Abstract
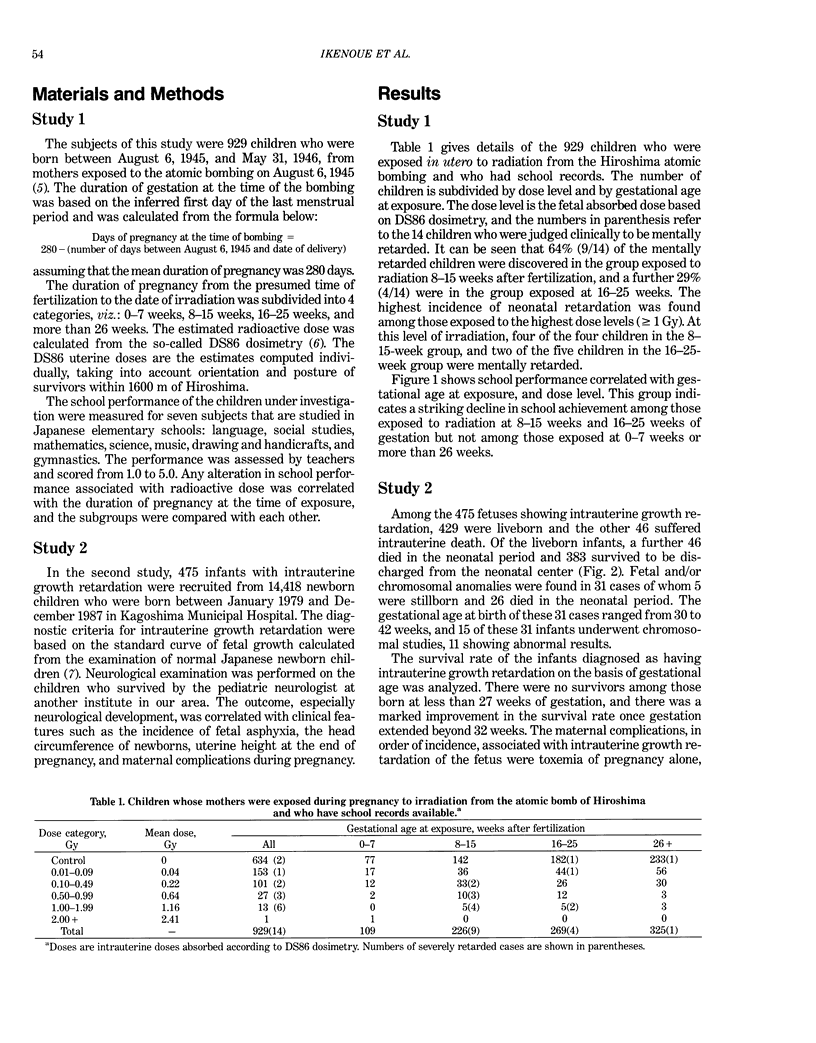
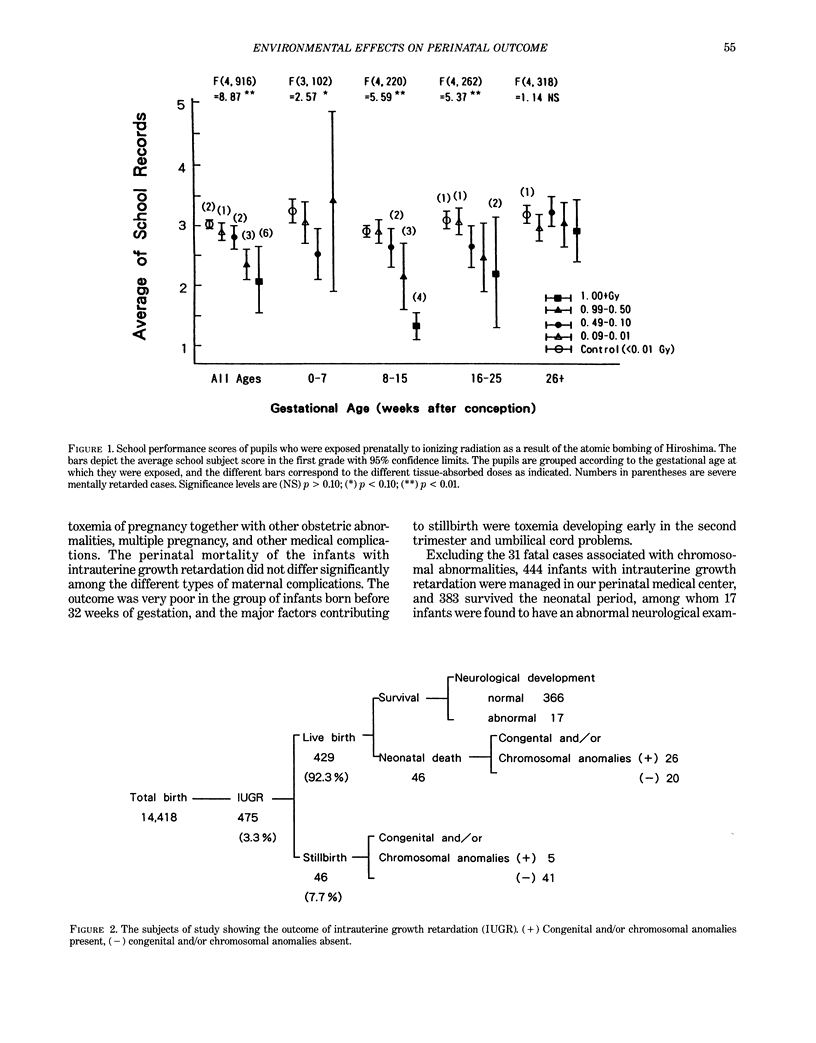
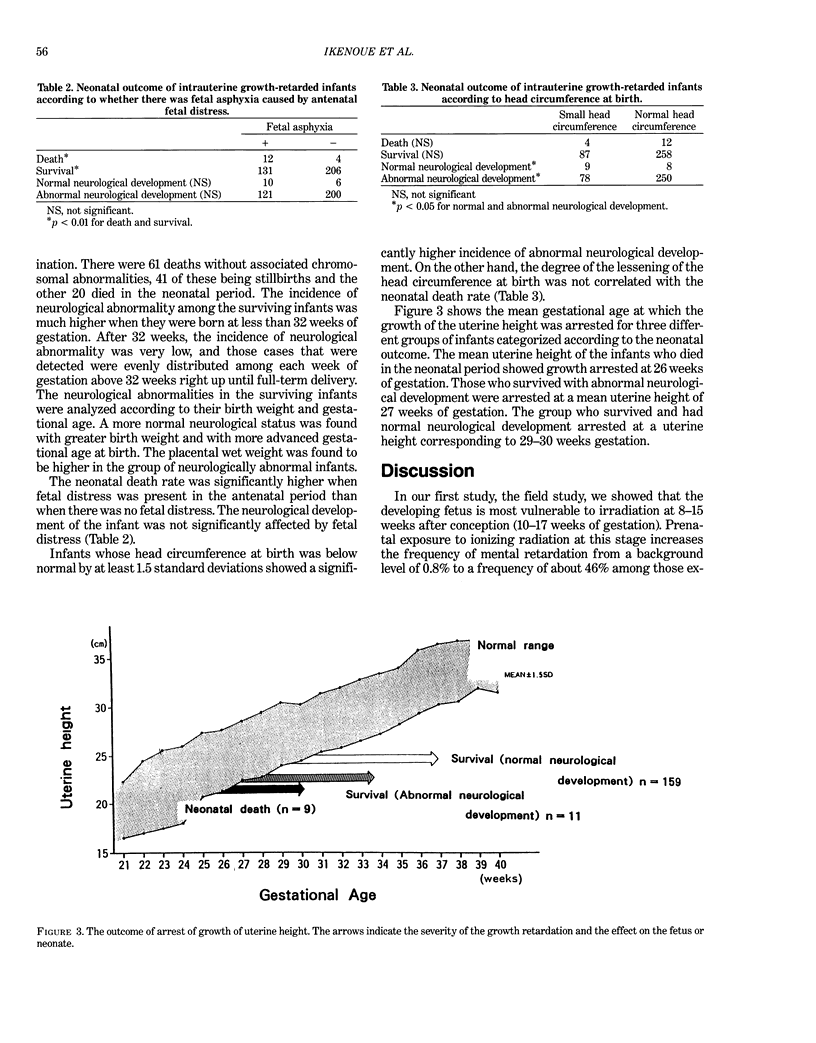
We performed two studies to investigate environmental factors in relation to neurological development in infants. The first, a field study, examined the elementary school performance of 929 children who were born from mothers exposed to the atomic bombing of Hiroshima, Japan, August 6, 1945. The most severe mental retardation was observed in the group exposed between 8 and 15 weeks following fertilization, and the second most severely damaged group was exposed between 16 and 25 weeks. The second, a clinical investigation, examined infants in the perinatal center who survived intrauterine growth retardation (IUGR). Those who survived with abnormal neurological development had a mean growth arrest corresponding to a uterine height of 27 weeks of gestation. This was at an earlier stage than those who survived with normal neurological development and had a mean growth arrest corresponding to 29-30 weeks of gestation. A smaller head circumference at birth was closely correlated with abnormal neurological sequelae. These results indicate that the brain development of the fetuses may have been affected by neurotoxic events similar to ionizing radiation. We emphasize the importance of avoiding neurotoxic stress to pregnant women when the fetus is in the critical period of neuronal development, before 27 weeks of gestational age.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Jones K. L., Chernoff G. F. Drugs and chemicals associated with intrauterine growth deficiency. J Reprod Med. 1978 Dec;21(6):365–370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr G. D. Organ dose estimates for the Japanese atomic-bomb survivors. Health Phys. 1979 Oct;37(4):487–508. doi: 10.1097/00004032-197910000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lechtig A., Yarbrough C., Delgado H., Habicht J. P., Martorell R., Klein R. E. Influence of maternal nutrition on birth weight. Am J Clin Nutr. 1975 Nov;28(11):1223–1233. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/28.11.1223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torres-Pereyra J. Emphasis on preventive perinatology: a suitable alternative for developing countries. Semin Perinatol. 1988 Oct;12(4):381–388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


