Abstract
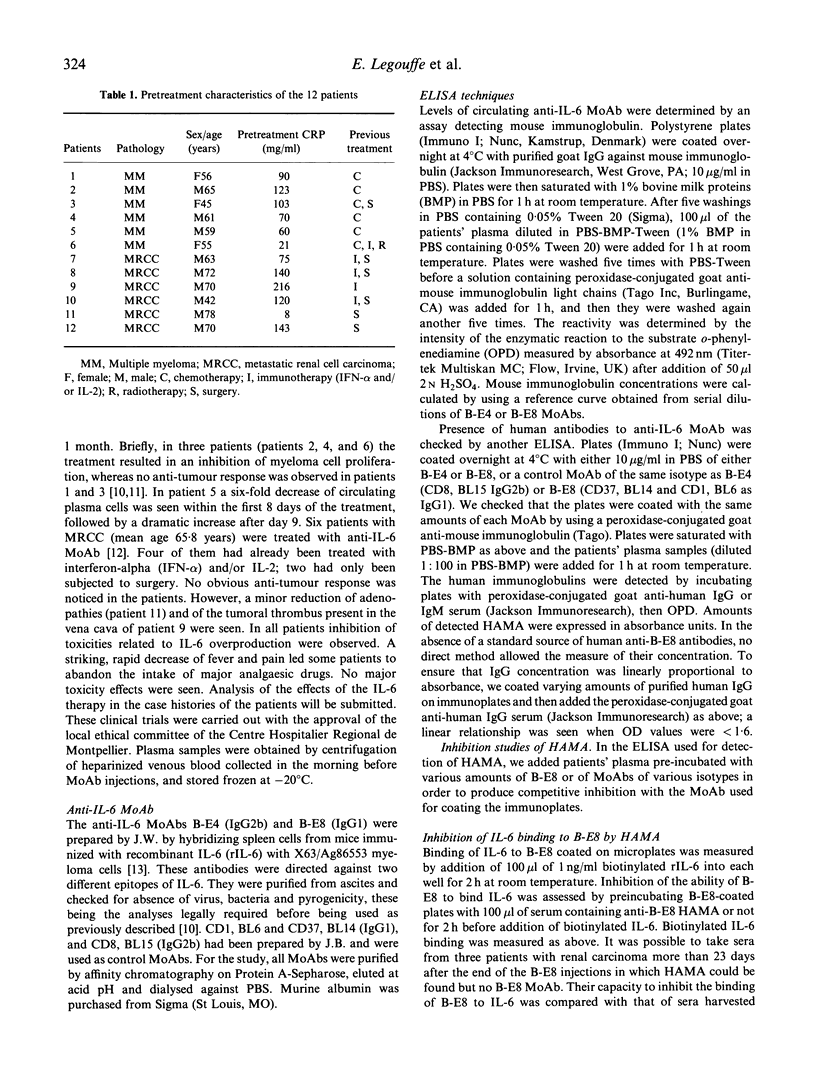
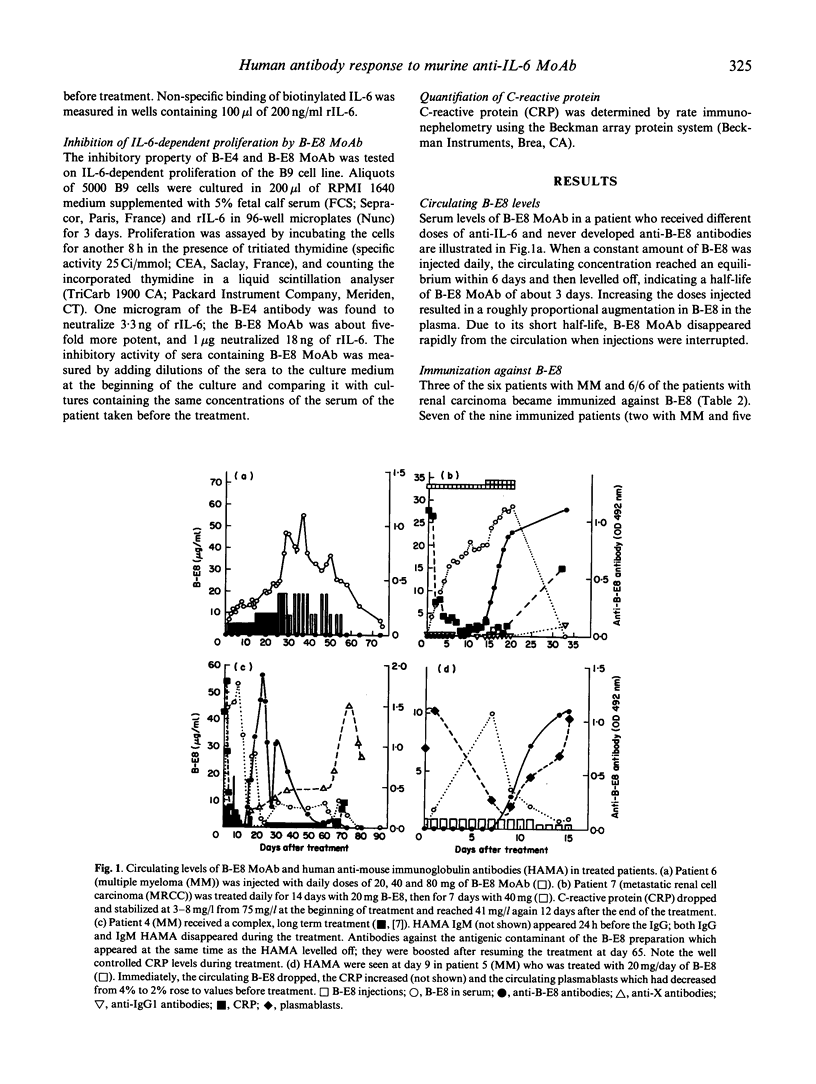
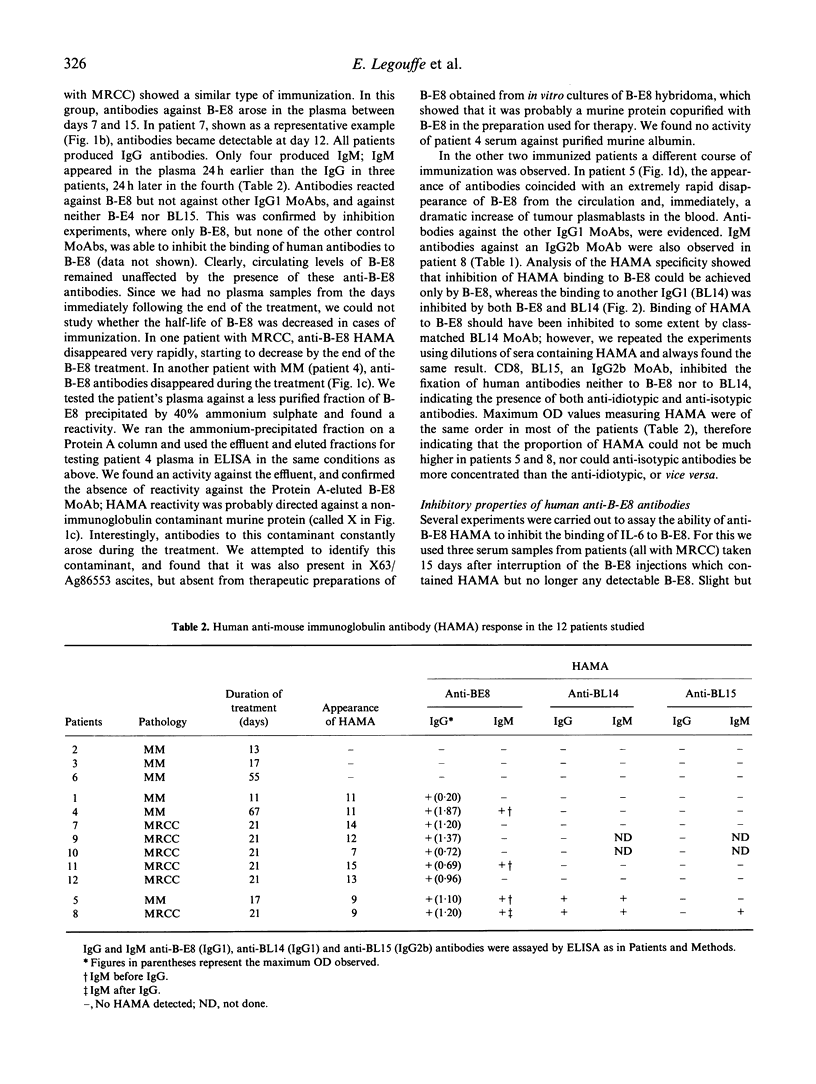
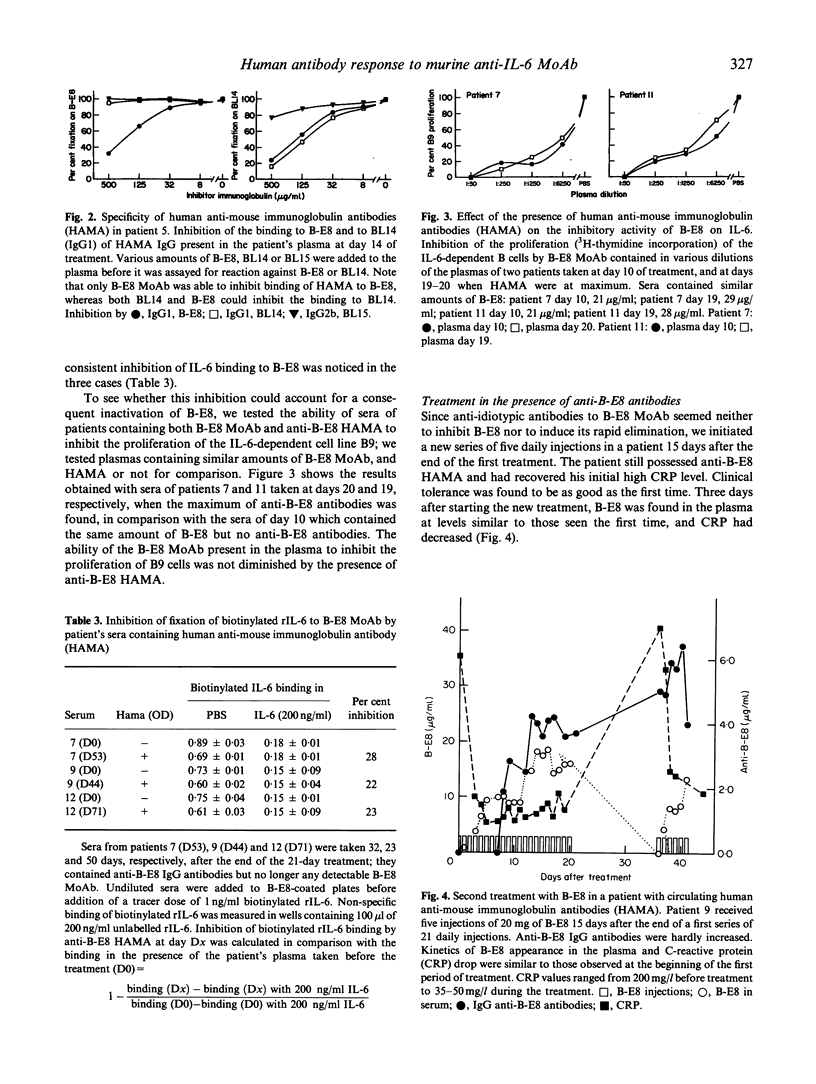
We analysed human anti-mouse antibodies (HAMA) in 12 patients (six with multiple myeloma (MM) and six with metastatic renal cell carcinoma (MRCC) who were treated with B-E8, an IgG1 MoAb against IL-6. Efficiency of the treatment was evidenced by the drop in the serum levels of C-reactive protein (CRP), the in vivo production of which is under the control of IL-6. Three patients with MM and the six patients with MRCC became immunized to the injected MoAb. HAMA appeared between days 7 and 15 after the beginning of the treatment. The nine patients made IgG antibodies; four also made IgM. All immunized patients made anti-idiotype antibodies specific to B-E8. Two of them also developed HAMA directed to murine IgG1 isotype; in these two patients B-E8 MoAb cleared rapidly from the circulation with loss of treatment efficiency. In the patients who developed only anti-idiotype antibodies, serum levels of B-E8 remained unchanged and CRP production remained inhibited, indicating that treatment remained efficient in the presence of HAMA. Circulating B-E8 MoAbs were still able to bind to IL-6 and to inhibit IL-6-dependent proliferation despite the presence of anti-idiotypic HAMA. Therefore, in contrast to HAMA produced against MoAb directed against cellular targets, HAMA against anti-IL-6 MoAb idiotopes led neither to clearance nor to functional inactivation of the injected MoAb. This was further shown by resuming the B-E8 treatment with success in a patient who still had anti-idiotypic HAMA.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chatenoud L., Bach J. F. Monoclonal antibodies to CD3 as immunosuppressants. Semin Immunol. 1990 Nov;2(6):437–447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatenoud L., Baudrihaye M. F., Chkoff N., Kreis H., Goldstein G., Bach J. F. Restriction of the human in vivo immune response against the mouse monoclonal antibody OKT3. J Immunol. 1986 Aug 1;137(3):830–838. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatenoud L., Baudrihaye M. F., Kreis H., Goldstein G., Schindler J., Bach J. F. Human in vivo antigenic modulation induced by the anti-T cell OKT3 monoclonal antibody. Eur J Immunol. 1982 Nov;12(11):979–982. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830121116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatenoud L., Jonker M., Villemain F., Goldstein G., Bach J. F. The human immune response to the OKT3 monoclonal antibody is oligoclonal. Science. 1986 Jun 13;232(4756):1406–1408. doi: 10.1126/science.3086976. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossbard M. L., Press O. W., Appelbaum F. R., Bernstein I. D., Nadler L. M. Monoclonal antibody-based therapies of leukemia and lymphoma. Blood. 1992 Aug 15;80(4):863–878. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton R. G. Monoclonal antibodies in the diagnosis and treatment of human diseases. Ann Biol Clin (Paris) 1989;47(10):575–581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaacs J. D. The antiglobulin response to therapeutic antibodies. Semin Immunol. 1990 Nov;2(6):449–456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawano M., Hirano T., Matsuda T., Taga T., Horii Y., Iwato K., Asaoku H., Tang B., Tanabe O., Tanaka H. Autocrine generation and requirement of BSF-2/IL-6 for human multiple myelomas. Nature. 1988 Mar 3;332(6159):83–85. doi: 10.1038/332083a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein B., Lu Z. Y., Gaillard J. P., Harousseau J. L., Bataille R. Inhibiting IL-6 in human multiple myeloma. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1992;182:237–244. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-77633-5_29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein B., Wijdenes J., Zhang X. G., Jourdan M., Boiron J. M., Brochier J., Liautard J., Merlin M., Clement C., Morel-Fournier B. Murine anti-interleukin-6 monoclonal antibody therapy for a patient with plasma cell leukemia. Blood. 1991 Sep 1;78(5):1198–1204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein B., Zhang X. G., Jourdan M., Boiron J. M., Portier M., Lu Z. Y., Wijdenes J., Brochier J., Bataille R. Interleukin-6 is the central tumor growth factor in vitro and in vivo in multiple myeloma. Eur Cytokine Netw. 1990 Oct-Nov;1(4):193–201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu Z. Y., Brochier J., Wijdenes J., Brailly H., Bataille R., Klein B. High amounts of circulating interleukin (IL)-6 in the form of monomeric immune complexes during anti-IL-6 therapy. Towards a new methodology for measuring overall cytokine production in human in vivo. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Nov;22(11):2819–2824. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830221110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARKS J. Antibody formation in myelomatosis. J Clin Pathol. 1953 Feb;6(1):62–63. doi: 10.1136/jcp.6.1.62. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miki S., Iwano M., Miki Y., Yamamoto M., Tang B., Yokokawa K., Sonoda T., Hirano T., Kishimoto T. Interleukin-6 (IL-6) functions as an in vitro autocrine growth factor in renal cell carcinomas. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jul 3;250(2):607–610. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80805-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiter C., Kakavand B., Rieber E. P., Schattenkirchner M., Riethmüller G., Krüger K. Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with monoclonal CD4 antibody M-T151. Clinical results and immunopharmacologic effects in an open study, including repeated administration. Arthritis Rheum. 1991 May;34(5):525–536. doi: 10.1002/art.1780340504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritz J., Pesando J. M., Sallan S. E., Clavell L. A., Notis-McConarty J., Rosenthal P., Schlossman S. F. Serotherapy of acute lymphoblastic leukemia with monoclonal antibody. Blood. 1981 Jul;58(1):141–152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shawler D. L., Bartholomew R. M., Smith L. M., Dillman R. O. Human immune response to multiple injections of murine monoclonal IgG. J Immunol. 1985 Aug;135(2):1530–1535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wendling D., Racadot E., Wijdenes J. Treatment of severe rheumatoid arthritis by anti-interleukin 6 monoclonal antibody. J Rheumatol. 1993 Feb;20(2):259–262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wijdenes J., Clement C., Klein B., Morel-Fourrier B., Vita N., Ferrara P., Peters A. Human recombinant dimeric IL-6 binds to its receptor as detected by anti-IL-6 monoclonal antibodies. Mol Immunol. 1991 Nov;28(11):1183–1192. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(91)90004-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


