Abstract
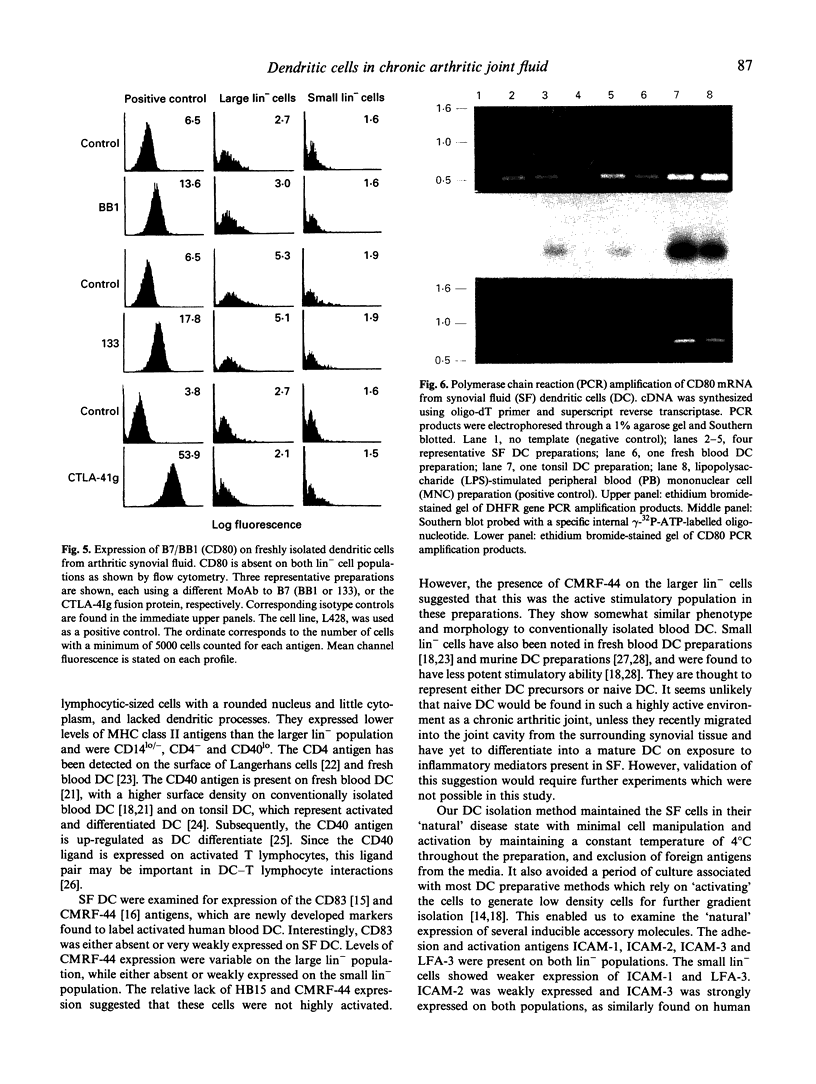
Dendritic cells (DC) act as potent primary antigen-presenting cells in many immune responses and therefore may have a role in the initiation and perpetuation of the synovial inflammation in chronic inflammatory arthritis. To examine their function, it is important to isolate fresh DC from arthritic joints without aberrant activation. We have developed a technique using minimal cell manipulation to isolate DC from the synovial fluid of chronic arthritic patients. Using this method, DC were shown to be potent allostimulatory cells, with 63-90% of cells lacking lineage-specific markers (lin-), but positive for MHC class II molecules. Two morphologically distinct populations of these cells were identified in 10 out of 13 DC preparations. Both populations expressed CD40, intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1), ICAM-2, ICAM-3 and leucocyte function associated antigen-3 (LFA-3), but the predominant population, which was larger and more typical of cultured blood DC, had a higher density of these antigens compared with the minor population, which were smaller and morphologically similar to lymphocytes. Two new MoAbs which label activated human blood DC, HB15 (CD83) and CMRF-44, were tested. CD83 labelled very weakly or not at all, whereas CMRF-44 was positive on the larger cells only. Likewise, the costimulator molecule, B7/BB1 (CD80), was not detected on the surface of either synovial lin- cell population, reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) showed little or no CD80 mRNA, and no binding of the CTLA-4Ig fusion protein was found. These results suggest that synovial DC are not, despite the inflammatory environment, in a fully activated state.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Azuma M., Ito D., Yagita H., Okumura K., Phillips J. H., Lanier L. L., Somoza C. B70 antigen is a second ligand for CTLA-4 and CD28. Nature. 1993 Nov 4;366(6450):76–79. doi: 10.1038/366076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barkley D. E., Feldmann M., Maini R. N. Cells with dendritic morphology and bright interleukin-1 alpha staining circulate in the blood of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 Apr;80(1):25–31. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb06436.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boussiotis V. A., Freeman G. J., Gribben J. G., Daley J., Gray G., Nadler L. M. Activated human B lymphocytes express three CTLA-4 counterreceptors that costimulate T-cell activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 1;90(23):11059–11063. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.23.11059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burmester G. R., Dimitriu-Bona A., Waters S. J., Winchester R. J. Identification of three major synovial lining cell populations by monoclonal antibodies directed to Ia antigens and antigens associated with monocytes/macrophages and fibroblasts. Scand J Immunol. 1983 Jan;17(1):69–82. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1983.tb00767.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egner W., Andreesen R., Hart D. N. Allostimulatory cells in fresh human blood: heterogeneity in antigen-presenting cell populations. Transplantation. 1993 Oct;56(4):945–950. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199310000-00032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman G. J., Gribben J. G., Boussiotis V. A., Ng J. W., Restivo V. A., Jr, Lombard L. A., Gray G. S., Nadler L. M. Cloning of B7-2: a CTLA-4 counter-receptor that costimulates human T cell proliferation. Science. 1993 Nov 5;262(5135):909–911. doi: 10.1126/science.7694363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girolomoni G., Simon J. C., Bergstresser P. R., Cruz P. D., Jr Freshly isolated spleen dendritic cells and epidermal Langerhans cells undergo similar phenotypic and functional changes during short-term culture. J Immunol. 1990 Nov 1;145(9):2820–2826. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding B., Knight S. C. The distribution of dendritic cells in the synovial fluids of patients with arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1986 Mar;63(3):594–600. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart D. N., McKenzie J. L. Isolation and characterization of human tonsil dendritic cells. J Exp Med. 1988 Jul 1;168(1):157–170. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.1.157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart D. N., Prickett T. C. Intercellular adhesion molecule-2 (ICAM-2) expression on human dendritic cells. Cell Immunol. 1993 May;148(2):447–454. doi: 10.1006/cimm.1993.1126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart D. N., Starling G. C., Calder V. L., Fernando N. S. B7/BB-1 is a leucocyte differentiation antigen on human dendritic cells induced by activation. Immunology. 1993 Aug;79(4):616–620. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hock B. D., Starling G. C., Daniel P. B., Hart D. N. Characterization of CMRF-44, a novel monoclonal antibody to an activation antigen expressed by the allostimulatory cells within peripheral blood, including dendritic cells. Immunology. 1994 Dec;83(4):573–581. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollenbaugh D., Grosmaire L. S., Kullas C. D., Chalupny N. J., Braesch-Andersen S., Noelle R. J., Stamenkovic I., Ledbetter J. A., Aruffo A. The human T cell antigen gp39, a member of the TNF gene family, is a ligand for the CD40 receptor: expression of a soluble form of gp39 with B cell co-stimulatory activity. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(12):4313–4321. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05530.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmdahl R., Tarkowski A., Jonsson R. Involvement of macrophages and dendritic cells in synovial inflammation of collagen induced arthritis in DBA/1 mice and spontaneous arthritis in MRL/lpr mice. Autoimmunity. 1991;8(4):271–280. doi: 10.3109/08916939109007634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight S. C., Farrant J., Chan J., Bryant A., Bedford P. A., Bateman C. Induction of autoimmunity with dendritic cells: studies on thyroiditis in mice. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1988 Sep;48(3):277–289. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(88)90021-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight S. C., Mertin J., Stackpoole A., Clark J. Induction of immune responses in vivo with small numbers of veiled (dendritic) cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(19):6032–6035. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.19.6032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen C. P., Ritchie S. C., Pearson T. C., Linsley P. S., Lowry R. P. Functional expression of the costimulatory molecule, B7/BB1, on murine dendritic cell populations. J Exp Med. 1992 Oct 1;176(4):1215–1220. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.4.1215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linsley P. S., Brady W., Urnes M., Grosmaire L. S., Damle N. K., Ledbetter J. A. CTLA-4 is a second receptor for the B cell activation antigen B7. J Exp Med. 1991 Sep 1;174(3):561–569. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.3.561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro J. M., Freedman A. S., Aster J. C., Gribben J. G., Lee N. C., Rhynhart K. K., Banchereau J., Nadler L. M. In vivo expression of the B7 costimulatory molecule by subsets of antigen-presenting cells and the malignant cells of Hodgkin's disease. Blood. 1994 Feb 1;83(3):793–798. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Doherty U., Steinman R. M., Peng M., Cameron P. U., Gezelter S., Kopeloff I., Swiggard W. J., Pope M., Bhardwaj N. Dendritic cells freshly isolated from human blood express CD4 and mature into typical immunostimulatory dendritic cells after culture in monocyte-conditioned medium. J Exp Med. 1993 Sep 1;178(3):1067–1076. doi: 10.1084/jem.178.3.1067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson S., Knight S. C. Susceptibility of human peripheral blood dendritic cells to infection by human immunodeficiency virus. J Gen Virol. 1987 Apr;68(Pt 4):1177–1181. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-4-1177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prickett T. C., McKenzie J. L., Hart D. N. Adhesion molecules on human tonsil dendritic cells. Transplantation. 1992 Feb;53(2):483–490. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199202010-00041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romani N., Lenz A., Glassel H., Stössel H., Stanzl U., Majdic O., Fritsch P., Schuler G. Cultured human Langerhans cells resemble lymphoid dendritic cells in phenotype and function. J Invest Dermatol. 1989 Nov;93(5):600–609. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12319727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuler G., Steinman R. M. Murine epidermal Langerhans cells mature into potent immunostimulatory dendritic cells in vitro. J Exp Med. 1985 Mar 1;161(3):526–546. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.3.526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stagg A. J., Elsley W. A., Pickett M. A., Ward M. E., Knight S. C. Primary human T-cell responses to the major outer membrane protein of Chlamydia trachomatis. Immunology. 1993 May;79(1):1–9. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stagg A. J., Harding B., Hughes R. A., Keat A., Knight S. C. The distribution and functional properties of dendritic cells in patients with seronegative arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991 Apr;84(1):66–71. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1991.tb08125.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas R., Davis L. S., Lipsky P. E. Isolation and characterization of human peripheral blood dendritic cells. J Immunol. 1993 Feb 1;150(3):821–834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verschure P. J., Van Noorden C. J., Dijkstra C. D. Macrophages and dendritic cells during the early stages of antigen-induced arthritis in rats: immunohistochemical analysis of cryostat sections of the whole knee joint. Scand J Immunol. 1989 Mar;29(3):371–381. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1989.tb01136.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verwilghen J., Lovis R., De Boer M., Linsley P. S., Haines G. K., Koch A. E., Pope R. M. Expression of functional B7 and CTLA4 on rheumatoid synovial T cells. J Immunol. 1994 Aug 1;153(3):1378–1385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vremec D., Zorbas M., Scollay R., Saunders D. J., Ardavin C. F., Wu L., Shortman K. The surface phenotype of dendritic cells purified from mouse thymus and spleen: investigation of the CD8 expression by a subpopulation of dendritic cells. J Exp Med. 1992 Jul 1;176(1):47–58. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.1.47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waalen K., Thoen J., Førre O., Hovig T., Teigland J., Natvig J. B. Rheumatoid synovial dendritic cells as stimulators in allogeneic and autologous mixed leukocyte reactions--comparison with autologous monocytes as stimulator cells. Scand J Immunol. 1986 Feb;23(2):233–241. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1986.tb01962.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood G. S., Warner N. L., Warnke R. A. Anti-Leu-3/T4 antibodies react with cells of monocyte/macrophage and Langerhans lineage. J Immunol. 1983 Jul;131(1):212–216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou L. J., Schwarting R., Smith H. M., Tedder T. F. A novel cell-surface molecule expressed by human interdigitating reticulum cells, Langerhans cells, and activated lymphocytes is a new member of the Ig superfamily. J Immunol. 1992 Jul 15;149(2):735–742. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vere Tyndall A., Knight S. C., Edwards A. J., Clarke J. B. Veiled (dendritic) cells in synovial fluid. Lancet. 1983 Feb 26;1(8322):472–473. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91468-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dinther-Janssen A. C., Pals S. T., Scheper R., Breedveld F., Meijer C. J. Dendritic cells and high endothelial venules in the rheumatoid synovial membrane. J Rheumatol. 1990 Jan;17(1):11–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




