Abstract
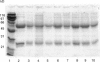
The mechanism of IgA deposition in the kidneys in IgA nephropathy is unknown. Mesangial IgA is of the IgA1 subclass, and since no consistent antigenic target for the IgA1 has been described, we have investigated the glycosylation of the molecule, as a potential non-immunological abnormality which may contribute to its deposition. IgA1 is rich in carbohydrate, carrying N-linked moieties in common with IgG, but also O-linked sugars, which are rare in serum proteins, and not expressed by IgG or IgA2. Lectin binding assays were designed to examine the expression of terminal galactose on the N-linked carbohydrate chains of purified serum IgG and IgA1, and the O-linked sugars of IgA1 and C1 inhibitor (one of the very few other serum proteins with O-linked glycosylation). No evidence was found for abnormalities of N-linked glycosylation of either isotype in IgA nephropathy compared with matched controls. However, in IgA nephropathy, reduced terminal galactosylation of the hinge region O-linked moieties was demonstrated; this was not seen in C1 inhibitor, which showed normal or increased galactosylation of the O-linked sugars. This abnormality of IgA1 has considerable implications for the pathogenesis of IgA nephropathy, since the O-linked sugars lie in an important functional location within the IgA1 molecule, close to the ligand of Fc receptors. Changes in the carbohydrates in this site may therefore affect interactions with receptors and extracellular proteins, leading to anomalous handling of the IgA1 protein in this condition, including failure of normal clearance mechanisms, and mesangial deposition.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andre P. M., Le Pogamp P., Chevet D. Impairment of jacalin binding to serum IgA in IgA nephropathy. J Clin Lab Anal. 1990;4(2):115–119. doi: 10.1002/jcla.1860040208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axford J. S., Sumar N., Alavi A., Isenberg D. A., Young A., Bodman K. B., Roitt I. M. Changes in normal glycosylation mechanisms in autoimmune rheumatic disease. J Clin Invest. 1992 Mar;89(3):1021–1031. doi: 10.1172/JCI115643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger E. G., Kozdrowski I. Permanent mixed-field polyagglutinable erythrocytes lack galactosyltransferase activity. FEBS Lett. 1978 Sep 1;93(1):105–108. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80815-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenfeld O. O., Lalezari P., Khorshidi M., Puglia K., Fukuda M. O-linked oligosaccharides of glycophorins A and B in erythrocytes of two individuals with the Tn polyagglutinability syndrome. Blood. 1992 Nov 1;80(9):2388–2395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartron J. P., Andreu G., Cartron J., Bird G. W., Salmon C., Gerbal A. Demonstration of T-transferase deficiency in Tn-polyagglutinable blood samples. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Dec 1;92(1):111–119. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12728.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartron J. P., Nurden A. T. Galactosyltransferase and membrane glycoprotein abnormality in human platelets from Tn-syndrome donors. Nature. 1979 Dec 6;282(5739):621–623. doi: 10.1038/282621a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppo R., Amore A., Gianoglio B., Reyna A., Peruzzi L., Roccatello D., Alessi D., Sena L. M. Serum IgA and macromolecular IgA reacting with mesangial matrix components. Contrib Nephrol. 1993;104:162–171. doi: 10.1159/000422409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field M. C., Dwek R. A., Edge C. J., Rademacher T. W. O-linked oligosaccharides from human serum immunoglobulin A1. Biochem Soc Trans. 1989 Dec;17(6):1034–1035. doi: 10.1042/bst0171034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorter A., Hiemstra P. S., van der Voort E. A., van Es L. A., Daha M. R. Binding of human IgA1 to rat peritoneal macrophages. Immunology. 1988 Jun;64(2):207–212. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths H. R., Lunec J. The effects of oxygen free radicals on the carbohydrate moiety of IgG. FEBS Lett. 1989 Mar 13;245(1-2):95–99. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80199-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gómez-Guerrero C., González E., Egido J. Evidence for a specific IgA receptor in rat and human mesangial cells. J Immunol. 1993 Dec 15;151(12):7172–7181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada T., Hobby P., Courteau M., Knight J. F., Williams D. G. Charge distribution of plasma IgA in IgA nephropathy. Clin Exp Immunol. 1989 Aug;77(2):211–214. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mestecky J., Tomana M., Crowley-Nowick P. A., Moldoveanu Z., Julian B. A., Jackson S. Defective galactosylation and clearance of IgA1 molecules as a possible etiopathogenic factor in IgA nephropathy. Contrib Nephrol. 1993;104:172–182. doi: 10.1159/000422410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monteiro R. C., Chevailler A., Noel L. H., Lesavre P. Serum IgA preferentially binds to cationic polypeptides in IgA nephropathy. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Aug;73(2):300–306. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monteiro R. C., Halbwachs-Mecarelli L., Roque-Barreira M. C., Noel L. H., Berger J., Lesavre P. Charge and size of mesangial IgA in IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int. 1985 Oct;28(4):666–671. doi: 10.1038/ki.1985.181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pemberton R. T. Studies on the human red cell agglutinins of the swan mussel (Anodonta cygnea). Vox Sang. 1969 Jun;16(6):457–464. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1969.tb04772.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roccatello D., Picciotto G., Torchio M., Ropolo R., Ferro M., Franceschini R., Quattrocchio G., Cacace G., Coppo R., Sena L. M. Removal systems of immunoglobulin A and immunoglobulin A containing complexes in IgA nephropathy and cirrhosis patients. The role of asialoglycoprotein receptors. Lab Invest. 1993 Dec;69(6):714–723. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumar N., Bodman K. B., Rademacher T. W., Dwek R. A., Williams P., Parekh R. B., Edge J., Rook G. A., Isenberg D. A., Hay F. C. Analysis of glycosylation changes in IgG using lectins. J Immunol Methods. 1990 Jul 20;131(1):127–136. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(90)90242-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thurnher M., Clausen H., Fierz W., Lanzavecchia A., Berger E. G. T cell clones with normal or defective O-galactosylation from a patient with permanent mixed-field polyagglutinability. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Jul;22(7):1835–1842. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220724. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]