Abstract
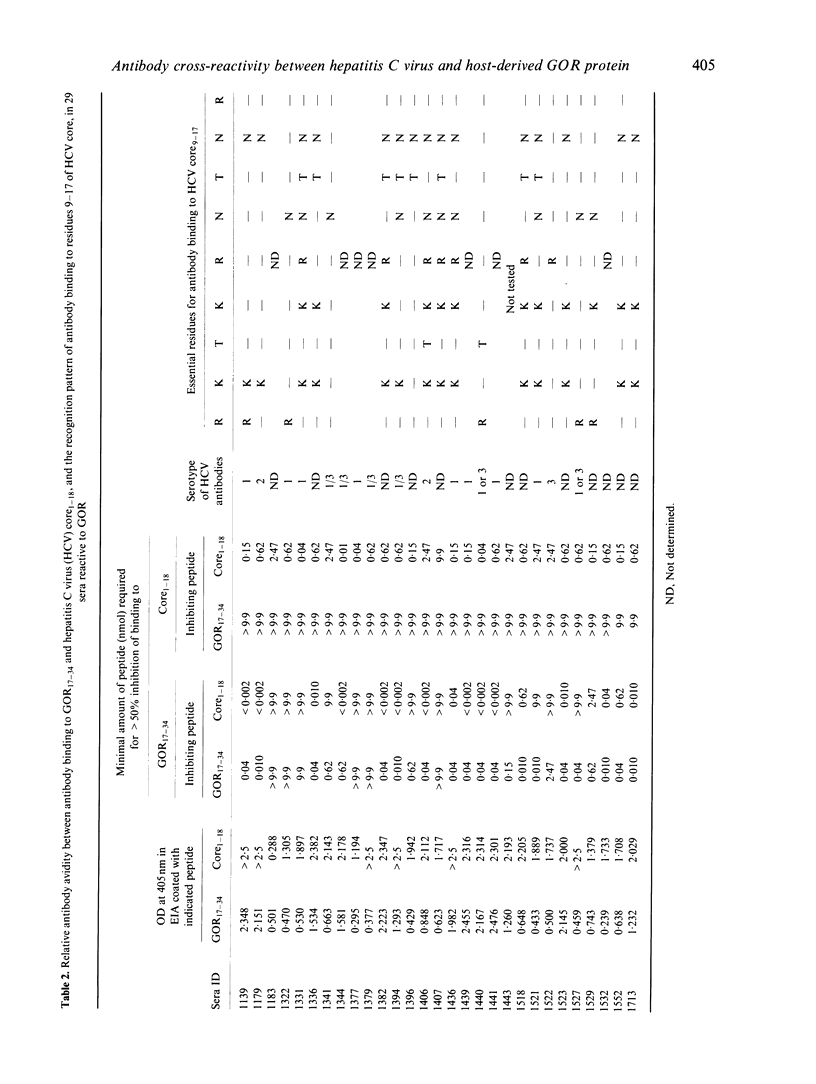
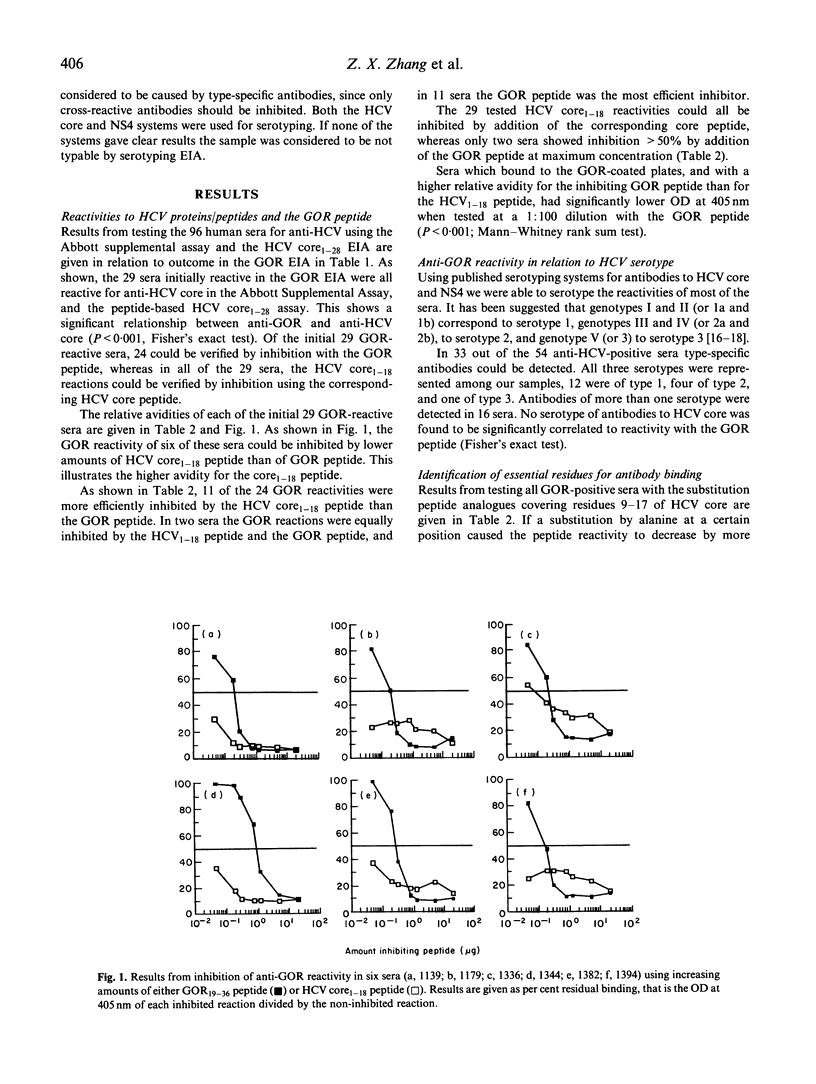
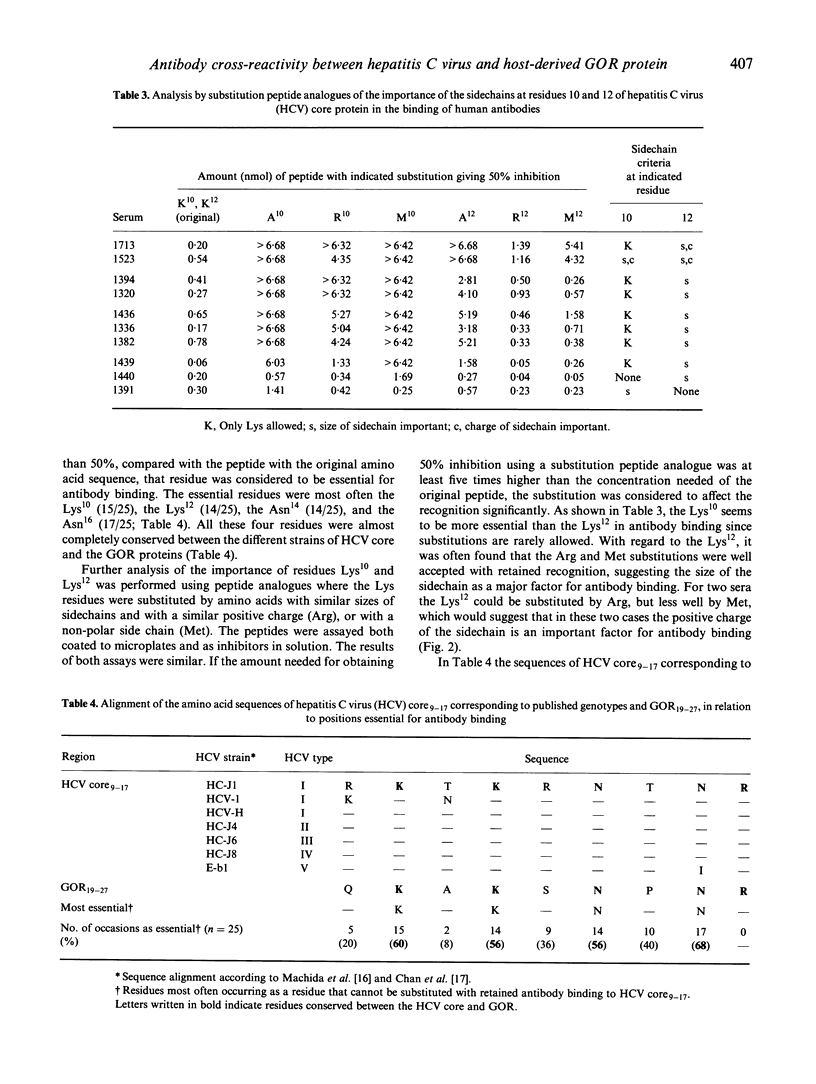
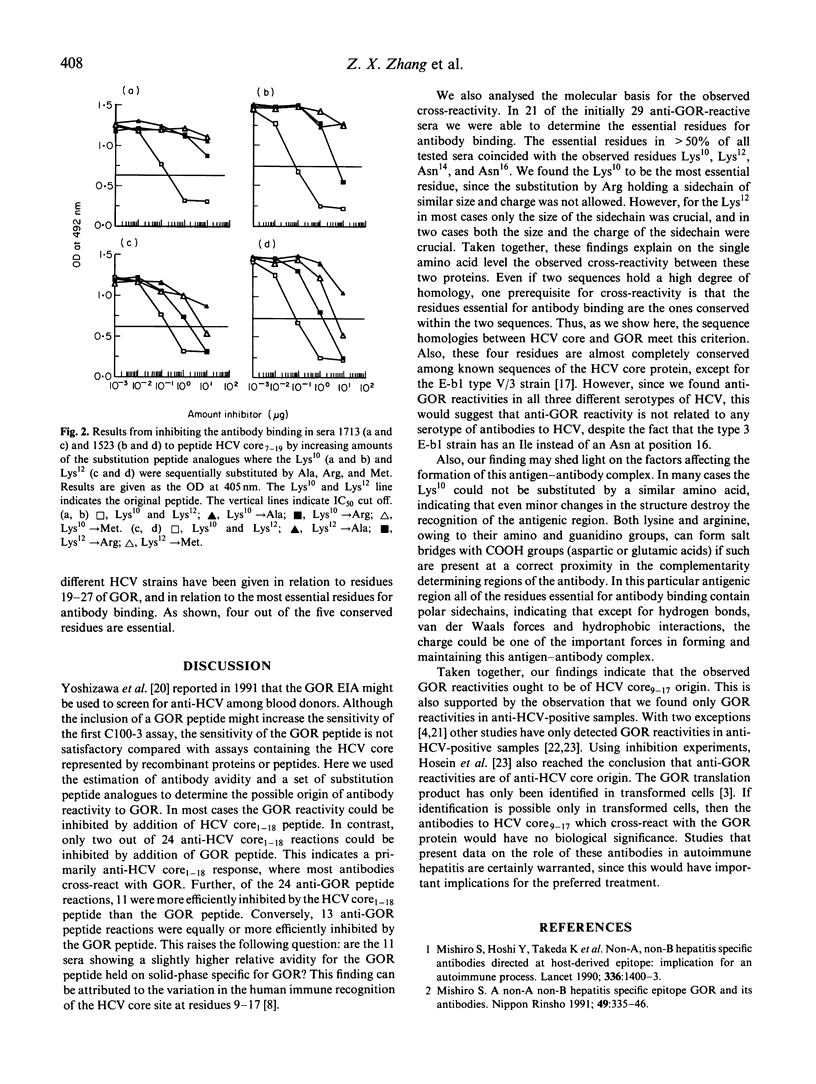
The presence of antibodies reactive to a recently cloned host-derived antigen GOR is highly correlated with the presence of antibodies to the hepatitis C virus (HCV). We explored the molecular basis for this observation, and address the following question: are antibodies reactive with GOR19-27 (QKAKSNPNR) a result of a cross-reactivity triggered by the antigenic region at residues 9-17 of HCV core (RKTKRNTNR)? We compared the relative antibody avidity between antibodies reactive to both regions, and determined the residues essential for antibody binding using substitution peptide analogues. Of 96 sera assayed, 60 were found positive for anti-HCV, and of these 55 were found to react with HCV core. Twenty-nine sera were found reactive to the GOR peptide, and these were all reactive to HCV core. In most cases the relative antibody avidity of antibodies reactive to GOR was higher for the HCV core peptide. In 21 of the GOR-reactive sera we were able to determine the essential residues for antibody binding. The essential residues in > 50% of all tested sera coincided with the well conserved residues Lys10, Lys12, Asn14, and Asn16. Also, reactivity to GOR was not related to any certain serotype of antibodies to HCV. Taken together, these findings explain at the molecular level the observed cross-reactivity between these two proteins, since sequence homology per se is not evidence for cross-reactivity.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chan S. W., McOmish F., Holmes E. C., Dow B., Peutherer J. F., Follett E., Yap P. L., Simmonds P. Analysis of a new hepatitis C virus type and its phylogenetic relationship to existing variants. J Gen Virol. 1992 May;73(Pt 5):1131–1141. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-73-5-1131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosein B., Fang X., Wang C. Y. Anti-HCV, anti-GOR, and autoimmunity. Lancet. 1992 Apr 4;339(8797):871–871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotwal G. J., Baroudy B. M., Kuramoto I. K., McDonald F. F., Schiff G. M., Holland P. V., Zeldis J. B. Detection of acute hepatitis C virus infection by ELISA using a synthetic peptide comprising a structural epitope. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4486–4489. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenzi M., Cassani F., Ballardini G., Bianchi F. B., Mishiro S., Unoura M., Kaneko S., Kobayashi K. Anti-HCV, anti-GOR, and autoimmunity. Lancet. 1992 Apr 4;339(8797):871–872. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machida A., Ohnuma H., Tsuda F., Munekata E., Tanaka T., Akahane Y., Okamoto H., Mishiro S. Two distinct subtypes of hepatitis C virus defined by antibodies directed to the putative core protein. Hepatology. 1992 Oct;16(4):886–891. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840160406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magrin S., Pinzello G., Craxì A., Almasio P., Pagliaro L. Anti-HCV, anti-GOR, and autoimmunity. Lancet. 1992 Apr 4;339(8797):871–871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehta S. U., Mishiro S., Sekiguchi K., Leung T., Dawson G. J., Pendy L. M., Peterson D. A., Devare S. G. Immune response to GOR, a marker for non-A, non-B hepatitis and its correlation with hepatitis C virus infection. J Clin Immunol. 1992 May;12(3):178–184. doi: 10.1007/BF00918086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel G., Ritter A., Gerken G., Meyer zum Büschenfelde K. H., Decker R., Manns M. P. Anti-GOR and hepatitis C virus in autoimmune liver diseases. Lancet. 1992 Feb 1;339(8788):267–269. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)91332-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishiro S., Hoshi Y., Takeda K., Yoshikawa A., Gotanda T., Takahashi K., Akahane Y., Yoshizawa H., Okamoto H., Tsuda F. Non-A, non-B hepatitis specific antibodies directed at host-derived epitope: implication for an autoimmune process. Lancet. 1990 Dec 8;336(8728):1400–1403. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)93101-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishiro S., Takeda K., Hoshi Y., Yoshikawa A., Gotanda T., Itoh Y. An autoantibody cross-reactive to hepatitis C virus core and a host nuclear antigen. Autoimmunity. 1991;10(4):269–273. doi: 10.3109/08916939109001900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishiro S. [A non-A non-B hepatitis specific epitope GOR and its antibodies]. Nihon Rinsho. 1991 Feb;49(2):335–346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto H., Munekata E., Tsuda F., Takahashi K., Yotsumoto S., Tanaka T., Tachibana K., Akahane Y., Sugai Y., Miyakawa Y. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for antibodies against the capsid protein of hepatitis C virus with a synthetic oligopeptide. Jpn J Exp Med. 1990 Aug;60(4):223–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto H., Okada S., Sugiyama Y., Yotsumoto S., Tanaka T., Yoshizawa H., Tsuda F., Miyakawa Y., Mayumi M. The 5'-terminal sequence of the hepatitis C virus genome. Jpn J Exp Med. 1990 Jun;60(3):167–177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto H., Tsuda F., Machida A., Munekata E., Akahane Y., Sugai Y., Mashiko K., Mitsui T., Tanaka T., Miyakawa Y. Antibodies against synthetic oligopeptides deduced from the putative core gene for the diagnosis of hepatitis virus infection. Hepatology. 1992 Feb;15(2):180–186. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840150203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmonds P., Rose K. A., Graham S., Chan S. W., McOmish F., Dow B. C., Follett E. A., Yap P. L., Marsden H. Mapping of serotype-specific, immunodominant epitopes in the NS-4 region of hepatitis C virus (HCV): use of type-specific peptides to serologically differentiate infections with HCV types 1, 2, and 3. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Jun;31(6):1493–1503. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.6.1493-1503.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steward M. W., Stanley C. M., Dimarchi R., Mulcahy G., Doel T. R. High-affinity antibody induced by immunization with a synthetic peptide is associated with protection of cattle against foot-and-mouth disease. Immunology. 1991 Jan;72(1):99–103. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sällberg M., Rudén U., Magnius L. O., Norrby E., Wahren B. Rapid "tea-bag" peptide synthesis using 9-fluorenylmethoxycarbonyl (Fmoc) protected amino acids applied for antigenic mapping of viral proteins. Immunol Lett. 1991 Sep;30(1):59–68. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(91)90090-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sällberg M., Rudén U., Wahren B., Magnius L. O. Antigenic regions within the hepatitis C virus envelope 1 and non-structural proteins: identification of an IgG3-restricted recognition site with the envelope 1 protein. Clin Exp Immunol. 1993 Mar;91(3):489–494. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1993.tb05929.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sällberg M., Rudén U., Wahren B., Magnius L. O. Immune response to a single peptide containing an immunodominant region of hepatitis C virus core protein: the isotypes and the recognition site. Immunol Lett. 1992 Jun;33(1):27–33. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(92)90089-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sällberg M., Rudén U., Wahren B., Magnius L. O. Immunodominant regions within the hepatitis C virus core and putative matrix proteins. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Aug;30(8):1989–1994. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.8.1989-1994.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi K., Boonmar S., Kubo Y., Katayama T., Harada H., Ohbayashi A., Choo Q. L., Kuo G., Houghton M., Saito I. Hepatitis C viral cDNA clones isolated from a healthy carrier donor implicated in post-transfusion non-A, non-B hepatitis. Gene. 1990 Jul 16;91(2):287–291. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90102-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi K., Kubo Y., Boonmar S., Watanabe Y., Katayama T., Choo Q. L., Kuo G., Houghton M., Saito I., Miyamura T. Nucleotide sequence of core and envelope genes of the hepatitis C virus genome derived directly from human healthy carriers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Aug 11;18(15):4626–4626. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.15.4626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshizawa H., Nojiri N., Takahashi K. Measurement of anti-GOR antibodies in prevention of post-transfusion non-A, non-B hepatitis. Lancet. 1991 Jan 5;337(8732):47–48. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)93364-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


