Abstract
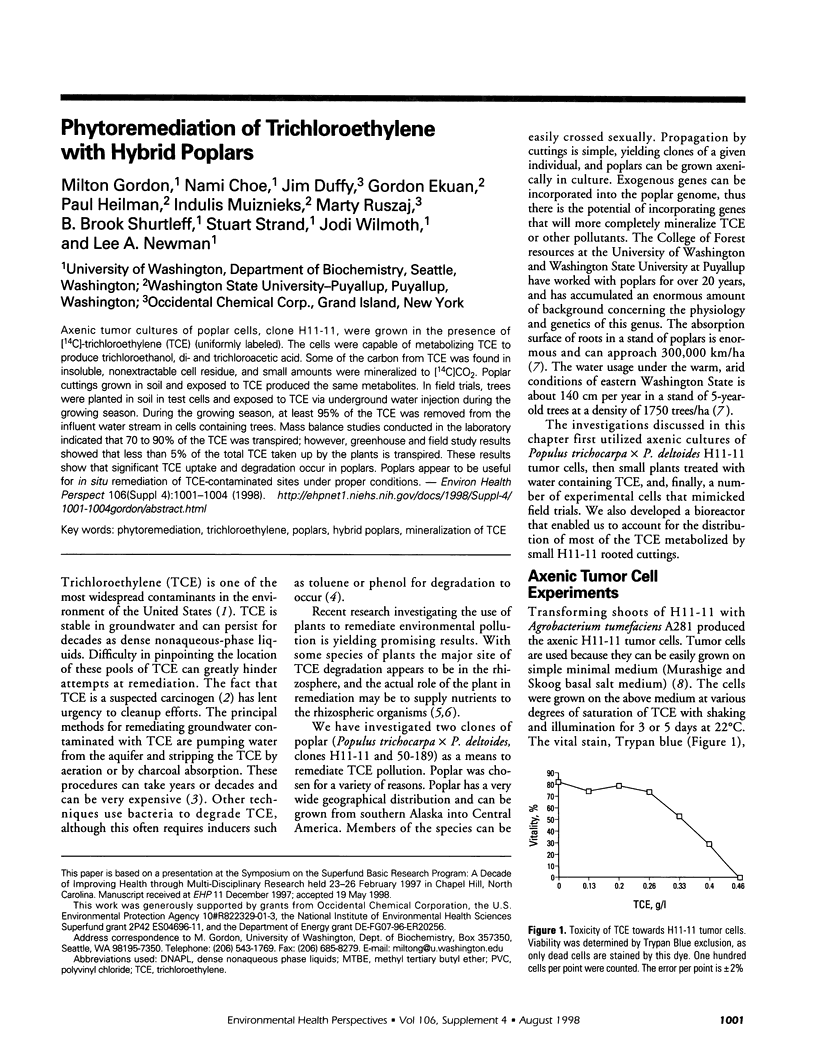
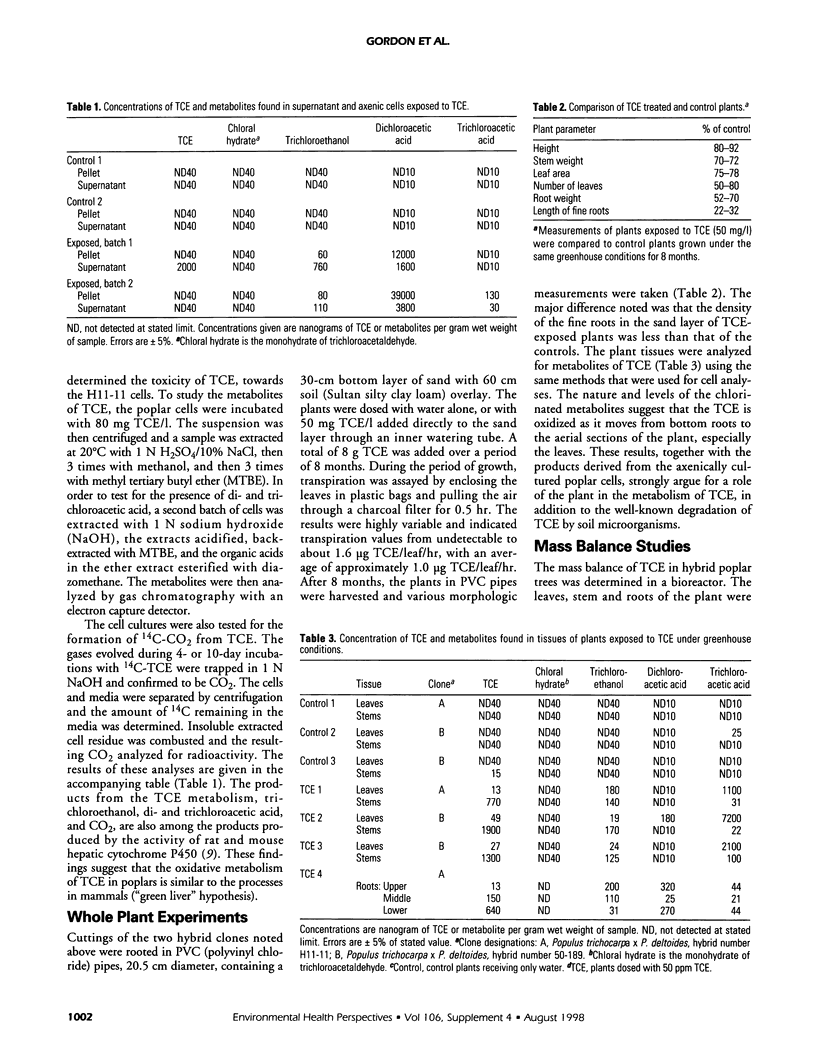
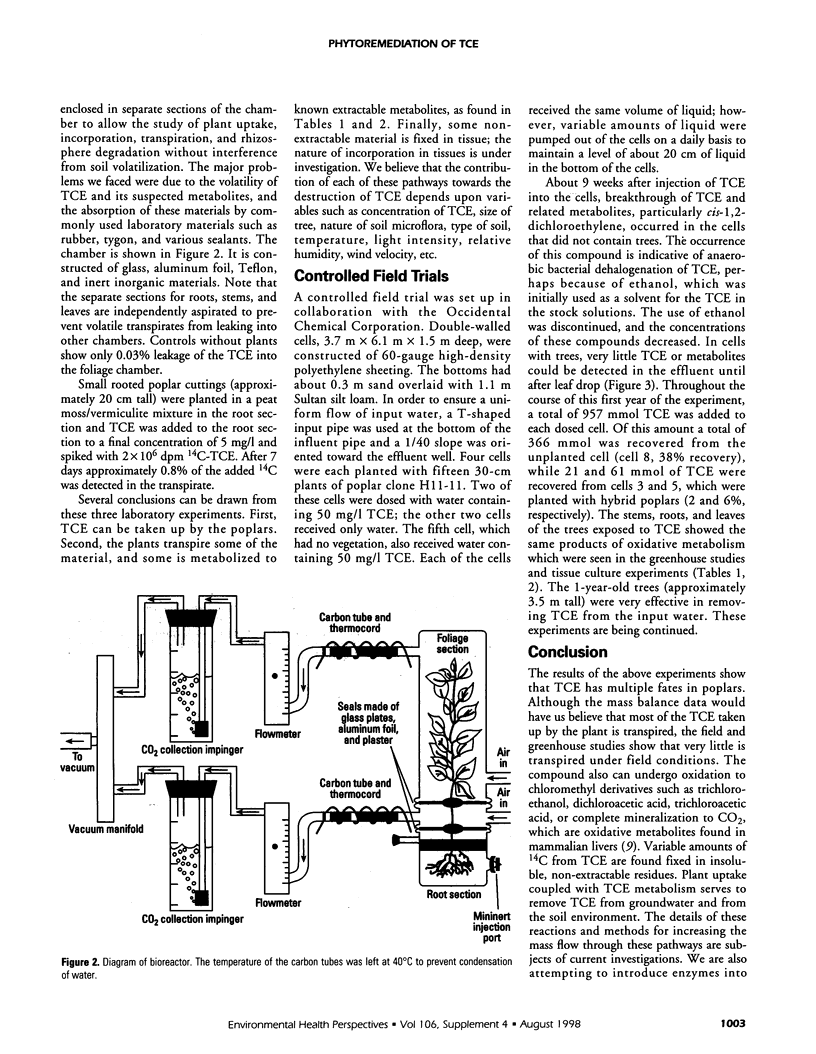
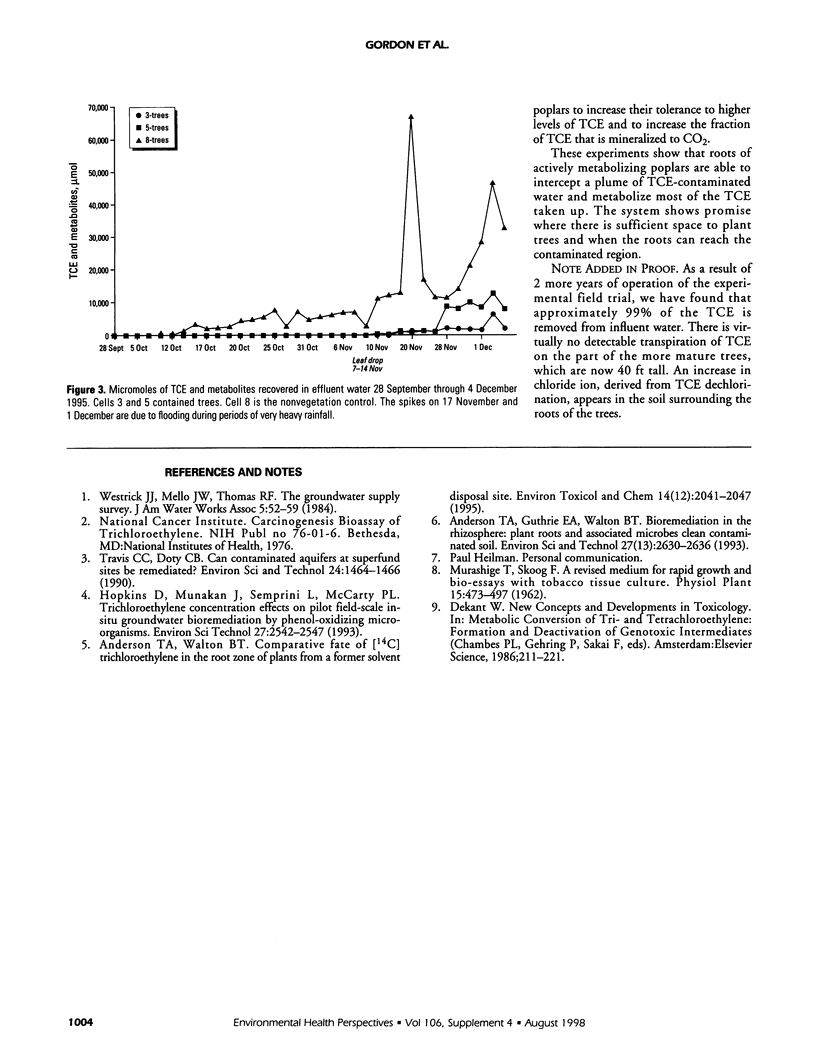
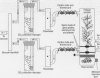
Axenic tumor cultures of poplar cells, clone H11-11, were grown in the presence of [14C]-trichloroethylene (TCE) (uniformly labeled). The cells were capable of metabolizing TCE to produce trichloroethanol, di- and trichloroacetic acid. Some of the carbon from TCE was found in insoluble, nonextractable cell residue, and small amounts were mineralized to [14C]CO2. Poplar cuttings grown in soil and exposed to TCE produced the same metabolites. In field trials, trees were planted in soil in test cells and exposed to TCE via underground water injection during the growing season. During the growing season, at least 95% of the TCE was removed from the influent water stream in cells containing trees. Mass balance studies conducted in the laboratory indicated that 70 to 90% of the TCE was transpired; however, greenhouse and field study results showed that less than 5% of the total TCE taken up by the plants is transpired. These results show that significant TCE uptake and degradation occur in poplars. Poplars appear to be useful for in situ remediation of TCE-contaminated sites under proper conditions.
Full text
PDF