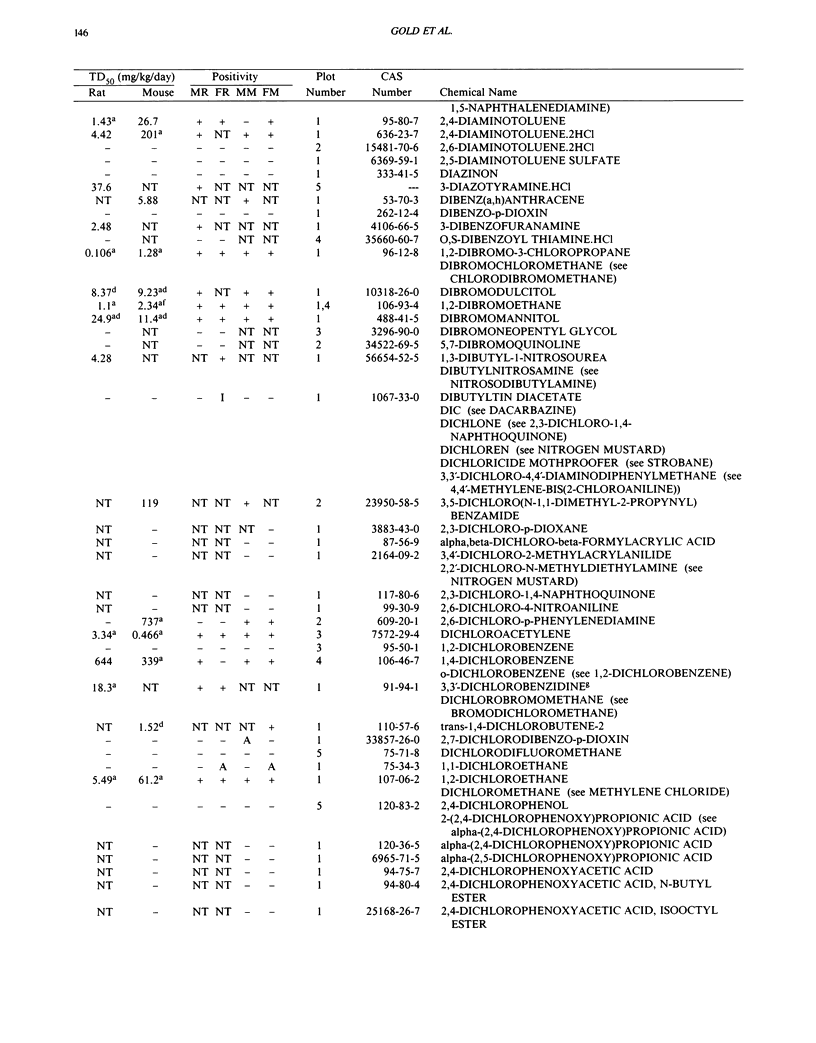
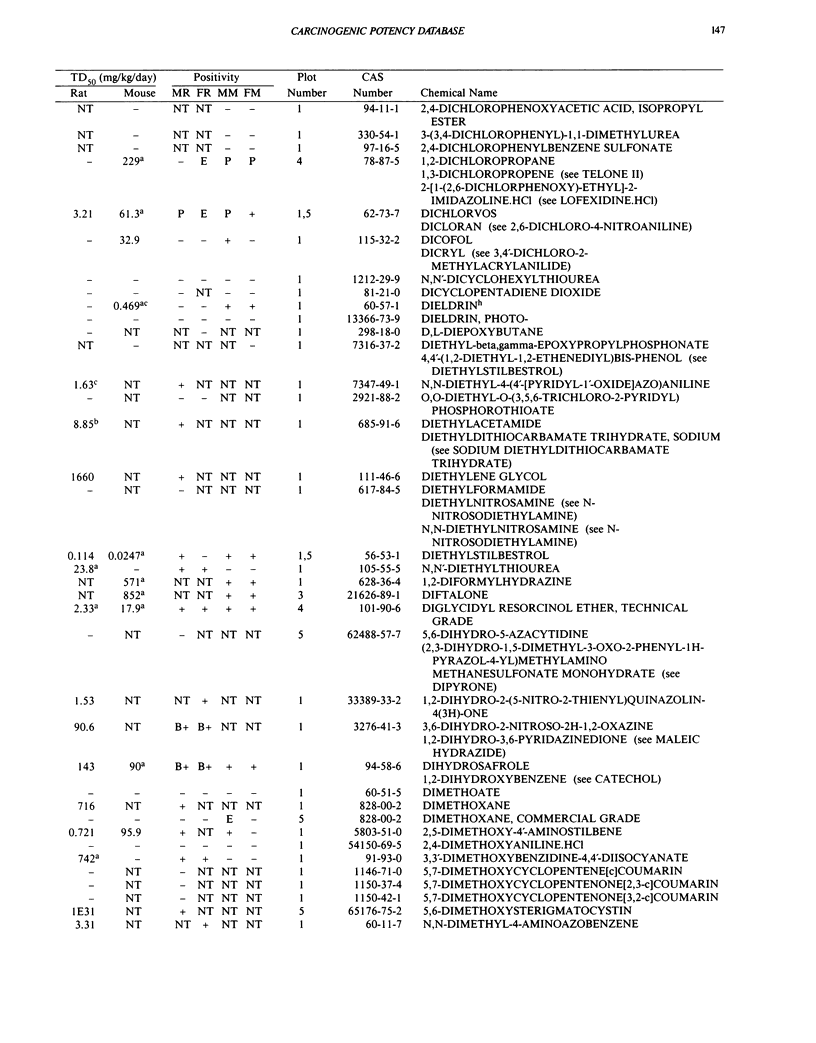
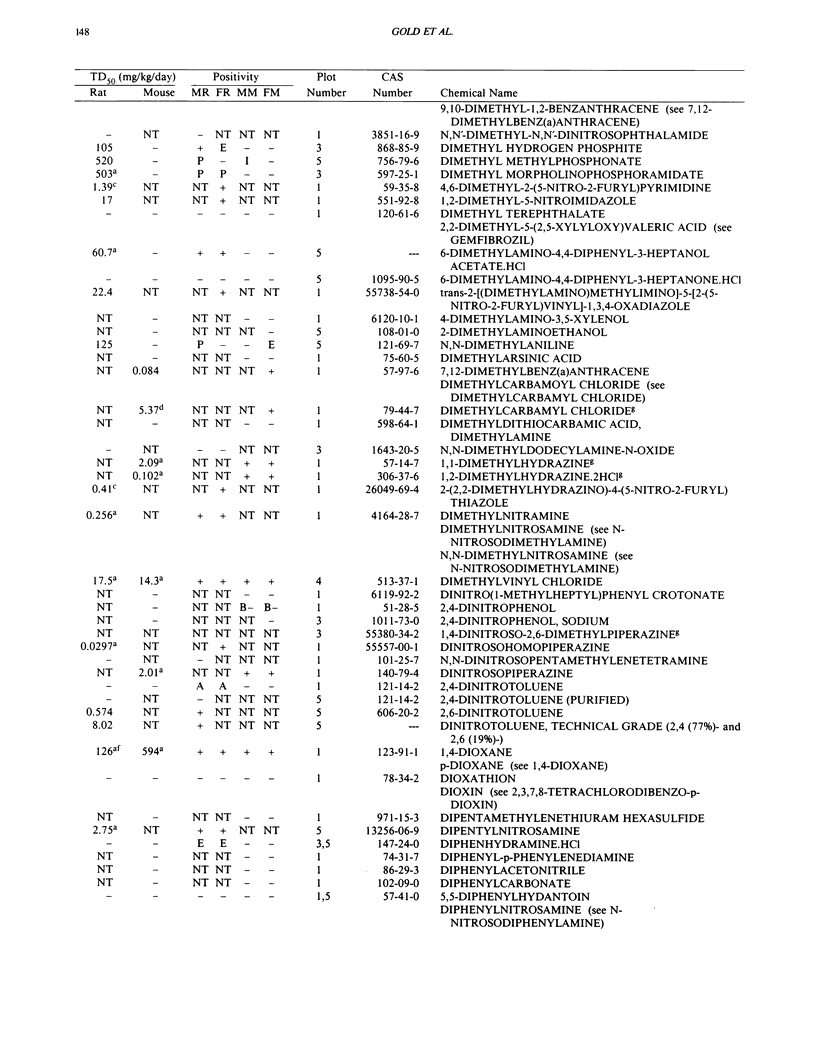
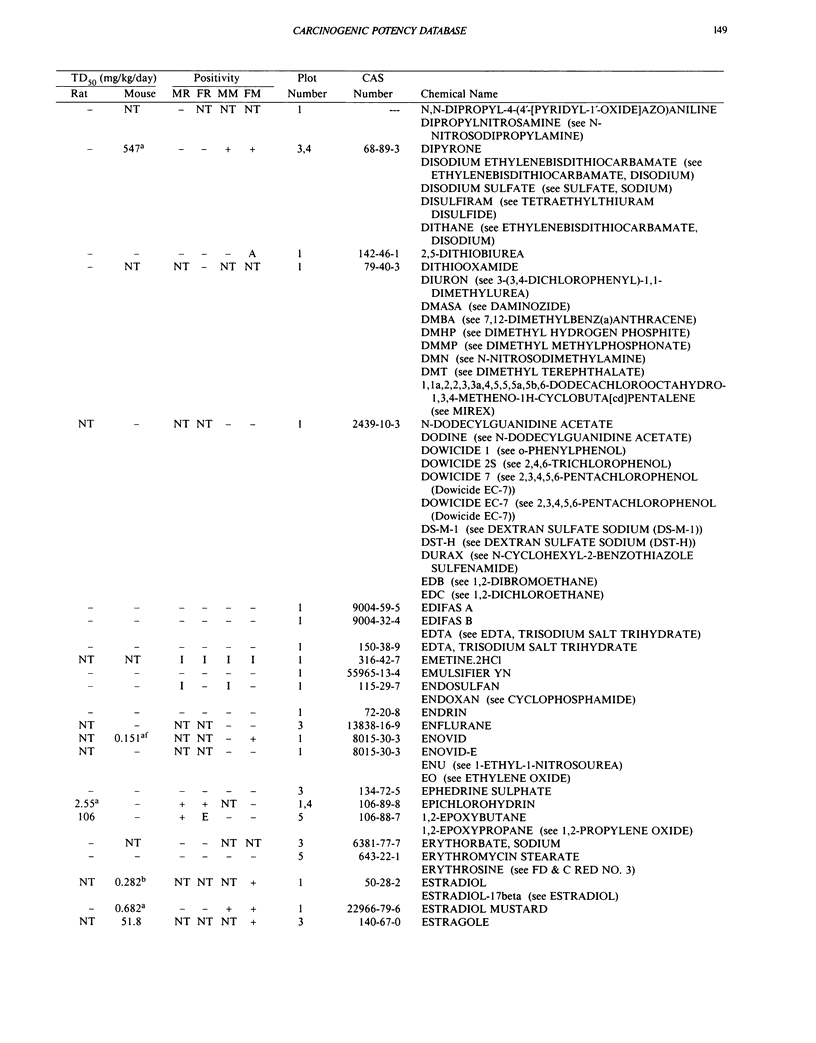
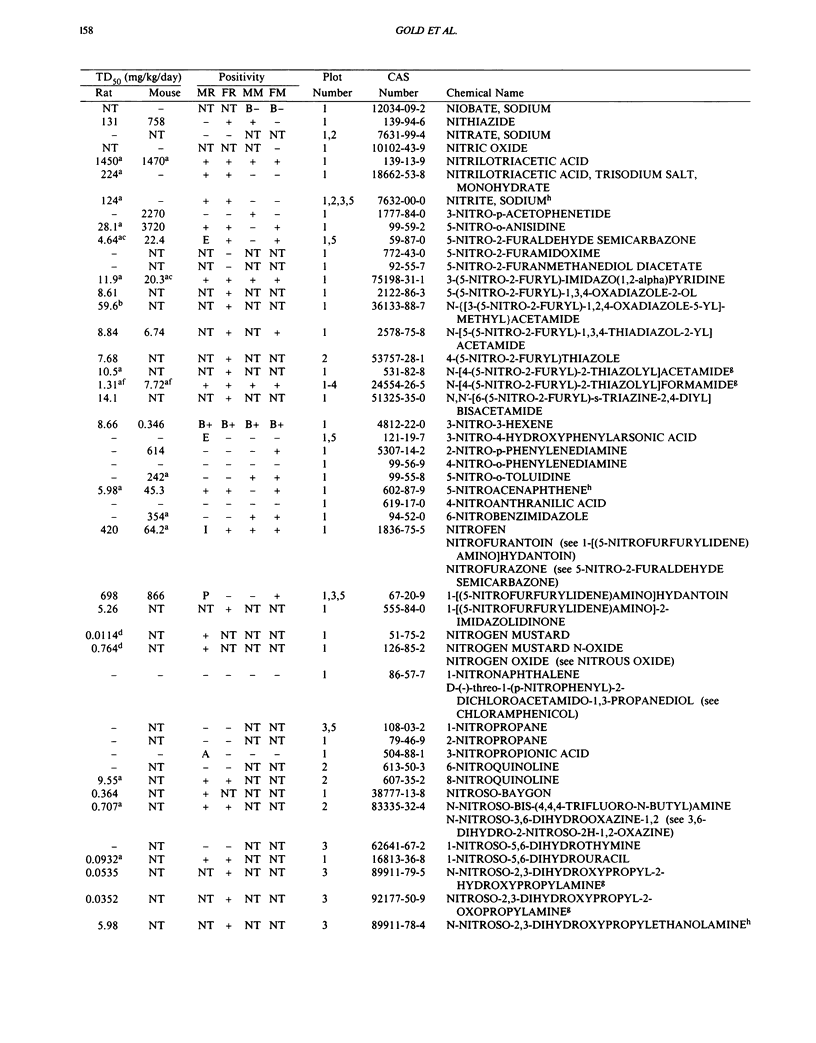
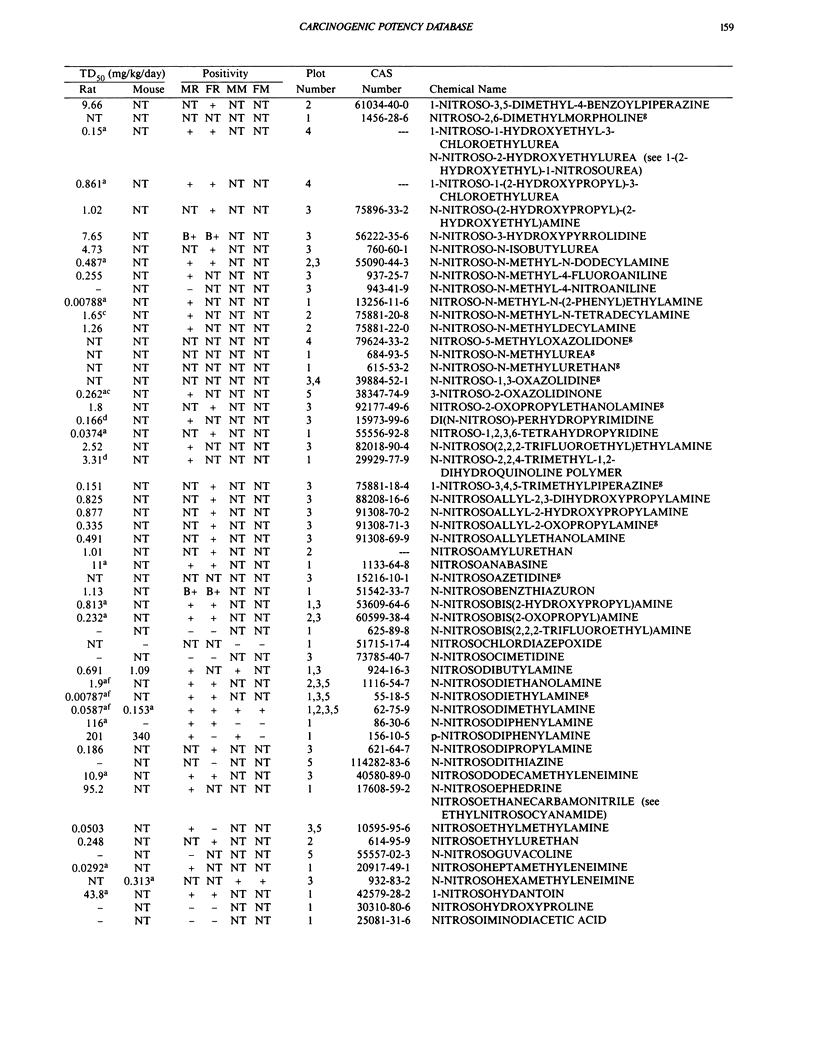
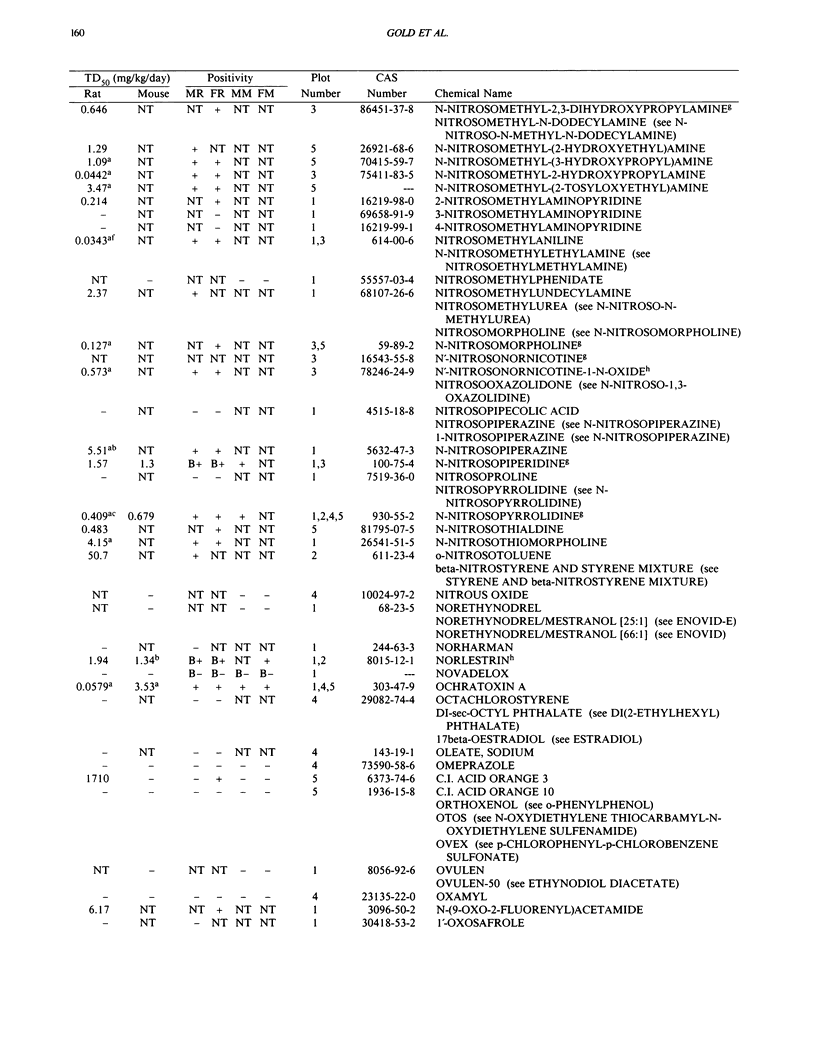
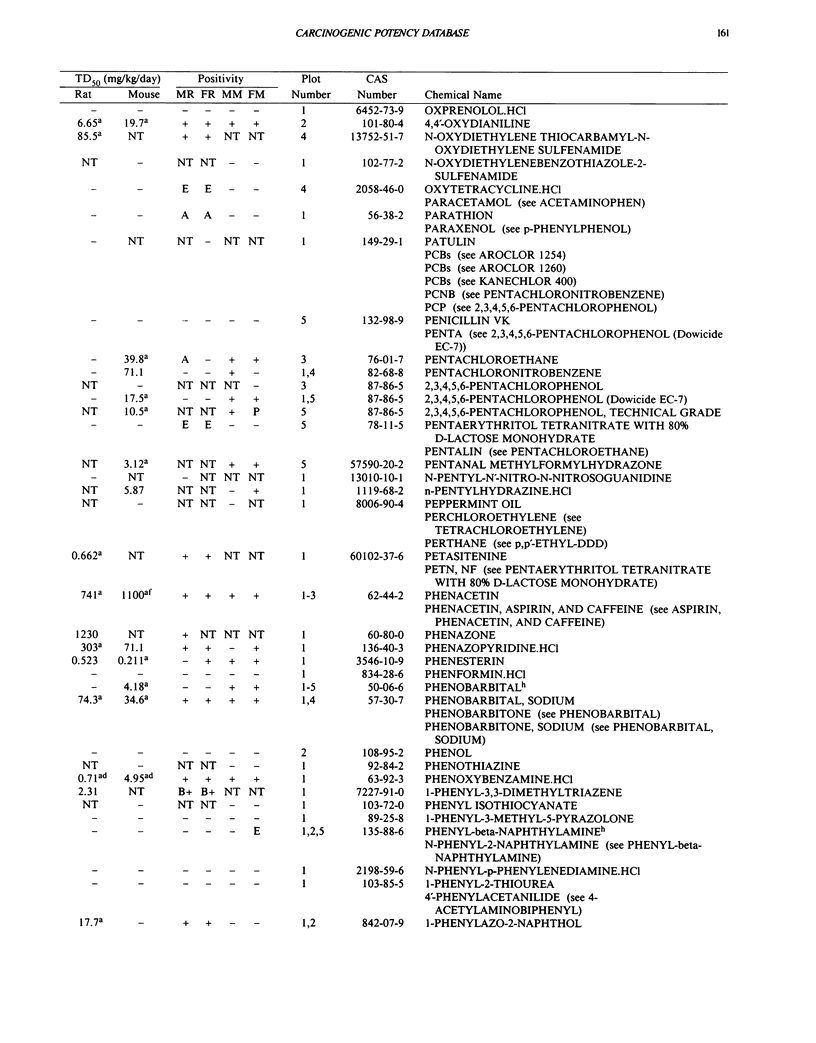
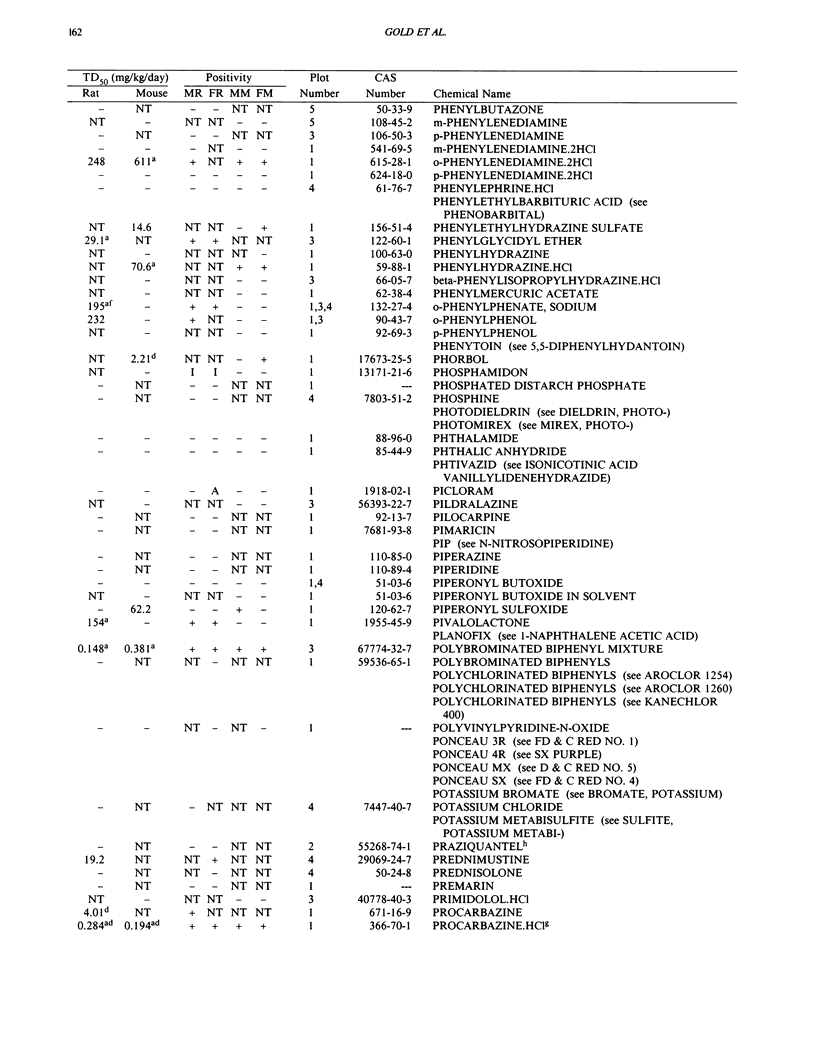
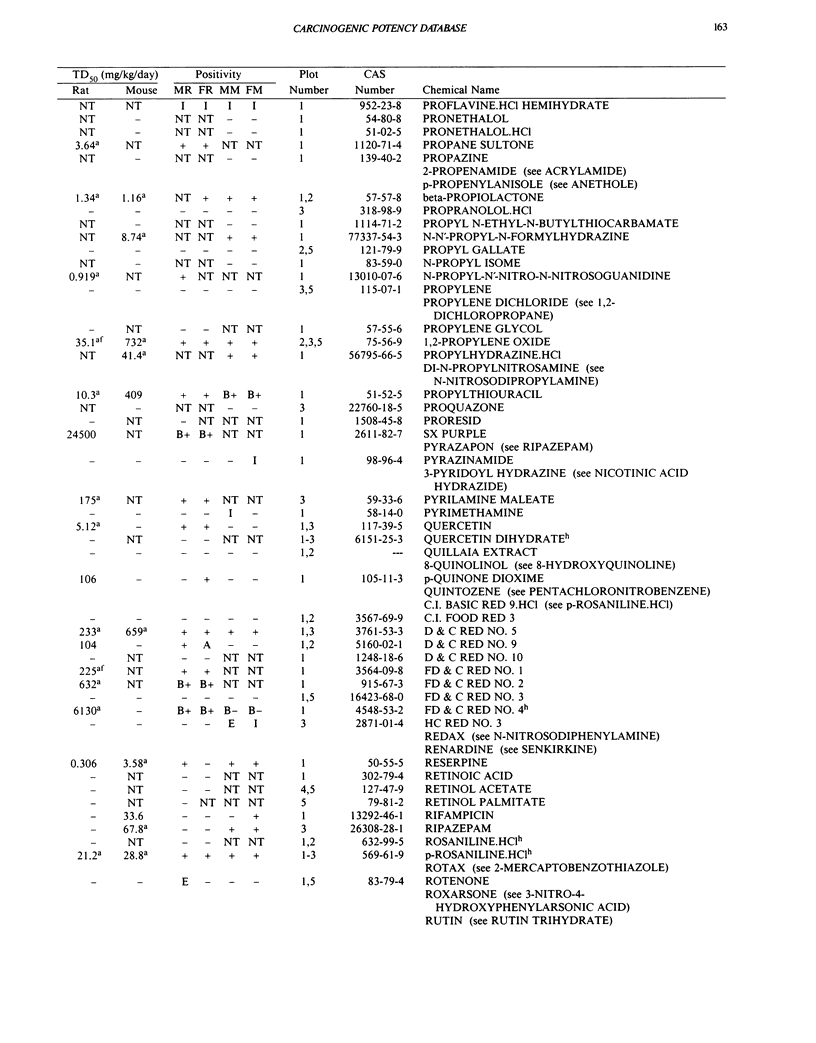
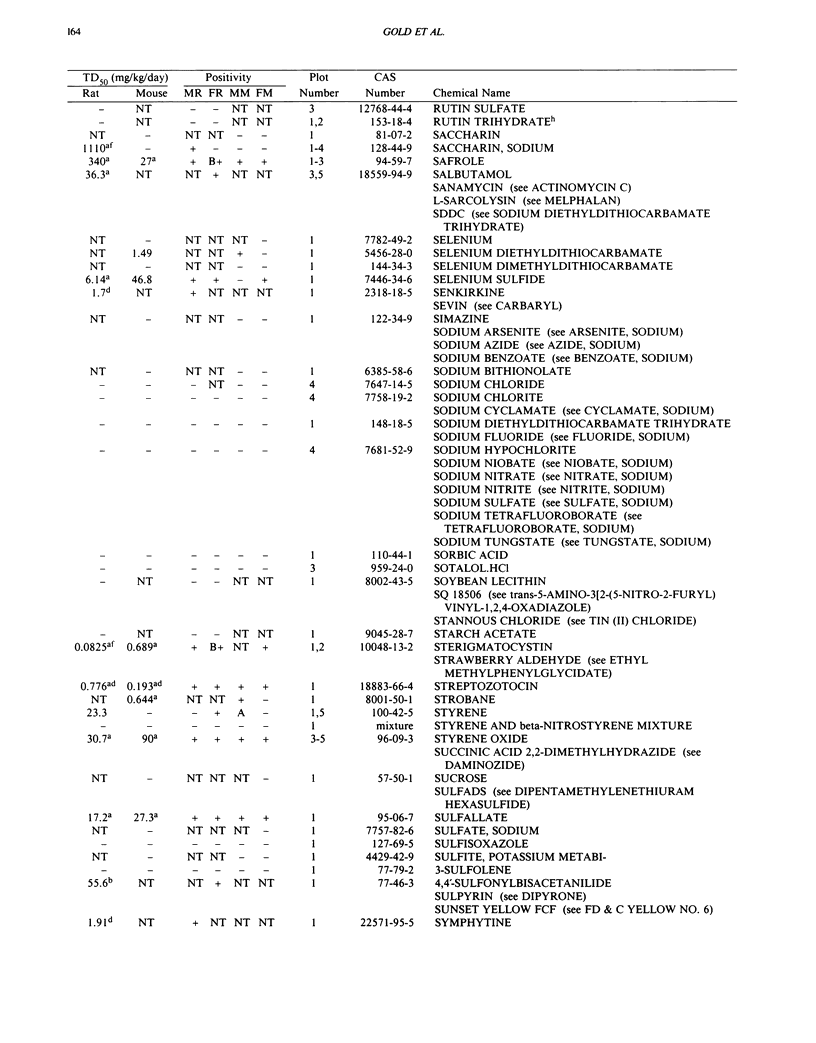
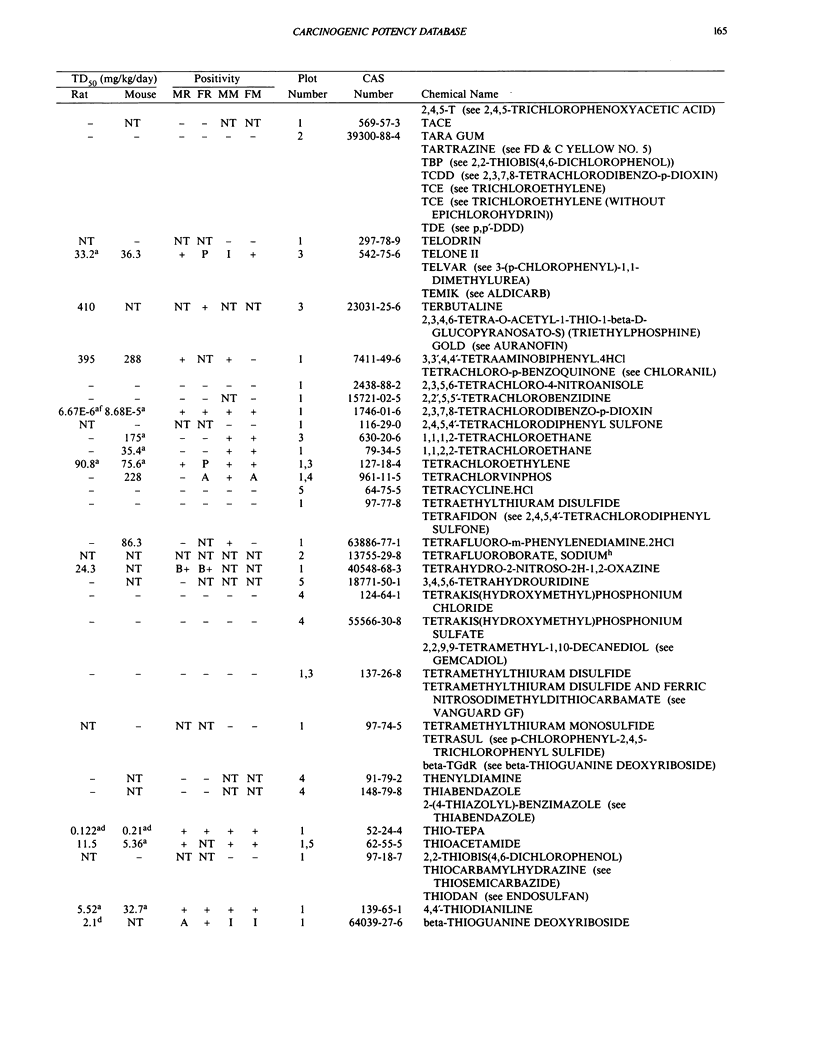
This paper is the fifth plot of the Carcinogenic Potency Database (CPDB) that first appeared in this journal in 1984 (1-5). We report here results of carcinogenesis bioassays published in the general literature between January 1987 and December 1988, and in technical reports of the National Toxicology Program between July 1987 and December 1989. This supplement includes results of 412 long-term, chronic experiments of 147 test compounds and reports the same information about each experiment in the same plot format as the earlier papers: the species and strain of test animal, the route and duration of compound administration, dose level and other aspects of experimental protocol, histopathology and tumor incidence, TD50 (carcinogenic potency) and its statistical significance, dose response, author's opinion about carcinogenicity, and literature citation. We refer the reader to the 1984 publications (1,5,6) for a guide to the plot of the database, a complete description of the numerical index of carcinogenic potency, and a discussion of the sources of data, the rationale for the inclusion of particular experiments and particular target sites, and the conventions adopted in summarizing the literature. The five plots of the database are to be used together, as results of individual experiments that were published earlier are not repeated. In all, the five plots include results of 4487 experiments on 1136 chemicals. Several analyses based on the CPDB that were published earlier are described briefly, and updated results based on all five plots are given for the following earlier analyses: the most potent TD50 value by species, reproducibility of bioassay results, positivity rates, and prediction between species.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF




















































Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ames B. N. Endogenous oxidative DNA damage, aging, and cancer. Free Radic Res Commun. 1989;7(3-6):121–128. doi: 10.3109/10715768909087933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ames B. N., Gold L. S. Animal cancer tests and cancer prevention. J Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 1992;(12):125–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ames B. N., Gold L. S. Chemical carcinogenesis: too many rodent carcinogens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7772–7776. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ames B. N., Gold L. S. Dietary carcinogens, environmental pollution, and cancer: some misconceptions. Med Oncol Tumor Pharmacother. 1990;7(2-3):69–85. doi: 10.1007/BF02988534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ames B. N., Gold L. S. Too many rodent carcinogens: mitogenesis increases mutagenesis. Science. 1990 Aug 31;249(4972):970–971. doi: 10.1126/science.2136249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ames B. N., Profet M., Gold L. S. Dietary pesticides (99.99% all natural). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7777–7781. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ames B. N., Profet M., Gold L. S. Nature's chemicals and synthetic chemicals: comparative toxicology. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7782–7786. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
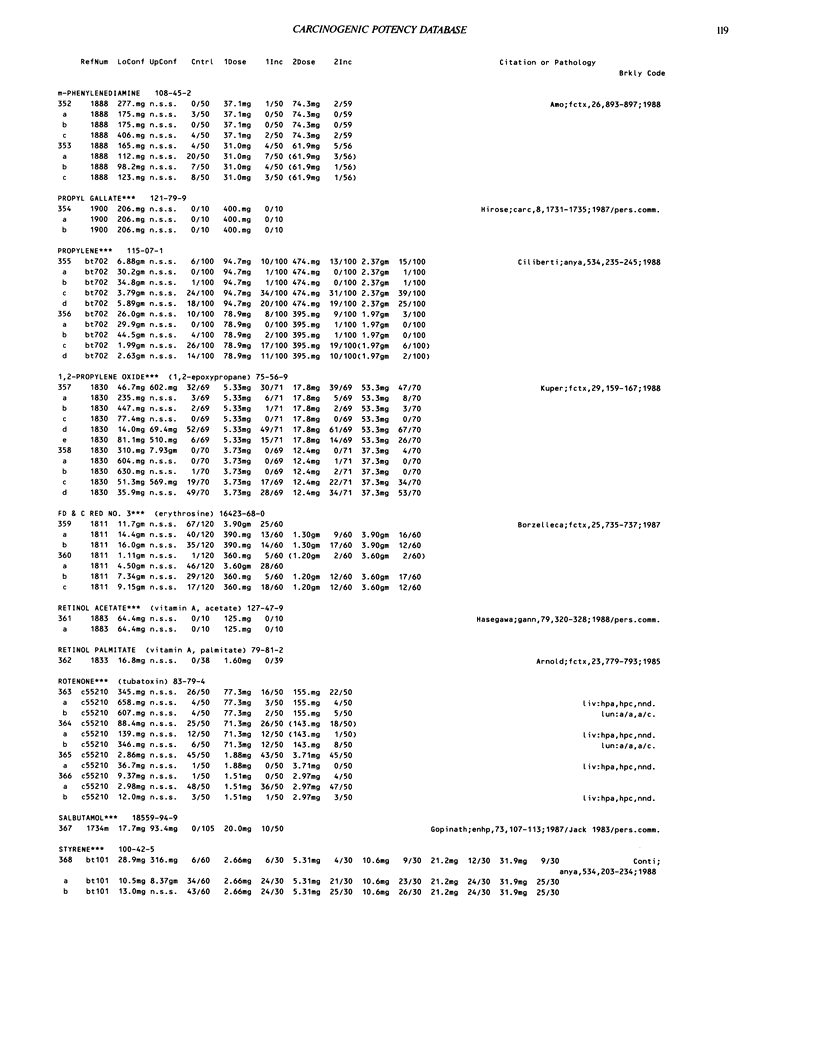
- Amo H., Matsuyama M., Amano H., Yamada C., Kawai M., Miyata N., Nakadate M. Carcinogenicity and toxicity study of m-phenylenediamine administered in the drinking-water to (C57BL/6 x C3H/He)F1 mice. Food Chem Toxicol. 1988 Nov-Dec;26(11-12):893–897. doi: 10.1016/0278-6915(88)90086-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Annapurna V. V., Mukundan M. A., Sesikeran B., Bamji M. S. Long-term effects of female sex steroids on female rat liver in an initiator-promoter model of hepatocarcinogenesis. Indian J Biochem Biophys. 1988 Dec;25(6):708–713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Annapurna V. V., Mukundan M. A., Sesikeran B., Bamji M. S. Long-term effects of female sex steroids on female rat liver in an initiator-promoter model of hepatocarcinogenesis. Indian J Biochem Biophys. 1988 Dec;25(6):708–713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnold D. L., Moodie C. A., Charbonneau S. M., Grice H. C., McGuire P. F., Bryce F. R., Collins B. T., Zawidzka Z. Z., Krewski D. R., Nera E. A. Long-term toxicity of hexachlorobenzene in the rat and the effect of dietary vitamin A. Food Chem Toxicol. 1985 Sep;23(9):779–793. doi: 10.1016/0278-6915(85)90278-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baden J. M., Kundomal Y. R., Mazze R. I., Kosek J. C. Carcinogen bioassay of isoflurane in mice. Anesthesiology. 1988 Nov;69(5):750–753. doi: 10.1097/00000542-198811000-00018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baden J. M., Kundomal Y. R., Mazze R. I., Kosek J. C. Carcinogen bioassay of isoflurane in mice. Anesthesiology. 1988 Nov;69(5):750–753. doi: 10.1097/00000542-198811000-00018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barten M. The effects of different MNNG (N-methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine) doses on the stomach and the upper small intestine of the rat. I. The frequency and histopathology of the induced tumours. Exp Pathol. 1987;31(3):147–152. doi: 10.1016/s0232-1513(87)80097-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger M. R., Schmähl D., Zerban H. Combination experiments with very low doses of three genotoxic N-nitrosamines with similar organotropic carcinogenicity in rats. Carcinogenesis. 1987 Nov;8(11):1635–1643. doi: 10.1093/carcin/8.11.1635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger M. R., Schmähl D., Zerban H. Combination experiments with very low doses of three genotoxic N-nitrosamines with similar organotropic carcinogenicity in rats. Carcinogenesis. 1987 Nov;8(11):1635–1643. doi: 10.1093/carcin/8.11.1635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger M. R., Schmähl D., Zerban H. Combination experiments with very low doses of three genotoxic N-nitrosamines with similar organotropic carcinogenicity in rats. Carcinogenesis. 1987 Nov;8(11):1635–1643. doi: 10.1093/carcin/8.11.1635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein L., Gold L. S., Ames B. N., Pike M. C., Hoel D. G. Some tautologous aspects of the comparison of carcinogenic potency in rats and mice. Fundam Appl Toxicol. 1985 Feb;5(1):79–86. doi: 10.1016/0272-0590(85)90051-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borzelleca J. F., Hallagan J. B. A chronic toxicity/carcinogenicity study of FD & C Yellow No. 5 (tartrazine) in mice. Food Chem Toxicol. 1988 Mar;26(3):189–194. doi: 10.1016/0278-6915(88)90118-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borzelleca J. F., Hallagan J. B. Lifetime toxicity/carcinogenicity study of FD & C Red No. 3 (erythrosine) in mice. Food Chem Toxicol. 1987 Oct;25(10):735–737. doi: 10.1016/0278-6915(87)90227-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosan W. S., Shank R. C., MacEwen J. D., Gaworski C. L., Newberne P. M. Methylation of DNA guanine during the course of induction of liver cancer in hamsters by hydrazine or dimethylnitrosamine. Carcinogenesis. 1987 Mar;8(3):439–444. doi: 10.1093/carcin/8.3.439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosan W. S., Shank R. C., MacEwen J. D., Gaworski C. L., Newberne P. M. Methylation of DNA guanine during the course of induction of liver cancer in hamsters by hydrazine or dimethylnitrosamine. Carcinogenesis. 1987 Mar;8(3):439–444. doi: 10.1093/carcin/8.3.439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnett C. M., Corbett J. F. Failure of short-term in vitro mutagenicity tests to predict the animal carcinogenicity of hair dyes. Food Chem Toxicol. 1987 Sep;25(9):703–707. doi: 10.1016/0278-6915(87)90104-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnett C. M., Corbett J. F. Failure of short-term in vitro mutagenicity tests to predict the animal carcinogenicity of hair dyes. Food Chem Toxicol. 1987 Sep;25(9):703–707. doi: 10.1016/0278-6915(87)90104-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr B. I., Rahbar S., Asmeron Y., Riggs A., Winberg C. D. Carcinogenicity and haemoglobin synthesis induction by cytidine analogues. Br J Cancer. 1988 Apr;57(4):395–402. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1988.89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr B. I., Rahbar S., Asmeron Y., Riggs A., Winberg C. D. Carcinogenicity and haemoglobin synthesis induction by cytidine analogues. Br J Cancer. 1988 Apr;57(4):395–402. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1988.89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavaliere A., Bufalari A., Vitali R. 5-Azacytidine carcinogenesis in BALB/c mice. Cancer Lett. 1987 Oct;37(1):51–58. doi: 10.1016/0304-3835(87)90145-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciliberti A., Maltoni C., Perino G. Long-term carcinogenicity bioassays on propylene administered by inhalation to Sprague-Dawley rats and Swiss mice. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;534:235–245. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb30113.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conti B., Maltoni C., Perino G., Ciliberti A. Long-term carcinogenicity bioassays on styrene administered by inhalation, ingestion and injection and styrene oxide administered by ingestion in Sprague-Dawley rats, and para-methylstyrene administered by ingestion in Sprague-Dawley rats and Swiss mice. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;534:203–234. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb30112.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conti B., Maltoni C., Perino G., Ciliberti A. Long-term carcinogenicity bioassays on styrene administered by inhalation, ingestion and injection and styrene oxide administered by ingestion in Sprague-Dawley rats, and para-methylstyrene administered by ingestion in Sprague-Dawley rats and Swiss mice. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;534:203–234. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb30112.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodd D. C., Port C. D., Deslex P., Regnier B., Sanders P., Indacochea-Redmond N. Two-year evaluation of misoprostol for carcinogenicity in CD Sprague-Dawley rats. Toxicol Pathol. 1987;15(2):125–133. doi: 10.1177/019262338701500201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elashoff R. M., Fears T. R., Schneiderman M. A. Statistical analysis of a carcinogen mixture experiment. I. Liver carcinogens. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1987 Sep;79(3):509–526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elashoff R. M., Fears T. R., Schneiderman M. A. Statistical analysis of a carcinogen mixture experiment. I. Liver carcinogens. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1987 Sep;79(3):509–526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elashoff R. M., Fears T. R., Schneiderman M. A. Statistical analysis of a carcinogen mixture experiment. I. Liver carcinogens. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1987 Sep;79(3):509–526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elashoff R. M., Fears T. R., Schneiderman M. A. Statistical analysis of a carcinogen mixture experiment. I. Liver carcinogens. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1987 Sep;79(3):509–526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernst H., Ohshima H., Bartsch H., Mohr U., Reichart P. Tumorigenicity study in Syrian hamsters fed areca nut together with nitrite. Carcinogenesis. 1987 Dec;8(12):1843–1845. doi: 10.1093/carcin/8.12.1843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernst H., Ohshima H., Bartsch H., Mohr U., Reichart P. Tumorigenicity study in Syrian hamsters fed areca nut together with nitrite. Carcinogenesis. 1987 Dec;8(12):1843–1845. doi: 10.1093/carcin/8.12.1843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiala E. S., Czerniak R., Castonguay A., Conaway C. C., Rivenson A. Assay of 1-nitropropane, 2-nitropropane, 1-azoxypropane and 2-azoxypropane for carcinogenicity by gavage in Sprague-Dawley rats. Carcinogenesis. 1987 Dec;8(12):1947–1949. doi: 10.1093/carcin/8.12.1947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujii K., Nomoto K., Ishidate M., Jr, Nakamura K. Chronic toxicity of charred fish meat in Wistar rats. Nutr Cancer. 1987;9(2-3):185–193. doi: 10.1080/01635588709513926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita Y., Wakabayashi K., Takayama S., Nagao M., Sugimura T. Induction of oral cavity cancer by 3-diazotyramine, a nitrosated product of tyramine present in foods. Carcinogenesis. 1987 Apr;8(4):527–529. doi: 10.1093/carcin/8.4.527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold L. S., Backman G. M., Hooper N. K., Peto R. Ranking the potential carcinogenic hazards to workers from exposures to chemicals that are tumorigenic in rodents. Environ Health Perspect. 1987 Dec;76:211–219. doi: 10.1289/ehp.8776211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold L. S., Bernstein L., Kaldor J., Backman G., Hoel D. An empirical comparison of methods used to estimate carcinogenic potency in long-term animal bioassays: lifetable vs summary incidence data. Fundam Appl Toxicol. 1986 Feb;6(2):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0272-0590(86)90239-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold L. S., Bernstein L., Magaw R., Slone T. H. Interspecies extrapolation in carcinogenesis: prediction between rats and mice. Environ Health Perspect. 1989 May;81:211–219. doi: 10.1289/ehp.8981211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold L. S., Sawyer C. B., Magaw R., Backman G. M., de Veciana M., Levinson R., Hooper N. K., Havender W. R., Bernstein L., Peto R. A carcinogenic potency database of the standardized results of animal bioassays. Environ Health Perspect. 1984 Dec;58:9–319. doi: 10.1289/ehp.84589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold L. S., Slone T. H., Backman G. M., Eisenberg S., Da Costa M., Wong M., Manley N. B., Rohrbach L., Ames B. N. Third chronological supplement to the carcinogenic potency database: standardized results of animal bioassays published through December 1986 and by the National Toxicology Program through June 1987. Environ Health Perspect. 1990 Mar;84:215–286. doi: 10.1289/ehp.9084215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold L. S., Slone T. H., Backman G. M., Magaw R., Da Costa M., Lopipero P., Blumenthal M., Ames B. N. Second chronological supplement to the Carcinogenic Potency Database: standardized results of animal bioassays published through December 1984 and by the National Toxicology Program through May 1986. Environ Health Perspect. 1987 Oct;74:237–329. doi: 10.1289/ehp.8774237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold L. S., Slone T. H., Bernstein L. Summary of carcinogenic potency and positivity for 492 rodent carcinogens in the carcinogenic potency database. Environ Health Perspect. 1989 Feb;79:259–272. doi: 10.1289/ehp.8979259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
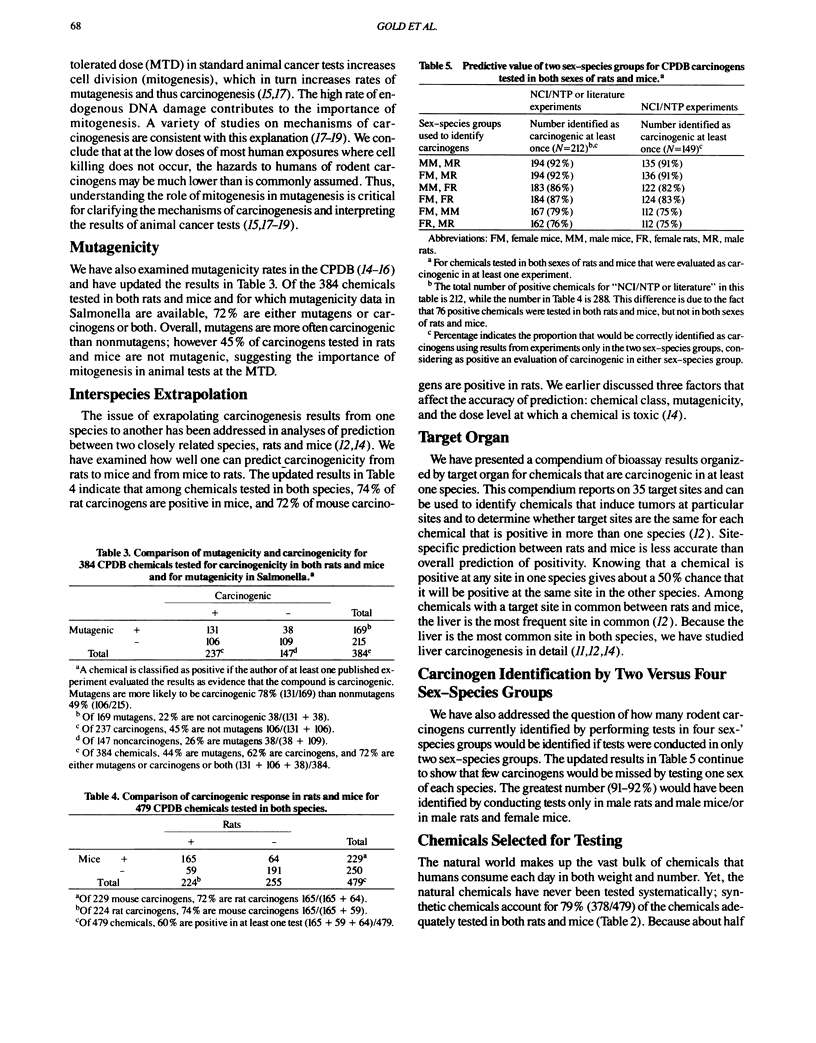
- Gold L. S., Slone T. H., Manley N. B., Bernstein L. Target organs in chronic bioassays of 533 chemical carcinogens. Environ Health Perspect. 1991 Jun;93:233–246. doi: 10.1289/ehp.9193233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold L. S., Slone T. H., Stern B. R., Manley N. B., Ames B. N. Rodent carcinogens: setting priorities. Science. 1992 Oct 9;258(5080):261–265. doi: 10.1126/science.1411524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold L. S., Ward J. M., Bernstein L., Stern B. Association between carcinogenic potency and tumor pathology in rodent carcinogenesis bioassays. Fundam Appl Toxicol. 1986 May;6(4):677–690. doi: 10.1016/0272-0590(86)90181-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold L. S., Wright C., Bernstein L., deVeciana M. Reproducibility of results in "near-replicate" carcinogenesis bioassays. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1987 Jun;78(6):1149–1158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold L. S., de Veciana M., Backman G. M., Magaw R., Lopipero P., Smith M., Blumenthal M., Levinson R., Bernstein L., Ames B. N. Chronological supplement to the Carcinogenic Potency Database: standardized results of animal bioassays published through December 1982. Environ Health Perspect. 1986 Aug;67:161–200. doi: 10.1289/ehp.8667161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gopinath C., Gibson W. A. Mesovarian leiomyomas in the rat. Environ Health Perspect. 1987 Aug;73:107–113. doi: 10.1289/ehp.8773107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gopinath C., Gibson W. A. Mesovarian leiomyomas in the rat. Environ Health Perspect. 1987 Aug;73:107–113. doi: 10.1289/ehp.8773107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenman D. L., Highman B., Chen J. J., Schieferstein G. J., Norvell M. J. Influence of age on induction of mammary tumors by diethylstilbestrol in C3H/HeN mice with low murine mammary tumor virus titer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1986 Oct;77(4):891–898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenman D. L., Highman B., Chen J. J., Schieferstein G. J., Norvell M. J. Influence of age on induction of mammary tumors by diethylstilbestrol in C3H/HeN mice with low murine mammary tumor virus titer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1986 Oct;77(4):891–898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasegawa R., Takahashi M., Furukawa F., Toyoda K., Sato H., Hayashi Y. Co-carcinogenic effect of retinyl acetate on forestomach carcinogenesis of male F344 rats induced with butylated hydroxyanisole. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1988 Mar;79(3):320–328. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.1988.tb01594.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasegawa R., Takahashi M., Furukawa F., Toyoda K., Sato H., Hayashi Y. Co-carcinogenic effect of retinyl acetate on forestomach carcinogenesis of male F344 rats induced with butylated hydroxyanisole. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1988 Mar;79(3):320–328. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.1988.tb01594.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasegawa R., Takahashi M., Furukawa F., Toyoda K., Sato H., Hayashi Y. Co-carcinogenic effect of retinyl acetate on forestomach carcinogenesis of male F344 rats induced with butylated hydroxyanisole. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1988 Mar;79(3):320–328. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.1988.tb01594.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirose M., Fukushima S., Shirai T., Hasegawa R., Kato T., Tanaka H., Asakawa E., Ito N. Stomach carcinogenicity of caffeic acid, sesamol and catechol in rats and mice. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1990 Mar;81(3):207–212. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.1990.tb02550.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirose M., Kurata Y., Tsuda H., Fukushima S., Ito N. Catechol strongly enhances rat stomach carcinogenesis: a possible new environmental stomach carcinogen. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1987 Nov;78(11):1144–1149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirose M., Kurata Y., Tsuda H., Fukushima S., Ito N. Catechol strongly enhances rat stomach carcinogenesis: a possible new environmental stomach carcinogen. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1987 Nov;78(11):1144–1149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirose M., Masuda A., Tsuda H., Uwagawa S., Ito N. Enhancement of BHA-induced proliferative rat forestomach lesion development by simultaneous treatment with other antioxidants. Carcinogenesis. 1987 Nov;8(11):1731–1735. doi: 10.1093/carcin/8.11.1731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirose M., Masuda A., Tsuda H., Uwagawa S., Ito N. Enhancement of BHA-induced proliferative rat forestomach lesion development by simultaneous treatment with other antioxidants. Carcinogenesis. 1987 Nov;8(11):1731–1735. doi: 10.1093/carcin/8.11.1731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirose M., Masuda A., Tsuda H., Uwagawa S., Ito N. Enhancement of BHA-induced proliferative rat forestomach lesion development by simultaneous treatment with other antioxidants. Carcinogenesis. 1987 Nov;8(11):1731–1735. doi: 10.1093/carcin/8.11.1731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirose M., Masuda A., Tsuda H., Uwagawa S., Ito N. Enhancement of BHA-induced proliferative rat forestomach lesion development by simultaneous treatment with other antioxidants. Carcinogenesis. 1987 Nov;8(11):1731–1735. doi: 10.1093/carcin/8.11.1731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirose M., Masuda A., Tsuda H., Uwagawa S., Ito N. Enhancement of BHA-induced proliferative rat forestomach lesion development by simultaneous treatment with other antioxidants. Carcinogenesis. 1987 Nov;8(11):1731–1735. doi: 10.1093/carcin/8.11.1731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirose M., Masuda A., Tsuda H., Uwagawa S., Ito N. Enhancement of BHA-induced proliferative rat forestomach lesion development by simultaneous treatment with other antioxidants. Carcinogenesis. 1987 Nov;8(11):1731–1735. doi: 10.1093/carcin/8.11.1731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inai K., Kobuke T., Nambu S., Takemoto T., Kou E., Nishina H., Fujihara M., Yonehara S., Suehiro S., Tsuya T. Hepatocellular tumorigenicity of butylated hydroxytoluene administered orally to B6C3F1 mice. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1988 Jan;79(1):49–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.1988.tb00010.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jack D., Poynter D., Spurling N. W. Beta-adrenoceptor stimulants and mesovarian leiomyomas in the rat. Toxicology. 1983 Jul-Aug;27(3-4):315–320. doi: 10.1016/0300-483x(83)90026-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jang J. J., Takahashi M., Furukawa F., Toyoda K., Hasegawa R., Sato H., Hayashi Y. Long-term in vivo carcinogenicity study of phenytoin (5,5-diphenylhydantoin) in F344 rats. Food Chem Toxicol. 1987 Sep;25(9):697–702. doi: 10.1016/0278-6915(87)90103-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jang J. J., Takahashi M., Furukawa F., Toyoda K., Hasegawa R., Sato H., Hayashi Y. Long-term in vivo carcinogenicity study of phenytoin (5,5-diphenylhydantoin) in F344 rats. Food Chem Toxicol. 1987 Sep;25(9):697–702. doi: 10.1016/0278-6915(87)90103-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato T., Ohgaki H., Hasegawa H., Sato S., Takayama S., Sugimura T. Carcinogenicity in rats of a mutagenic compound, 2-amino-3,8-dimethylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoxaline. Carcinogenesis. 1988 Jan;9(1):71–73. doi: 10.1093/carcin/9.1.71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koepke S. R., Creasia D. R., Knutsen G. L., Michejda C. J. Carcinogenicity of hydroxyalkylnitrosamines in F344 rats: contrasting behavior of beta- and gamma-hydroxylated nitrosamines. Cancer Res. 1988 Mar 15;48(6):1533–1536. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koepke S. R., Creasia D. R., Knutsen G. L., Michejda C. J. Carcinogenicity of hydroxyalkylnitrosamines in F344 rats: contrasting behavior of beta- and gamma-hydroxylated nitrosamines. Cancer Res. 1988 Mar 15;48(6):1533–1536. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuroda K., Terao K., Akao M. Inhibitory effect of fumaric acid on hepatocarcinogenesis by thioacetamide in rats. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1987 Nov;79(5):1047–1051. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuroda K., Terao K., Akao M. Inhibitory effect of fumaric acid on hepatocarcinogenesis by thioacetamide in rats. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1987 Nov;79(5):1047–1051. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurokawa Y., Aoki S., Matsushima Y., Takamura N., Imazawa T., Hayashi Y. Dose-response studies on the carcinogenicity of potassium bromate in F344 rats after long-term oral administration. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1986 Oct;77(4):977–982. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurokawa Y., Aoki S., Matsushima Y., Takamura N., Imazawa T., Hayashi Y. Dose-response studies on the carcinogenicity of potassium bromate in F344 rats after long-term oral administration. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1986 Oct;77(4):977–982. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurokawa Y., Matsushima Y., Takamura N., Imazawa T., Hayashi Y. Relationship between the duration of treatment and the incidence of renal cell tumors in male F344 rats administered potassium bromate. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1987 Apr;78(4):358–364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurokawa Y., Matsushima Y., Takamura N., Imazawa T., Hayashi Y. Relationship between the duration of treatment and the incidence of renal cell tumors in male F344 rats administered potassium bromate. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1987 Apr;78(4):358–364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. P., Chromey N. C., Culik R., Barnes J. R., Schneider P. W. Toxicity of N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone (NMP): teratogenic, subchronic, and two-year inhalation studies. Fundam Appl Toxicol. 1987 Aug;9(2):222–235. doi: 10.1016/0272-0590(87)90045-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard T. B., Graichen M. E., Popp J. A. Dinitrotoluene isomer-specific hepatocarcinogenesis in F344 rats. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1987 Dec;79(6):1313–1319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard T. B., Graichen M. E., Popp J. A. Dinitrotoluene isomer-specific hepatocarcinogenesis in F344 rats. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1987 Dec;79(6):1313–1319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard T. B., Graichen M. E., Popp J. A. Dinitrotoluene isomer-specific hepatocarcinogenesis in F344 rats. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1987 Dec;79(6):1313–1319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lijinsky W., Kovatch R. M. Carcinogenesis by nitrosohydroxyethylurea and nitrosomethoxyethylurea in F344 rats. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1988 Feb;79(2):181–186. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.1988.tb01575.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lijinsky W., Kovatch R. M. Chronic toxicity study of cyclohexanone in rats and mice. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1986 Oct;77(4):941–949. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lijinsky W., Kovatch R. M., Riggs C. W. Carcinogenesis by nitrosodialkylamines and azoxyalkanes given by gavage to rats and hamsters. Cancer Res. 1987 Aug 1;47(15):3968–3972. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lijinsky W., Kovatch R. M., Riggs C. W., Walters P. T. Dose-response study with N-nitrosomorpholine in drinking water of F-344 rats. Cancer Res. 1988 Apr 15;48(8):2089–2095. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lijinsky W., Kovatch R. M., Singer S. S. Carcinogenesis in F-344 rats induced by nitrosohydroxyalkyl-chloroethylureas. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 1986;112(3):221–228. doi: 10.1007/BF00395916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lijinsky W., Reuber M. D. Chronic carcinogenesis studies of acrolein and related compounds. Toxicol Ind Health. 1987 Sep;3(3):337–345. doi: 10.1177/074823378700300306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lijinsky W., Reuber M. D. Pathologic effects of chronic administration of hydrochlorothiazide, with and without sodium nitrite, to F344 rats. Toxicol Ind Health. 1987 Sep;3(3):413–422. doi: 10.1177/074823378700300313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda T., Sano N., Togei K., Shibata M., Izumi K., Otsuka H. Lack of carcinogenicity of phenytoin in (C57BL/6 x C3H)F1 mice. J Toxicol Environ Health. 1988;24(1):111–119. doi: 10.1080/15287398809531144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maekawa A., Matsuoka C., Onodera H., Tanigawa H., Furuta K., Kanno J., Jang J. J., Hayashi Y., Ogiu T. Lack of carcinogenicity of tartrazine (FD & C Yellow No. 5) in the F344 rat. Food Chem Toxicol. 1987 Dec;25(12):891–896. doi: 10.1016/0278-6915(87)90281-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maekawa A., Matsuoka C., Onodera H., Tanigawa H., Furuta K., Kanno J., Jang J. J., Hayashi Y., Ogiu T. Lack of carcinogenicity of tartrazine (FD & C Yellow No. 5) in the F344 rat. Food Chem Toxicol. 1987 Dec;25(12):891–896. doi: 10.1016/0278-6915(87)90281-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maltoni C., Ciliberti A., Cotti G., Perino G. Long-term carcinogenicity bioassays on acrylonitrile administered by inhalation and by ingestion to Sprague-Dawley rats. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;534:179–202. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb30111.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maltoni C., Ciliberti A., Cotti G., Perino G. Long-term carcinogenicity bioassays on acrylonitrile administered by inhalation and by ingestion to Sprague-Dawley rats. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;534:179–202. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb30111.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maltoni C., Conti B., Perino G., Di Maio V. Further evidence of benzene carcinogenicity. Results on Wistar rats and Swiss mice treated by ingestion. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;534:412–426. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb30131.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maltoni C., Conti B., Perino G., Di Maio V. Further evidence of benzene carcinogenicity. Results on Wistar rats and Swiss mice treated by ingestion. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;534:412–426. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb30131.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maltoni C., Cotti G. Carcinogenicity of vinyl chloride in Sprague-Dawley rats after prenatal and postnatal exposure. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;534:145–159. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb30108.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maltoni C., Cotti G. Carcinogenicity of vinyl chloride in Sprague-Dawley rats after prenatal and postnatal exposure. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;534:145–159. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb30108.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maltoni C., Cotti G., Perino G. Long-term carcinogenicity bioassays on methylene chloride administered by ingestion to Sprague-Dawley rats and Swiss mice and by inhalation to Sprague-Dawley rats. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;534:352–366. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb30122.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maltoni C., Lefemine G., Tovoli D., Perino G. Long-term carcinogenicity bioassays on three chlorofluorocarbons (trichlorofluoromethane, FC11; dichlorodifluoromethane, FC12; chlorodifluoromethane, FC22) administered by inhalation to Sprague-Dawley rats and Swiss mice. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;534:261–282. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb30116.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maltoni C., Lefemine G., Tovoli D., Perino G. Long-term carcinogenicity bioassays on three chlorofluorocarbons (trichlorofluoromethane, FC11; dichlorodifluoromethane, FC12; chlorodifluoromethane, FC22) administered by inhalation to Sprague-Dawley rats and Swiss mice. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;534:261–282. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb30116.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maltoni C., Lefemine G., Tovoli D., Perino G. Long-term carcinogenicity bioassays on three chlorofluorocarbons (trichlorofluoromethane, FC11; dichlorodifluoromethane, FC12; chlorodifluoromethane, FC22) administered by inhalation to Sprague-Dawley rats and Swiss mice. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;534:261–282. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb30116.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markiewicz V. R., Saunders L. Z., Geus R. J., Payne B. J., Hook J. B. Carcinogenicity study of auranofin, an orally administered gold compound, in mice. Fundam Appl Toxicol. 1988 Aug;11(2):277–284. doi: 10.1016/0272-0590(88)90152-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markiewicz V. R., Saunders L. Z., Geus R. J., Payne B. J., Hook J. B. Carcinogenicity study of auranofin, an orally administered gold compound, in mice. Fundam Appl Toxicol. 1988 Aug;11(2):277–284. doi: 10.1016/0272-0590(88)90152-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCann J., Gold L. S., Horn L., McGill R., Graedel T. E., Kaldor J. Statistical analysis of Salmonella test data and comparison to results of animal cancer tests. Mutat Res. 1988 May-Aug;205(1-4):183–195. doi: 10.1016/0165-1218(88)90017-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McManus B. M., Toth B., Patil K. D. Aortic rupture and aortic smooth muscle tumors in mice. Induction by p-hydrazinobenzoic acid hydrochloride of the cultivated mushroom Agaricus bisporus. Lab Invest. 1987 Jul;57(1):78–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meakawa A., Onodera H., Tanigawa H., Furuta K., Kanno J., Matsuoka C., Ogiu T., Hayashi Y. Long-term studies on carcinogenicity and promoting effect of phenylbutazone in DONRYU rats. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1987 Sep;79(3):577–584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirvish S. S., Weisenburger D. D., Salmasi S., Kaplan P. A. Carcinogenicity of 1-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-nitrosourea and 3-nitroso-2-oxazolidinone administered in drinking water to male MRC-Wistar rats: induction of bone, hematopoietic, intestinal, and liver tumors. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1987 Feb;78(2):387–393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizutani T., Mitsuoka T. Effect of dietary phenobarbital on spontaneous hepatic tumorigenesis in germfree C3H/He male mice. Cancer Lett. 1988 Apr;39(3):233–237. doi: 10.1016/0304-3835(88)90065-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizutani T., Mitsuoka T. Effect of dietary phenobarbital on spontaneous hepatic tumorigenesis in germfree C3H/He male mice. Cancer Lett. 1988 Apr;39(3):233–237. doi: 10.1016/0304-3835(88)90065-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori H., Sugie S., Yoshimi N., Kuniyasu T., Iwata H., Kawai K., Hamasaki T. Potential carcinogenicity of 5,6-dimethoxysterigmatocystin in rats. Carcinogenesis. 1988 Jun;9(6):1039–1042. doi: 10.1093/carcin/9.6.1039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori H., Sugie S., Yoshimi N., Kuniyasu T., Iwata H., Kawai K., Hamasaki T. Potential carcinogenicity of 5,6-dimethoxysterigmatocystin in rats. Carcinogenesis. 1988 Jun;9(6):1039–1042. doi: 10.1093/carcin/9.6.1039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nera E. A., Iverson F., Lok E., Armstrong C. L., Karpinski K., Clayson D. B. A carcinogenesis reversibility study of the effects of butylated hydroxyanisole on the forestomach and urinary bladder in male Fischer 344 rats. Toxicology. 1988 Dec 30;53(2-3):251–268. doi: 10.1016/0300-483x(88)90218-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nera E. A., Iverson F., Lok E., Armstrong C. L., Karpinski K., Clayson D. B. A carcinogenesis reversibility study of the effects of butylated hydroxyanisole on the forestomach and urinary bladder in male Fischer 344 rats. Toxicology. 1988 Dec 30;53(2-3):251–268. doi: 10.1016/0300-483x(88)90218-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nitschke K. D., Burek J. D., Bell T. J., Kociba R. J., Rampy L. W., McKenna M. J. Methylene chloride: a 2-year inhalation toxicity and oncogenicity study in rats. Fundam Appl Toxicol. 1988 Jul;11(1):48–59. doi: 10.1016/0272-0590(88)90269-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonoyama T., Fullerton F., Reznik G., Bucci T. J., Ward J. M. Mouse hepatoblastomas: a histologic, ultrastructural, and immunohistochemical study. Vet Pathol. 1988 Jul;25(4):286–296. doi: 10.1177/030098588802500407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonoyama T., Fullerton F., Reznik G., Bucci T. J., Ward J. M. Mouse hepatoblastomas: a histologic, ultrastructural, and immunohistochemical study. Vet Pathol. 1988 Jul;25(4):286–296. doi: 10.1177/030098588802500407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohgaki H., Hasegawa H., Suenaga M., Sato S., Takayama S., Sugimura T. Carcinogenicity in mice of a mutagenic compound, 2-amino-3,8-dimethylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoxaline (MeIQx) from cooked foods. Carcinogenesis. 1987 May;8(5):665–668. doi: 10.1093/carcin/8.5.665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohgaki H., Hasegawa H., Suenaga M., Sato S., Takayama S., Sugimura T. Carcinogenicity in mice of a mutagenic compound, 2-amino-3,8-dimethylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoxaline (MeIQx) from cooked foods. Carcinogenesis. 1987 May;8(5):665–668. doi: 10.1093/carcin/8.5.665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen P. E., Glaister J. R., Gaunt I. F., Pullinger D. H. Inhalation toxicity studies with 1,3-butadiene. 3. Two year toxicity/carcinogenicity study in rats. Am Ind Hyg Assoc J. 1987 May;48(5):407–413. doi: 10.1080/15298668791384959. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Port C. D., Dodd D. C., Deslex P., Regnier B., Sanders P., Indacochea-Redmond N. Twenty-one-month evaluation of misoprostol for carcinogenicity in CD-1 mice. Toxicol Pathol. 1987;15(2):134–142. doi: 10.1177/019262338701500202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Port C. D., Dodd D. C., Deslex P., Regnier B., Sanders P., Indacochea-Redmond N. Twenty-one-month evaluation of misoprostol for carcinogenicity in CD-1 mice. Toxicol Pathol. 1987;15(2):134–142. doi: 10.1177/019262338701500202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quast J. F., Calhoun L. L., Frauson L. E. 1,1,1-trichloroethane formulation: a chronic inhalation toxicity and oncogenicity study in Fischer 344 rats and B6c3F1 mice. Fundam Appl Toxicol. 1988 Nov;11(4):611–625. doi: 10.1016/0272-0590(88)90125-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quast J. F., Calhoun L. L., Frauson L. E. 1,1,1-trichloroethane formulation: a chronic inhalation toxicity and oncogenicity study in Fischer 344 rats and B6c3F1 mice. Fundam Appl Toxicol. 1988 Nov;11(4):611–625. doi: 10.1016/0272-0590(88)90125-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao M. S., Dwivedi R. S., Subbarao V., Reddy J. K. Induction of peroxisome proliferation and hepatic tumours in C57BL/6N mice by ciprofibrate, a hypolipidaemic compound. Br J Cancer. 1988 Jul;58(1):46–51. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1988.159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao M. S., Dwivedi R. S., Subbarao V., Reddy J. K. Induction of peroxisome proliferation and hepatic tumours in C57BL/6N mice by ciprofibrate, a hypolipidaemic compound. Br J Cancer. 1988 Jul;58(1):46–51. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1988.159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao M. S., Usuda N., Subbarao V., Reddy J. K. Absence of gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase activity in neoplastic lesions induced in the liver of male F-344 rats by di-(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate, a peroxisome proliferator. Carcinogenesis. 1987 Sep;8(9):1347–1350. doi: 10.1093/carcin/8.9.1347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivenson A., Hoffmann D., Prokopczyk B., Amin S., Hecht S. S. Induction of lung and exocrine pancreas tumors in F344 rats by tobacco-specific and Areca-derived N-nitrosamines. Cancer Res. 1988 Dec 1;48(23):6912–6917. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivenson A., Hoffmann D., Prokopczyk B., Amin S., Hecht S. S. Induction of lung and exocrine pancreas tumors in F344 rats by tobacco-specific and Areca-derived N-nitrosamines. Cancer Res. 1988 Dec 1;48(23):6912–6917. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivenson A., Hoffmann D., Prokopczyk B., Amin S., Hecht S. S. Induction of lung and exocrine pancreas tumors in F344 rats by tobacco-specific and Areca-derived N-nitrosamines. Cancer Res. 1988 Dec 1;48(23):6912–6917. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenkrantz H., Fleischman R. W. In vivo carcinogenesis assay of DL-methadone.HCl in rodents. Fundam Appl Toxicol. 1988 Nov;11(4):640–651. doi: 10.1016/0272-0590(88)90127-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenkrantz H., Fleischman R. W. In vivo carcinogenesis assay of DL-methadone.HCl in rodents. Fundam Appl Toxicol. 1988 Nov;11(4):640–651. doi: 10.1016/0272-0590(88)90127-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenkrantz H., Fleischman R. W. In vivo carcinogenesis assay of L-alpha-acetylmethadol.HCl in rodents. Fundam Appl Toxicol. 1988 Nov;11(4):626–639. doi: 10.1016/0272-0590(88)90126-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soffritti M., Maltoni C., Maffei F., Biagi R. Formaldehyde: an experimental multipotential carcinogen. Toxicol Ind Health. 1989 Oct;5(5):699–730. doi: 10.1177/074823378900500510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soffritti M., Maltoni C., Maffei F., Biagi R. Formaldehyde: an experimental multipotential carcinogen. Toxicol Ind Health. 1989 Oct;5(5):699–730. doi: 10.1177/074823378900500510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenbäck F., Weisburger J. H., Williams G. M. Effect of lifetime administration of dimethylaminoethanol on longevity, aging changes, and cryptogenic neoplasms in C3H mice. Mech Ageing Dev. 1988 Feb;42(2):129–138. doi: 10.1016/0047-6374(88)90068-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenbäck F., Weisburger J. H., Williams G. M. Effect of lifetime administration of dimethylaminoethanol on longevity, aging changes, and cryptogenic neoplasms in C3H mice. Mech Ageing Dev. 1988 Feb;42(2):129–138. doi: 10.1016/0047-6374(88)90068-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Togei K., Sano N., Maeda T., Shibata M., Otsuka H. Carcinogenicity of bucetin in (C57BL/6 X C3H)F1 mice. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1987 Nov;79(5):1151–1158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Togei K., Sano N., Maeda T., Shibata M., Otsuka H. Carcinogenicity of bucetin in (C57BL/6 X C3H)F1 mice. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1987 Nov;79(5):1151–1158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toth B. Carcinogenesis by N2-[gamma-L(+)-glutamyl]-4-carboxyphenylhydrazine of Agaricus bisporus in mice. Anticancer Res. 1986 Sep-Oct;6(5):917–920. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toth B. Carcinogenesis by N2-[gamma-L(+)-glutamyl]-4-carboxyphenylhydrazine of Agaricus bisporus in mice. Anticancer Res. 1986 Sep-Oct;6(5):917–920. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toth B., Raha C. R. Carcinogenesis by pentanal methylformylhydrazone of Gyromitra esculenta in mice. Mycopathologia. 1987 May;98(2):83–89. doi: 10.1007/BF00437293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trochimowicz H. J., Rusch G. M., Chiu T., Wood C. K. Chronic inhalation toxicity/carcinogenicity study in rats exposed to fluorocarbon 113 (FC-113). Fundam Appl Toxicol. 1988 Jul;11(1):68–75. doi: 10.1016/0272-0590(88)90271-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker R. F., Weideman C. A., Wheeldon E. B. Reduced disease in aged rats treated chronically with ibopamine, a catecholaminergic drug. Neurobiol Aging. 1988 May-Jun;9(3):291–301. doi: 10.1016/s0197-4580(88)80068-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff G. L., Roberts D. W., Morrissey R. L., Greenman D. L., Allen R. R., Campbell W. L., Bergman H., Nesnow S., Frith C. H. Tumorigenic responses to lindane in mice: potentiation by a dominant mutation. Carcinogenesis. 1987 Dec;8(12):1889–1897. doi: 10.1093/carcin/8.12.1889. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff G. L., Roberts D. W., Morrissey R. L., Greenman D. L., Allen R. R., Campbell W. L., Bergman H., Nesnow S., Frith C. H. Tumorigenic responses to lindane in mice: potentiation by a dominant mutation. Carcinogenesis. 1987 Dec;8(12):1889–1897. doi: 10.1093/carcin/8.12.1889. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woutersen R. A., Appelman L. M., Van Garderen-Hoetmer A., Feron V. J. Inhalation toxicity of acetaldehyde in rats. III. Carcinogenicity study. Toxicology. 1986 Oct;41(2):213–231. doi: 10.1016/0300-483x(86)90201-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woutersen R. A., Feron V. J. Inhalation toxicity of acetaldehyde in rats. IV. Progression and regression of nasal lesions after discontinuation of exposure. Toxicology. 1987 Dec 14;47(3):295–305. doi: 10.1016/0300-483x(87)90059-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woutersen R. A., Feron V. J. Inhalation toxicity of acetaldehyde in rats. IV. Progression and regression of nasal lesions after discontinuation of exposure. Toxicology. 1987 Dec 14;47(3):295–305. doi: 10.1016/0300-483x(87)90059-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


