Abstract
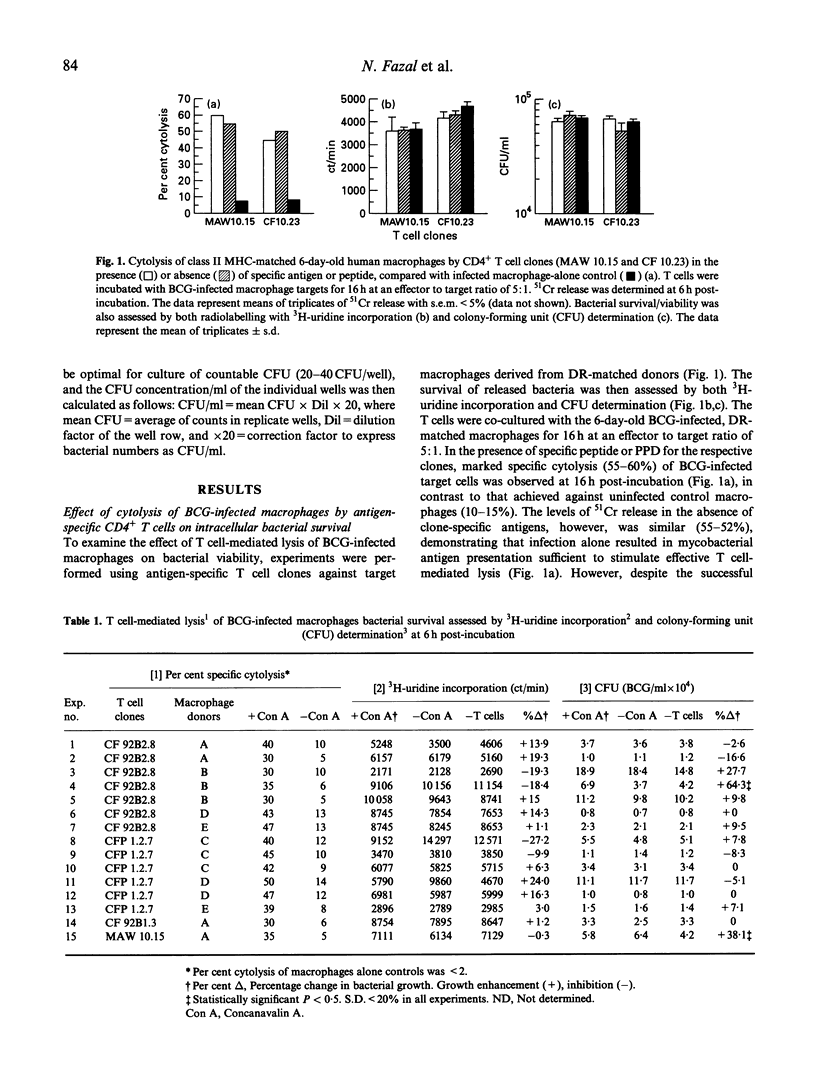
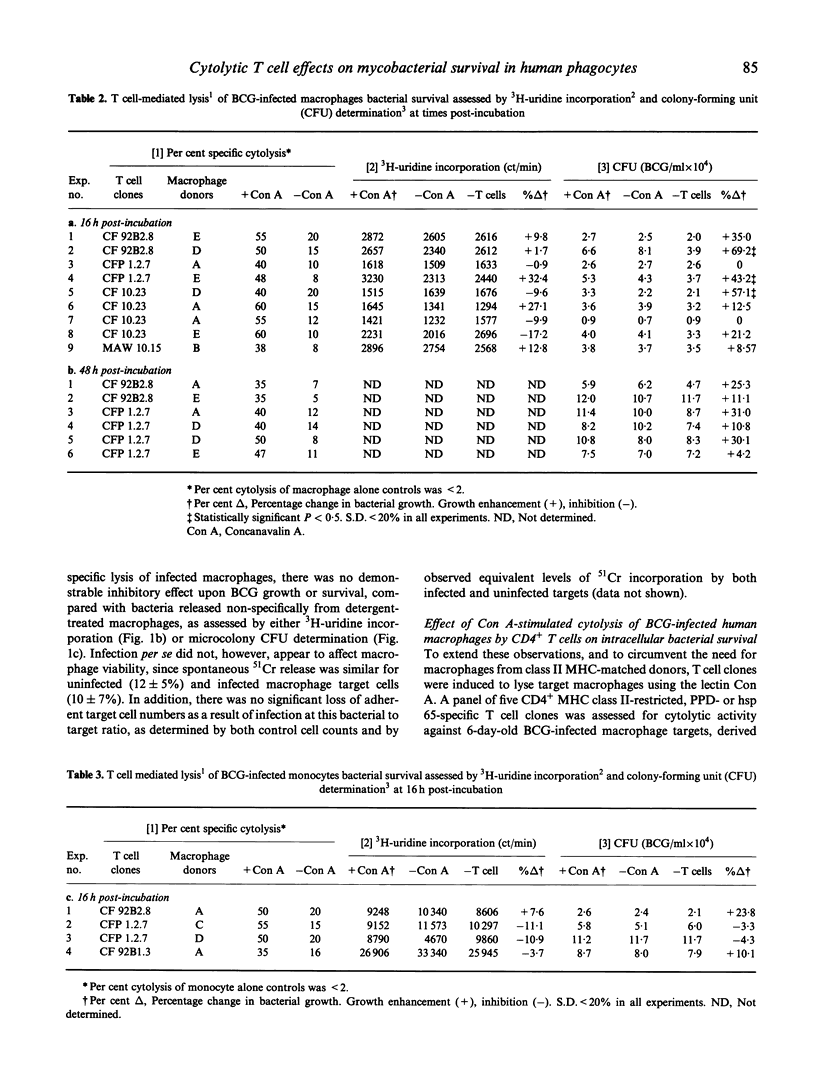
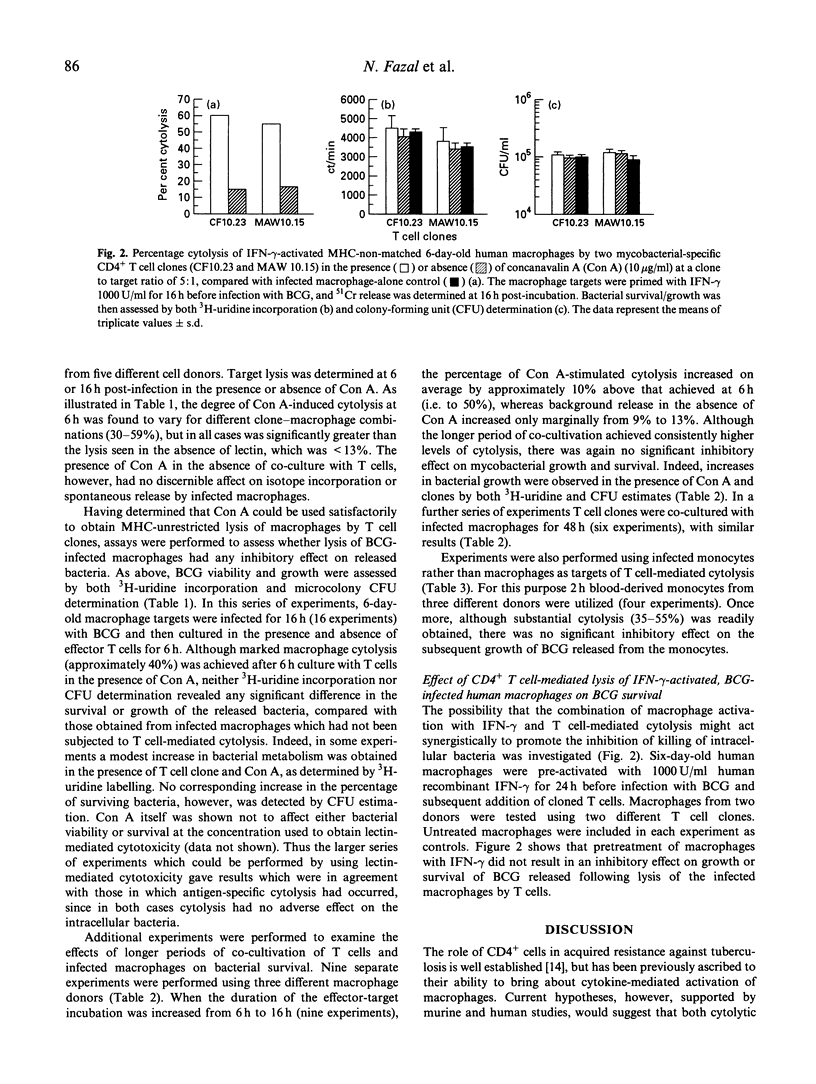
Human CD4+, mycobacteria-specific, cytolytic T cell clones were used to lyse BCG-infected macrophages, and the effect on the subsequent growth and viability of the organisms was examined. The survival of released bacteria following cell lysis was assessed by both 3H-uridine labelling and colony-forming unit (CFU) estimation. The results indicate that even when effective antigen-specific or lectin-mediated cytolysis of the infected macrophages was achieved, there was no evidence for a direct mycobactericidal effect on the intracellular bacteria. This remained the case even if the period of co-culture of T cells and macrophages was extended up to 48 h. Pretreatment of the macrophages with interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) was not able to act together with T cell-mediated lysis to produce inhibition of mycobacterial growth.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ab B. K., Kiessling R., Van Embden J. D., Thole J. E., Kumararatne D. S., Pisa P., Wondimu A., Ottenhoff T. H. Induction of antigen-specific CD4+ HLA-DR-restricted cytotoxic T lymphocytes as well as nonspecific nonrestricted killer cells by the recombinant mycobacterial 65-kDa heat-shock protein. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Feb;20(2):369–377. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bermudez L. E. Production of transforming growth factor-beta by Mycobacterium avium-infected human macrophages is associated with unresponsiveness to IFN-gamma. J Immunol. 1993 Mar 1;150(5):1838–1845. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Libero G., Flesch I., Kaufmann S. H. Mycobacteria-reactive Lyt-2+ T cell lines. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Jan;18(1):59–66. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fazal N., Bartlett R., Lammas D. A., Kumararatne D. S. A comparison of the different methods available for determining BCG-macrophage interactions in vitro, including a new method of colony counting in broth. FEMS Microbiol Immunol. 1992 Dec;5(5-6):355–362. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1992.tb05921.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flesch I., Kaufmann S. H. Mycobacterial growth inhibition by interferon-gamma-activated bone marrow macrophages and differential susceptibility among strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 15;138(12):4408–4413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaston J. S., Life P. F., Jenner P. J., Colston M. J., Bacon P. A. Recognition of a mycobacteria-specific epitope in the 65-kD heat-shock protein by synovial fluid-derived T cell clones. J Exp Med. 1990 Mar 1;171(3):831–841. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.3.831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock G. E., Cohn Z. A., Kaplan G. The generation of antigen-specific, major histocompatibility complex-restricted cytotoxic T lymphocytes of the CD4+ phenotype. Enhancement by the cutaneous administration of interleukin 2. J Exp Med. 1989 Mar 1;169(3):909–919. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.3.909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh C. S., Macatonia S. E., Tripp C. S., Wolf S. F., O'Garra A., Murphy K. M. Development of TH1 CD4+ T cells through IL-12 produced by Listeria-induced macrophages. Science. 1993 Apr 23;260(5107):547–549. doi: 10.1126/science.8097338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan G., Sheftel G., Job C. K., Mathur N. K., Nath I., Cohn Z. A. Efficacy of a cell-mediated reaction to the purified protein derivative of tuberculin in the disposal of Mycobacterium leprae from human skin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):5210–5214. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.5210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann S. H. CD8+ T lymphocytes in intracellular microbial infections. Immunol Today. 1988 Jun;9(6):168–174. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(88)91292-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann S. H. Immunity to intracellular bacteria. Annu Rev Immunol. 1993;11:129–163. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.11.040193.001021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann S. H., Rodewald H. R., Hug E., De Libero G. Cloned Listeria monocytogenes specific non-MHC-restricted Lyt-2+ T cells with cytolytic and protective activity. J Immunol. 1988 May 1;140(9):3173–3179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumararatne D. S., Pithie A. S., Drysdale P., Gaston J. S., Kiessling R., Iles P. B., Ellis C. J., Innes J., Wise R. Specific lysis of mycobacterial antigen-bearing macrophages by class II MHC-restricted polyclonal T cell lines in healthy donors or patients with tuberculosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 Jun;80(3):314–323. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb03287.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorgat F., Keraan M. M., Lukey P. T., Ress S. R. Evidence for in vivo generation of cytotoxic T cells. PPD-stimulated lymphocytes from tuberculous pleural effusions demonstrate enhanced cytotoxicity with accelerated kinetics of induction. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1992 Feb;145(2 Pt 1):418–423. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/145.2_Pt_1.418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molloy A., Meyn P. A., Smith K. D., Kaplan G. Recognition and destruction of Bacillus Calmette-Guerin-infected human monocytes. J Exp Med. 1993 Jun 1;177(6):1691–1698. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.6.1691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottenhoff T. H., Ab B. K., Van Embden J. D., Thole J. E., Kiessling R. The recombinant 65-kD heat shock protein of Mycobacterium bovis Bacillus Calmette-Guerin/M. tuberculosis is a target molecule for CD4+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes that lyse human monocytes. J Exp Med. 1988 Nov 1;168(5):1947–1952. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.5.1947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pithie A. D., Rahelu M., Kumararatne D. S., Drysdale P., Gaston J. S., Iles P. B., Innes J. A., Ellis C. J. Generation of cytolytic T cells in individuals infected by Mycobacterium tuberculosis and vaccinated with BCG. Thorax. 1992 Sep;47(9):695–701. doi: 10.1136/thx.47.9.695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rook G. A., Champion B. R., Steele J., Varey A. M., Stanford J. L. I-A restricted activation by T cell lines of anti-tuberculosis activity in murine macrophages. Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 Feb;59(2):414–420. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva M. T., Silva M. N., Appelberg R. Neutrophil-macrophage cooperation in the host defence against mycobacterial infections. Microb Pathog. 1989 May;6(5):369–380. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(89)90079-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker L., Lowrie D. B. Killing of Mycobacterium microti by immunologically activated macrophages. Nature. 1981 Sep 3;293(5827):69–71. doi: 10.1038/293069a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


