Abstract
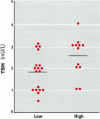
Animal studies have shown that dioxins influence plasma thyroid hormone concentrations. To investigate the effect of chlorinated dioxins and furans on thyroid hormone concentrations in humans, we studied 38 healthy breast-fed infants. The study population was divided into two groups according to the dioxin concentrations in milk fat of their mothers. Blood samples were taken at birth and at the ages of 1 and 11 weeks. At birth a tendency to higher total thyroxine (tT4) concentrations was found in the high exposure group. At the ages of 1 and 11 weeks the increase of mean tT4 concentrations and tT4/thyroxine-binding globulin ratios in the high exposure group reached significance as compared to the low exposure group. At birth and 1 week after birth, mean thyrotropin (TSH) concentrations were similar in both groups, but at the age of 11 weeks the mean TSH concentrations were significantly higher in the high exposure group. We postulate that the observed plasma tT4 elevation in infants exposed to dioxins before and after birth is the result of an effect on the thyroid hormone regulatory system.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bastomsky C. H. Enhanced thyroxine metabolism and high uptake goiters in rats after a single dose of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Endocrinology. 1977 Jul;101(1):292–296. doi: 10.1210/endo-101-1-292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bastomsky C. H. The biliary excretion of thyroxine and glucuronic acid conjugate in normal and Gunn rats. Endocrinology. 1973 Jan;92(1):35–40. doi: 10.1210/endo-92-1-35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beetstra J. B., van Engelen J. G., Karels P., van der Hoek H. J., de Jong M., Docter R., Krenning E. P., Hennemann G., Brouwer A., Visser T. J. Thyroxine and 3,3',5-triiodothyronine are glucuronidated in rat liver by different uridine diphosphate-glucuronyltransferases. Endocrinology. 1991 Feb;128(2):741–746. doi: 10.1210/endo-128-2-741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birrell J., Frost G. J., Parkin J. M. The development of children with congenital hypothyroidism. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1983 Aug;25(4):512–519. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1983.tb13798.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brouwer A. Inhibition of thyroid hormone transport in plasma of rats by polychlorinated biphenyls. Arch Toxicol Suppl. 1989;13:440–445. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74117-3_87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chopra I. J. A radioimmunoassay for measurement of thyroxine in unextracted serum. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1972 Jun;34(6):938–947. doi: 10.1210/jcem-34-6-938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorski J. R., Rozman K. Dose-response and time course of hypothyroxinemia and hypoinsulinemia and characterization of insulin hypersensitivity in 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD)-treated rats. Toxicology. 1987 Jun;44(3):297–307. doi: 10.1016/0300-483x(87)90031-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn H. B., Jr, Spiekerman A. M., Otto W. R., Hossalla D. E. Thyroid function tests in neonates fed human milk. Am J Dis Child. 1983 Mar;137(3):220–222. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1983.02140290012003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry E. C., Gasiewicz T. A. Changes in thyroid hormones and thyroxine glucuronidation in hamsters compared with rats following treatment with 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1987 Jun 30;89(2):165–174. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(87)90037-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson J. L., Jacobson S. W., Humphrey H. E. Effects of in utero exposure to polychlorinated biphenyls and related contaminants on cognitive functioning in young children. J Pediatr. 1990 Jan;116(1):38–45. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)81642-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones M. K., Weisenburger W. P., Sipes I. G., Russell D. H. Circadian alterations in prolactin, corticosterone, and thyroid hormone levels and down-regulation of prolactin receptor activity by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1987 Feb;87(2):337–350. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(87)90295-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelling C. K., Menahan L. A., Peterson R. E. Hepatic indices of thyroid status in rats treated with 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Biochem Pharmacol. 1987 Jan 15;36(2):283–291. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(87)90702-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen P. R. Direct immunoassay of triiodothyronine in human serum. J Clin Invest. 1972 Aug;51(8):1939–1949. doi: 10.1172/JCI107000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKinney J. D., Chae K., Oatley S. J., Blake C. C. Molecular interactions of toxic chlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans with thyroxine binding prealbumin. J Med Chem. 1985 Mar;28(3):375–381. doi: 10.1021/jm00381a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKinney J. D., Fawkes J., Jordan S., Chae K., Oatley S., Coleman R. E., Briner W. 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) as a potent and persistent thyroxine agonist: a mechanistic model for toxicity based on molecular reactivity. Environ Health Perspect. 1985 Sep;61:41–53. doi: 10.1289/ehp.856141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meberg A., Marstein S. Smoking during pregnancy--effects on the fetal thyroid function. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1986 Sep;75(5):762–766. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1986.tb10287.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagayama J., Tokudome S., Kuratsune M., Masuda Y. Transfer of polychlorinated dibenzofurans to the foetuses and offspring of mice. Food Cosmet Toxicol. 1980 Apr;18(2):153–157. doi: 10.1016/0015-6264(80)90069-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nau H., Bass R. Transfer of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) to the mouse embryo and fetus. Toxicology. 1981;20(4):299–308. doi: 10.1016/0300-483x(81)90037-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson D. G., Jr, Hoffman R. E., Needham L. L., Roberts D. W., Bagby J. R., Pirkle J. L., Falk H., Sampson E. J., Houk V. N. 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin levels in adipose tissue of exposed and control persons in Missouri. An interim report. JAMA. 1986 Nov 21;256(19):2683–2686. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter C. L., Moore R. W., Inhorn S. L., Hagen T. C., Peterson R. E. Thyroid status and thermogenesis in rats treated with 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1986 Jun 15;84(1):45–55. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(86)90415-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter C. L., Moore R. W., Inhorn S. L., Hagen T. C., Peterson R. E. Thyroid status and thermogenesis in rats treated with 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1986 Jun 15;84(1):45–55. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(86)90415-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter C. L., Sipes I. G., Russell D. H. Hypothyroxinemia and hypothermia in rats in response to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin administration. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1983 Jun 15;69(1):89–95. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(83)90123-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogan W. J., Gladen B. C., McKinney J. D., Carreras N., Hardy P., Thullen J., Tinglestad J., Tully M. Neonatal effects of transplacental exposure to PCBs and DDE. J Pediatr. 1986 Aug;109(2):335–341. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(86)80397-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth W., Voorman R., Aust S. D. Activity of thyroid hormone-inducible enzymes following treatment with 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1988 Jan;92(1):65–74. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(88)90228-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth W., Voorman R., Aust S. D. Activity of thyroid hormone-inducible enzymes following treatment with 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1988 Jan;92(1):65–74. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(88)90228-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vijlder J. J., van Voorthuizen W. F., van Dijk J. E., Rijnberk A., Tegelaers W. H. Hereditary congenital goiter with thyroglobulin deficiency in a breed of goats. Endocrinology. 1978 Apr;102(4):1214–1222. doi: 10.1210/endo-102-4-1214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]