Abstract
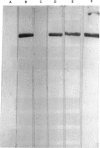
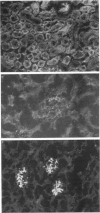
The importance of the idiotypic network is represented in experimental SLE induced by active immunization of naive mice with an anti-DNA idiotype (Ab1) emulsified in adjuvant. The mice after 4 months of incubation generate Ab3 having anti-DNA activity. In addition, the mice develop other serological markers for SLE associated with clinical and histopathological manifestations characteristic of the disease. To confirm further the etiological role of the idiotype in this experimental model, the mice were treated with specific anti-idiotypic antibodies (anti-Id) which were also conjugated to a toxin-saporin (Immunotoxin (IT)). Pretreatment of hybridoma cell line producing the anti-anti-Id (anti-DNA = (Ab3)) for 48 h with the anti-Id MoAb (Ab2) reduced the production of anti-DNA by 58%, while pretreatment with the IT resulted in 86% decrease in anti-DNA secretion (saporin alone had only 12% effect). The anti-Id MoAb had no effect on the production of immunoglobulin by an unrelated cell line. In vivo treatment of mice with experimental SLE led to a significant decrease in titres of serum autoantibodies, with diminished clinical manifestations. The results were more remarkable when the IT was employed. These suppressive effects were specific, since an anti-Id treatment of experimental anti-phospholipid syndrome was of no avail. The anti-Id effect was mediated via a reduction in specific anti-DNA antibody-forming cells, and lasted only while anti-Id injections were given. Discontinuation of the anti-Id injection was followed by a rise in titres of anti-DNA antibodies. No immunological escape of new anti-DNA Ids was noted. Our results point to the importance of pathogenic idiotypes in SLE and to the specific potential of implementing anti-idiotypic therapy, enhanced by the conjugation of the anti-Id to an immunotoxin, in particular one with low spontaneous toxicity.
Full text
PDF


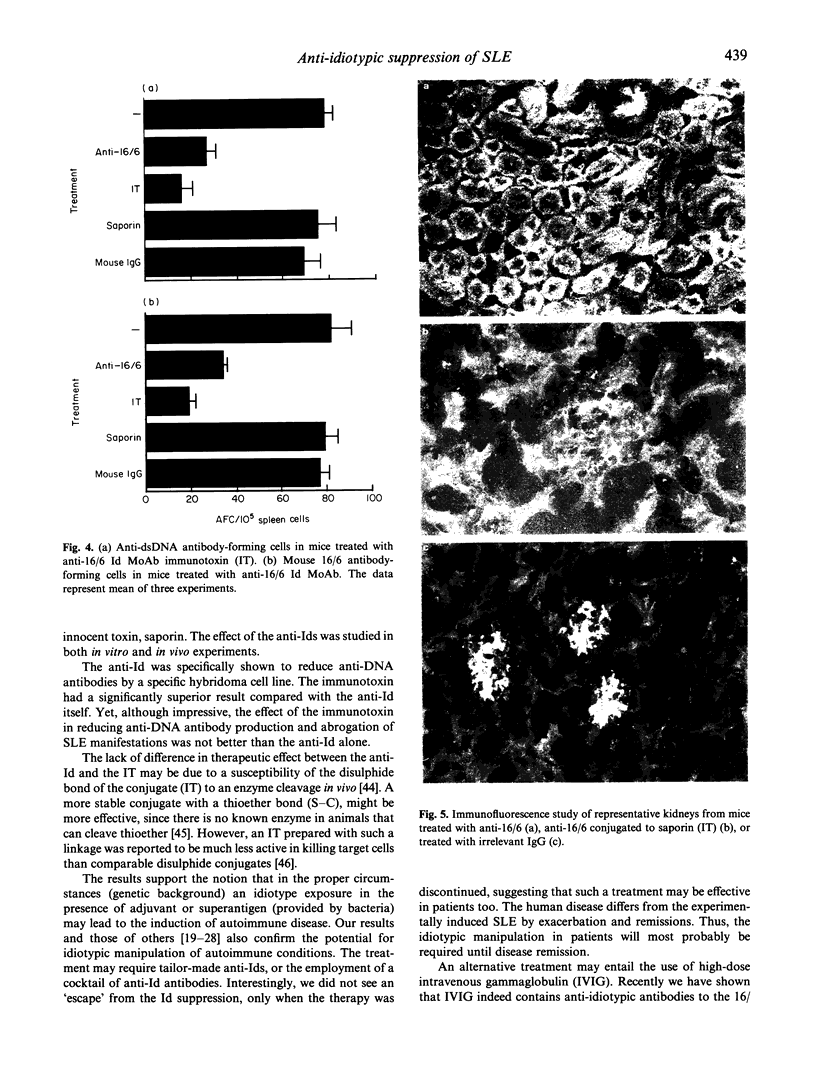


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agius M. A., Richman D. P. Suppression of development of experimental autoimmune myasthenia gravis with isogeneic monoclonal anti-idiotopic antibody. J Immunol. 1986 Oct 1;137(7):2195–2198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ando D. G., Ebling F. M., Hahn B. H. Detection of native and denatured DNA antibody forming cells by the enzyme-linked immunospot assay. A clinical study of (New Zealand black x New Zealand white)F1 mice. Arthritis Rheum. 1986 Sep;29(9):1139–1146. doi: 10.1002/art.1780290912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakimer R., Guilburd B., Zurgil N., Shoenfeld Y. The effect of intravenous gamma-globulin on the induction of experimental antiphospholipid syndrome. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1993 Oct;69(1):97–102. doi: 10.1006/clin.1993.1155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blank M., Ben-Bassat M., Shoenfeld Y. The effect of cyclosporin A on early and late stages of experimental lupus. Arthritis Rheum. 1992 Nov;35(11):1350–1355. doi: 10.1002/art.1780351116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blank M., Krup M., Mendlovic S., Fricke H., Mozes E., Talal N., Coates A. R., Shoenfeld Y. The importance of the pathogenic 16/6 idiotype in the induction of SLE in naive mice. Scand J Immunol. 1990 Jan;31(1):45–52. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1990.tb02741.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blank M., Mendlovic S., Fricke H., Mozes E., Talal N., Shoenfeld Y. Sex hormone involvement in the induction of experimental systemic lupus erythematosus by a pathogenic anti-DNA idiotype in naive mice. J Rheumatol. 1990 Mar;17(3):311–317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blank M., Mendlovic S., Mozes E., Coates A. R., Shoenfeld Y. Induction of systemic lupus erythematosus in naive mice with T-cell lines specific for human anti-DNA antibody SA-1 (16/6 Id+) and for mouse tuberculosis antibody TB/68 (16/6 Id+). Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1991 Sep;60(3):471–483. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(91)90102-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blank M., Smorodinsky I. N., Keydar I., Chaitchik S., Shoenfeld Y. The production of human monoclonal anti-MMTV antibodies by in vitro immunization with anti-idiotypic antibodies. Immunol Lett. 1991 Apr;28(1):65–71. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(91)90128-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blank M., Sredni B., Albeck M., Mozes E., Shoenfeld Y. The effect of the immunomodulator agent AS101 on interleukin-2 production in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) induced in mice by a pathogenic anti-DNA antibody. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 Mar;79(3):443–447. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb08109.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burdette S., Schwartz R. S. Current concepts: immunology. Idiotypes and idiotypic networks. N Engl J Med. 1987 Jul 23;317(4):219–224. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198707233170407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byers V. S., Baldwin R. W. Targeted kill: from umbrellas to monoclonal antibodies. J Clin Immunol. 1992 Nov;12(6):391–405. doi: 10.1007/BF00918851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carteron N. L., Schimenti C. L., Wofsy D. Treatment of murine lupus with F(ab')2 fragments of monoclonal antibody to L3T4. Suppression of autoimmunity does not depend on T helper cell depletion. J Immunol. 1989 Mar 1;142(5):1470–1475. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Kozak Y., Mirshahi M. Experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis: idiotypic regulation and disease suppression. Int Ophthalmol. 1990 Jan;14(1):43–56. doi: 10.1007/BF00131168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein A., Greenberg M., Diamond B., Grayzel A. I. Suppression of anti-DNA antibody synthesis in vitro by a cross-reactive antiidiotypic antibody. J Clin Invest. 1987 Mar;79(3):997–1000. doi: 10.1172/JCI112912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn B. H., Ebling F. M. Suppression of murine lupus nephritis by administration of an anti-idiotypic antibody to anti-DNA. J Immunol. 1984 Jan;132(1):187–190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerne N. K. Towards a network theory of the immune system. Ann Immunol (Paris) 1974 Jan;125C(1-2):373–389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koopman W. J., Schrohenloher R. E., Barton J. C., Greenleaf E. C. Suppression of in vitro monoclonal human rheumatoid factor synthesis by antiidiotypic antibody. Target cells and molecular requirements. J Clin Invest. 1983 Oct;72(4):1410–1419. doi: 10.1172/JCI111097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lappi D. A., Esch F. S., Barbieri L., Stirpe F., Soria M. Characterization of a Saponaria officinalis seed ribosome-inactivating protein: immunoreactivity and sequence homologies. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Jun 28;129(3):934–942. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91981-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manosroi J., von Kleist S., Manosroi A., Grunert F. Thermo-stability and antitumor activity on colon cancer cell lines of monoclonal anti-CEA antibody-saporin immunotoxin. J Korean Med Sci. 1992 Jun;7(2):128–135. doi: 10.3346/jkms.1992.7.2.128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendlovic S., Brocke S., Shoenfeld Y., Ben-Bassat M., Meshorer A., Bakimer R., Mozes E. Induction of a systemic lupus erythematosus-like disease in mice by a common human anti-DNA idiotype. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2260–2264. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordling C., Holmdahl R., Klareskog L. Down-regulation of collagen arthritis after in vivo treatment with a syngeneic monoclonal anti-idiotypic antibody to a cross-reactive idiotope on collagen II auto-antibodies. Immunology. 1991 Apr;72(4):486–490. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsnes S., Pihl A. Chimeric toxins. Pharmacol Ther. 1981;15(3):355–381. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(81)90050-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pastan I., Willingham M. C., FitzGerald D. J. Immunotoxins. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):641–648. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90506-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul E., Manheimer-Lory A., Livneh A., Solomon A., Aranow C., Ghossein C., Shefner R., Offen D., Pillinger M., Diamond B. Pathogenic anti-DNA antibodies in SLE: idiotypic families and genetic origins. Int Rev Immunol. 1990;5(3-4):295–313. doi: 10.3109/08830189009056736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roubaty C., Bedin C., Charreire J. Prevention of experimental autoimmune thyroiditis through the anti-idiotypic network. J Immunol. 1990 Mar 15;144(6):2167–2172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruegg C. L., Strand M. A synthetic peptide with sequence identity to the transmembrane protein GP41 of HIV-1 inhibits distinct lymphocyte activation pathways dependent on protein kinase C and intracellular calcium influx. Cell Immunol. 1991 Oct 1;137(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(91)90051-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki T., Koide Y., Yoshigaga K. Immune suppression of anti-DNA antibody production using anti-idiotypic antibody-neocarzinostatin conjugates. Methods Enzymol. 1989;178:422–432. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(89)78031-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki T., Muryoi T., Takai O., Tamate E., Ono Y., Koide Y., Ishida N., Yoshinaga K. Selective elimination of anti-DNA antibody-producing cells by antiidiotypic antibody conjugated with neocarzinostatin. J Clin Invest. 1986 Apr;77(4):1382–1386. doi: 10.1172/JCI112444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki T., Tamate E., Muryoi T., Takai O., Yoshinaga K. In vitro manipulation of human anti-DNA antibody production by anti-idiotypic antibodies conjugated with neocarzinostatin. J Immunol. 1989 Feb 15;142(4):1159–1165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoenfeld Y., Mozes E. Pathogenic idiotypes of autoantibodies in autoimmunity: lessons from new experimental models of SLE. FASEB J. 1990 Jun;4(9):2646–2651. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.4.9.2140806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smorodinsky N. I., Argov S., Ghendles Y., Bakimer R., Krup M., Lupu R., Keydar I., Shoenfeld Y. Human monoclonal antibodies derived from pleural effusion lymphocytes of a patient with breast carcinoma react with human breast cancer-associated antigens and mouse mammary tumor virus polypeptides. Exp Cell Biol. 1987;55(5):237–249. doi: 10.1159/000163422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stirpe F., Gasperi-Campani A., Barbieri L., Falasca A., Abbondanza A., Stevens W. A. Ribosome-inactivating proteins from the seeds of Saponaria officinalis L. (soapwort), of Agrostemma githago L. (corn cockle) and of Asparagus officinalis L. (asparagus), and from the latex of Hura crepitans L. (sandbox tree). Biochem J. 1983 Dec 15;216(3):617–625. doi: 10.1042/bj2160617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stirpe F., Olsnes S., Pihl A. Gelonin, a new inhibitor of protein synthesis, nontoxic to intact cells. Isolation, characterization, and preparation of cytotoxic complexes with concanavalin A. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 25;255(14):6947–6953. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teitelbaum D., Rauch J., Stollar B. D., Schwartz R. S. In vivo effects of antibodies against a high frequency idiotype of anti-DNA antibodies in MRL mice. J Immunol. 1984 Mar;132(3):1282–1285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomer Y., Shoenfeld Y. Successful treatment of psychosis secondary to SLE with high dose intravenous immunoglobulin. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1992 Jul-Aug;10(4):391–393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waisman A., Mozes E. Variable region sequences of autoantibodies from mice with experimental systemic lupus erythematosus. Eur J Immunol. 1993 Jul;23(7):1566–1573. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830230726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youle R. J., Neville D. M., Jr Kinetics of protein synthesis inactivation by ricin-anti-Thy 1.1 monoclonal antibody hybrids. Role of the ricin B subunit demonstrated by reconstitution. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 25;257(4):1598–1601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zanetti M., Mampaso F., Wilson C. B. Anti-idiotype as a probe in the analysis of autoimmune tubulointerstitial nephritis in the Brown Norway rat. J Immunol. 1983 Sep;131(3):1268–1273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou S. R., Whitaker J. N. Specific modulation of T cells and murine experimental allergic encephalomyelitis by monoclonal anti-idiotypic antibodies. J Immunol. 1993 Feb 15;150(4):1629–1642. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]