Abstract
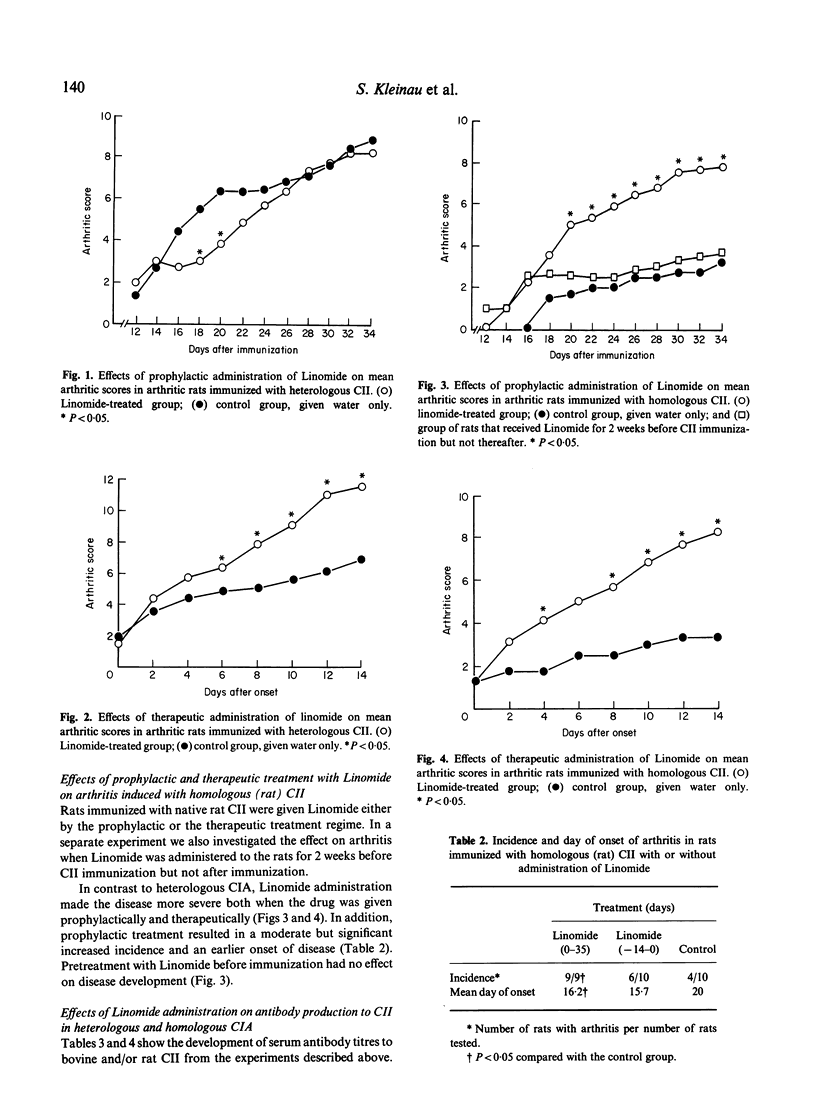
The effects of the immunomodulatory drug Linomide (LS-2616) have been investigated on two variants of collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) in Lewis rats, i.e. arthritis induced either with heterologous (bovine) or with homologous (rat) collagen type II (CII). Treatment with Linomide from the day of immunization (prophylactic) had a mild ameliorative effect on the severity of arthritis in the heterologous CIA, while the homologous CIA was strongly augmented. In both models, Linomide treatment caused a more severe arthritis when given from onset of clinical signs of disease and onwards (therapeutic). Serum antibody levels to CII were significantly decreased by prophylactic Linomide treatment in rats immunized with heterologous CII, while elevated levels of anti-rat CII antibodies were seen in the homologous model. No effect on antibody levels was seen with the therapeutic treatment regime. The opposing effects of prophylactic treatment with Linomide in heterologous versus homologous CIA indicate that the immune response to an autoantigen may be regulated differently from that to a foreign antigen. These results further strengthen the view that heterologous and homologous CIA should be regarded as separate experimental models, and that the studies on homologous CIA may represent a novel approach for future studies of autoimmune responses and evaluation of anti-rheumatic drugs.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Courtenay J. S., Dallman M. J., Dayan A. D., Martin A., Mosedale B. Immunisation against heterologous type II collagen induces arthritis in mice. Nature. 1980 Feb 14;283(5748):666–668. doi: 10.1038/283666a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon F. J. The pathogenesis of murine systemic lupus erythematosus. Rous--Whipple Award lecture. Am J Pathol. 1979 Oct;97(1):10–16. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmdahl R., Andersson M., Enander I., Goldschmidt T., Jansson L., Larsson P., Mo J., Nordling C., Klareskog L. Nature of the type II collagen autoimmunity in mice susceptible to collagen-induced arthritis. Int Rev Immunol. 1988 Sep;4(1):49–64. doi: 10.3109/08830188809044770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmdahl R., Jansson L., Andersson M., Larsson E. Immunogenetics of type II collagen autoimmunity and susceptibility to collagen arthritis. Immunology. 1988 Oct;65(2):305–310. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmdahl R., Jansson L., Gullberg D., Rubin K., Forsberg P. O., Klareskog L. Incidence of arthritis and autoreactivity of anti-collagen antibodies after immunization of DBA/1 mice with heterologous and autologous collagen II. Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 Dec;62(3):639–646. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmdahl R., Jansson L., Larsson E., Rubin K., Klareskog L. Homologous type II collagen induces chronic and progressive arthritis in mice. Arthritis Rheum. 1986 Jan;29(1):106–113. doi: 10.1002/art.1780290114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller E. J. Structural studies on cartilage collagen employing limited cleavage and solubilization with pepsin. Biochemistry. 1972 Dec 19;11(26):4903–4909. doi: 10.1021/bi00776a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stålhandske T., Kalland T. Effects of the novel immunomodulator LS 2616 on the delayed-type hypersensitivity reaction to Bordetella pertussis in the rat. Immunopharmacology. 1986 Apr;11(2):87–92. doi: 10.1016/0162-3109(86)90028-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarkowski A., Gunnarsson K., Nilsson L. A., Lindholm L., Stålhandske T. Successful treatment of autoimmunity in MRL/1 mice with LS-2616, a new immunomodulator. Arthritis Rheum. 1986 Nov;29(11):1405–1409. doi: 10.1002/art.1780291115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarkowski A., Gunnarsson K., Stålhandske T. Effects of LS-2616 administration upon the autoimmune disease of (NZB x NZW) F1 hybrid mice. Immunology. 1986 Dec;59(4):589–594. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trentham D. E. Collagen arthritis as a relevant model for rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Aug;25(8):911–916. doi: 10.1002/art.1780250801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trentham D. E., Townes A. S., Kang A. H. Autoimmunity to type II collagen an experimental model of arthritis. J Exp Med. 1977 Sep 1;146(3):857–868. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.3.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trentham D. E., Townes A. S., Kang A. H., David J. R. Humoral and cellular sensitivity to collagen in type II collagen-induced arthritis in rats. J Clin Invest. 1978 Jan;61(1):89–96. doi: 10.1172/JCI108929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


