Abstract
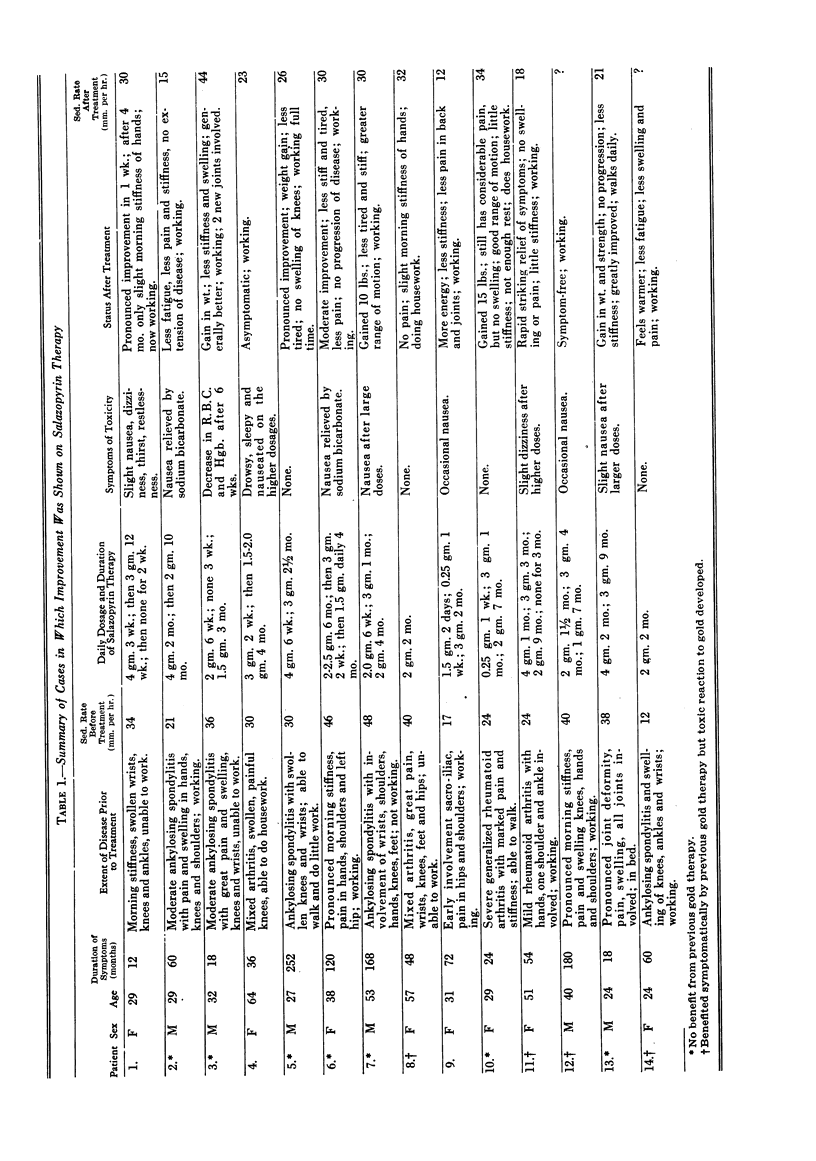
Thirty patients with rheumatoid arthritis were treated with Salazopyrin® for periods from two months to one year.
Fourteen patients were symptomatically relieved in varying degrees. This group included seven patients not previously benefited by gold therapy and four who had had toxic reaction to gold. The sedimentation rates tended to remain elevated in spite of symptomatic improvement. Extension of disease to joints not formerly involved appeared in only one patient under treatment.
Continuation of small dosage for long intervals seemed advantageous in the small number of patients treated in this study.
Fourteen patients were not relieved symptomatically by Salazopyrin, but they did not become worse. This group included eight patients with severe, advanced disease, six of whom had not been benefited by chrysotherapy.
In one patient there was a moderate reduction in erythrocyte count and in hemoglobin. One patient refused medication, claiming extreme nervousness.
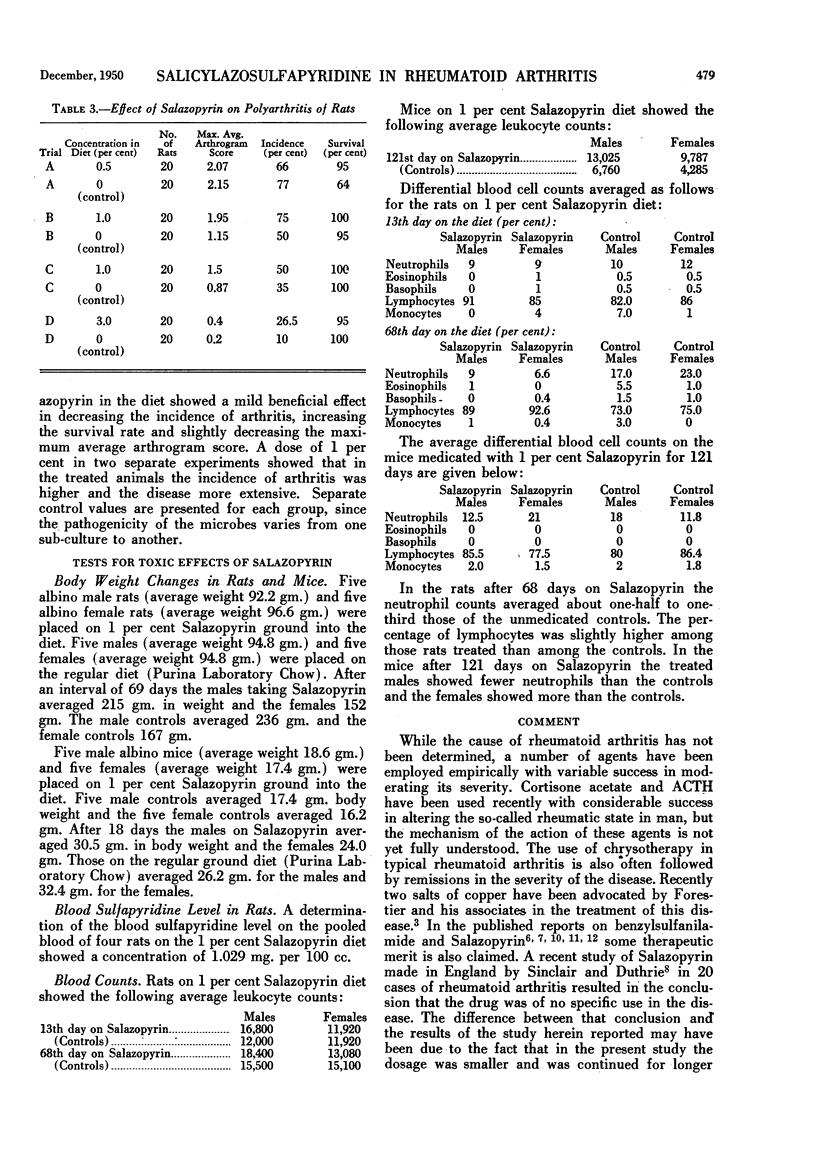
Salazopyrin is variably and comparatively poorly absorbed in man.
In experimental polyarthritis of rats, administration of 0.5 per cent Salazopyrin in the diet produced a slight beneficial effect, while 1 per cent made the infection worse. Changes in body weight and in leukocyte content in the blood of rats and mice showed Salazopyrin to have minimal toxic effect in these rodents.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Findlay G. M. Pleuropneumonia-Like Organisms and Arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1946 Sep;5(5):153–160. doi: 10.1136/ard.5.5.153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARR L. J. A. The role of benzylsulfanilamide, other sulfonamides, epinephrine, and calcium in rheumatoid and infective arthritis. Stanford Med Bull. 1949 Nov;7(4):152–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabin A. B., Warren J. THE THERAPEUTIC EFFECTIVENESS OF A PRACTICALLY NONTOXIC NEW COMPOUND (CALCIUM AUROTHIOMALATE) IN EXPERIMENTAL, PROLIFERATIVE, CHRONIC ARTHRITIS OF MICE. Science. 1940 Dec 6;92(2397):535–536. doi: 10.1126/science.92.2397.535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinclair R. J., Duthie J. J. Salazopyrin in the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1949 Sep;8(3):226–231. doi: 10.1136/ard.8.3.226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


