Abstract
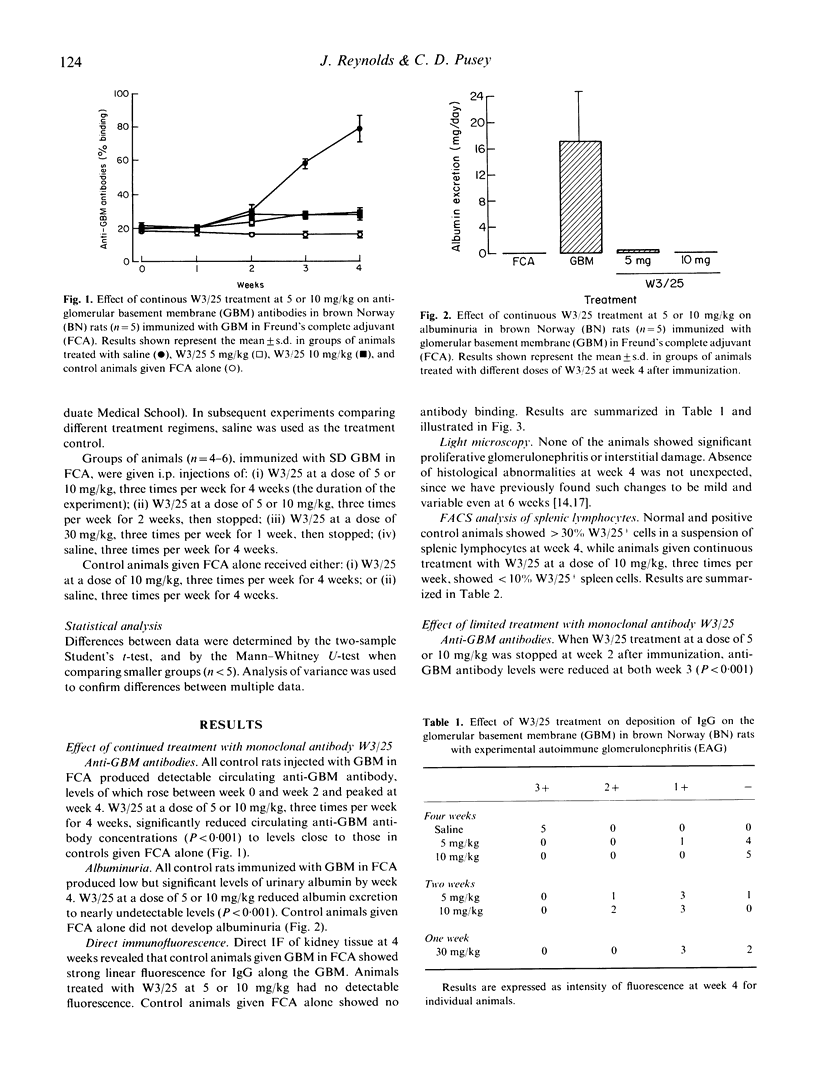
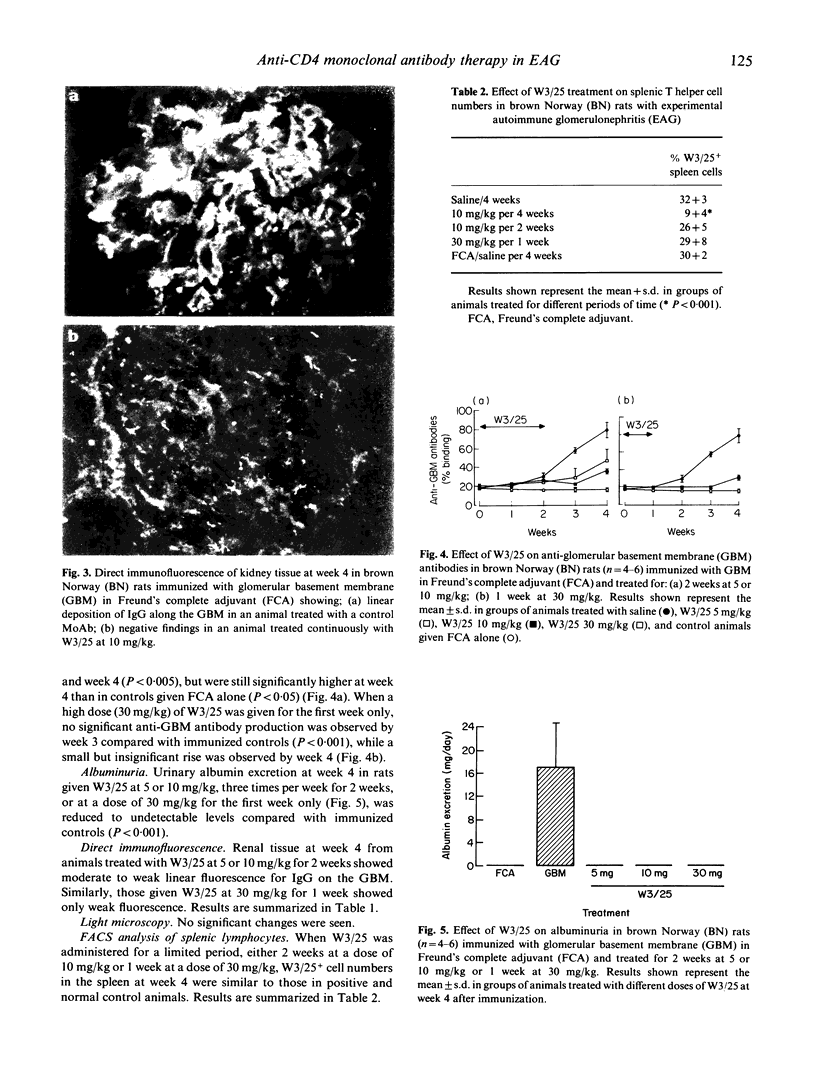
Experimental autoimmune glomerulonephritis (EAG) was induced in brown Norway (BN) rats by a single i.m. injection of homologous glomerular basement membrane (GBM) in Freund's complete adjuvant. This model of anti-GBM disease is characterized by the development, over several weeks, of circulating and deposited anti-GBM antibodies, accompanied by albuminuria. We examined the effects of treatment with MoAb W3/25 (anti-CD4) at different doses, starting at the time of immunization and continued for the duration of the study or for a limited period only. Continued treatment with W3/25, at a dose of 5 or 10 mg/kg intraperitoneally three times per week for 4 weeks, produced a marked reduction in circulating anti-GBM antibodies, absence of detectable deposited antibody and virtual absence of albuminuria. When W3/25 treatment, at 5 or 10 mg/kg, was stopped after 2 weeks, there was still a significant reduction in anti-GBM antibodies and albuminuria at 4 weeks. A similar effect on the disease was achieved when W3/25 was administered only three times during the first week at a dose of 30 mg/kg. Animals injected with W3/25 at a dose of 10 mg/kg through the course of disease showed < 10% W3/25+ cells by FACS analysis of splenic lymphocytes at week 4, while controls and animals treated for shorter periods showed > 30% W3/25+ cells. These results demonstrate that W3/25 can prevent the development of EAG, and that this effect is not dependent on persistent depletion of T cells. Further work is necessary to determine whether anti-T cell therapy is effective in established EAG, and may be worth investigating in human anti-GBM disease.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bowman C., Green C., Borysiewicz L., Lockwood C. M. Circulating T-cell populations during mercuric chloride-induced nephritis in the Brown Norway rat. Immunology. 1987 Aug;61(4):515–520. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman C., Peters D. K., Lockwood C. M. Anti-glomerular basement membrane autoantibodies in the Brown Norway rat: detection by a solid-phase radioimmunoassay. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Jul 29;61(3):325–333. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90227-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brideau R. J., Carter P. B., McMaster W. R., Mason D. W., Williams A. F. Two subsets of rat T lymphocytes defined with monoclonal antibodies. Eur J Immunol. 1980 Aug;10(8):609–615. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830100807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cashman S. J., Pusey C. D., Evans D. J. Extraglomerular distribution of immunoreactive Goodpasture antigen. J Pathol. 1988 May;155(1):61–70. doi: 10.1002/path.1711550110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greiner D. L., Angelillo M., Wayne A. L., Fitzgerald K. M., Rozenski D., Cutler L. S. Experimental autoallergic sialadenitis in the LEW rat. III. Role of CD4+ T cells in EAS induction. Cell Immunol. 1991 Jul;135(2):354–359. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(91)90280-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch F., Couderc J., Sapin C., Fournie G., Druet P. Polyclonal effect of HgCl2 in the rat, its possible role in an experimental autoimmune disease. Eur J Immunol. 1982 Jul;12(7):620–625. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830120716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmdahl R., Olsson T., Moran T., Klareskog L. In vivo treatment of rats with monoclonal anti-T-cell antibodies. Immunohistochemical and functional analysis in normal rats and in experimental allergic neuritis. Scand J Immunol. 1985 Aug;22(2):157–169. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1985.tb01868.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchings P., O'Reilly L., Parish N. M., Waldmann H., Cooke A. The use of a non-depleting anti-CD4 monoclonal antibody to re-establish tolerance to beta cells in NOD mice. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Jul;22(7):1913–1918. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung S., Krämer S., Schluesener H. J., Hünig T., Toyka K., Hartung H. P. Prevention and therapy of experimental autoimmune neuritis by an antibody against T cell receptors-alpha/beta. J Immunol. 1992 Jun 15;148(12):3768–3775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kong Y. M., Waldmann H., Cobbold S., Giraldo A. A., Fuller B. E., Simon L. L. Pathogenic mechanisms in murine autoimmune thyroiditis: short- and long-term effects of in vivo depletion of CD4+ and CD8+ cells. Clin Exp Immunol. 1989 Sep;77(3):428–433. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurell C. B. Quantitative estimation of proteins by electrophoresis in agarose gel containing antibodies. Anal Biochem. 1966 Apr;15(1):45–52. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90246-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner R. A., Glassock R. J., Dixon F. J. The role of anti-glomerular basement membrane antibody in the pathogenesis of human glomerulonephritis. J Exp Med. 1967 Dec 1;126(6):989–1004. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.6.989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Like A. A., Biron C. A., Weringer E. J., Byman K., Sroczynski E., Guberski D. L. Prevention of diabetes in BioBreeding/Worcester rats with monoclonal antibodies that recognize T lymphocytes or natural killer cells. J Exp Med. 1986 Oct 1;164(4):1145–1159. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.4.1145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters D. K., Rees A. J., Lockwood C. M., Pusey C. D. Treatment and prognosis in antibasement membrane antibody-mediated nephritis. Transplant Proc. 1982 Sep;14(3):513–521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pusey C. D., Bowman C., Morgan A., Weetman A. P., Hartley B., Lockwood C. M. Kinetics and pathogenicity of autoantibodies induced by mercuric chloride in the brown Norway rat. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 Jul;81(1):76–82. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb05294.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pusey C. D., Holland M. J., Cashman S. J., Sinico R. A., Lloveras J. J., Evans D. J., Lockwood C. M. Experimental autoimmune glomerulonephritis induced by homologous and isologous glomerular basement membrane in Brown-Norway rats. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1991;6(7):457–465. doi: 10.1093/ndt/6.7.457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds J., Cashman S. J., Evans D. J., Pusey C. D. Cyclosporin A in the prevention and treatment of experimental autoimmune glomerulonephritis in the brown Norway rat. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991 Jul;85(1):28–32. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1991.tb05677.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds J., Sallie B. A., Syrganis C., Pusey C. D. The role of T-helper lymphocytes in priming for experimental autoimmune glomerulonephritis in the BN rat. J Autoimmun. 1993 Oct;6(5):571–585. doi: 10.1006/jaut.1993.1047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEBLAY R. W. Glomerulonephritis induced in sheep by injections of heterologous glomerular basement membrane and Freund's complete adjuvant. J Exp Med. 1962 Aug 1;116:253–272. doi: 10.1084/jem.116.2.253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sado Y., Kagawa M., Naito I., Okigaki T. Properties of bovine nephritogenic antigen that induces anti-GBM nephritis in rats and its similarity to the Goodpasture antigen. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1991;60(5):345–351. doi: 10.1007/BF02899566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sado Y., Naito I. Experimental autoimmune glomerulonephritis in rats by soluble isologous or homologous antigens from glomerular and tubular basement membranes. Br J Exp Pathol. 1987 Oct;68(5):695–704. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sado Y., Okigaki T., Takamiya H., Seno S. Experimental autoimmune glomerulonephritis with pulmonary hemorrhage in rats. The dose-effect relationship of the nephritogenic antigen from bovine glomerular basement membrane. J Clin Lab Immunol. 1984 Dec;15(4):199–204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage C. O., Pusey C. D., Bowman C., Rees A. J., Lockwood C. M. Antiglomerular basement membrane antibody mediated disease in the British Isles 1980-4. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1986 Feb 1;292(6516):301–304. doi: 10.1136/bmj.292.6516.301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schorlemmer H. U., Kanzy E. J., Kurrle R., Seiler F. R. Inhibitory effects of the anti-rat T-cell receptor (TCR) monoclonal antibody (MAb) R73 on various experimental autoimmune diseases. Agents Actions. 1991 Sep;34(1-2):161–164. doi: 10.1007/BF01993266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinha A. A., Lopez M. T., McDevitt H. O. Autoimmune diseases: the failure of self tolerance. Science. 1990 Jun 15;248(4961):1380–1388. doi: 10.1126/science.1972595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steblay R. W., Rudofsky U. H. Experimental autoimmune antiglomerular basement membrane antibody-induced glomerulonephritis. I. The effects of injecting sheep with human, homologous or autologous lung basement membranes and complete Freund's adjuvant. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1983 Apr;27(1):65–80. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(83)90057-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuffers-Heiman M., Günther E., van Es L. A. Induction of autoimmunity to antigens of the glomerular basement membrane in inbred Brown-Norway rats. Immunology. 1979 Apr;36(4):759–767. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner N., Mason P. J., Brown R., Fox M., Povey S., Rees A., Pusey C. D. Molecular cloning of the human Goodpasture antigen demonstrates it to be the alpha 3 chain of type IV collagen. J Clin Invest. 1992 Feb;89(2):592–601. doi: 10.1172/JCI115625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van den Broek M. F., Van de Langerijt L. G., Van Bruggen M. C., Billingham M. E., Van den Berg W. B. Treatment of rats with monoclonal anti-CD4 induces long-term resistance to streptococcal cell wall-induced arthritis. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Jan;22(1):57–61. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldor M. K., Sriram S., Hardy R., Herzenberg L. A., Herzenberg L. A., Lanier L., Lim M., Steinman L. Reversal of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis with monoclonal antibody to a T-cell subset marker. Science. 1985 Jan 25;227(4685):415–417. doi: 10.1126/science.3155574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C. B., Dixon F. J. Anti-glomerular basement membrane antibody-induced glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int. 1973 Feb;3(2):74–89. doi: 10.1038/ki.1973.14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wraith D. C., McDevitt H. O., Steinman L., Acha-Orbea H. T cell recognition as the target for immune intervention in autoimmune disease. Cell. 1989 Jun 2;57(5):709–715. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90786-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshino S., Schlipköter E., Kinne R., Hünig T., Emmrich F. Suppression and prevention of adjuvant arthritis in rats by a monoclonal antibody to the alpha/beta T cell receptor. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Dec;20(12):2805–2808. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830201241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]