Abstract
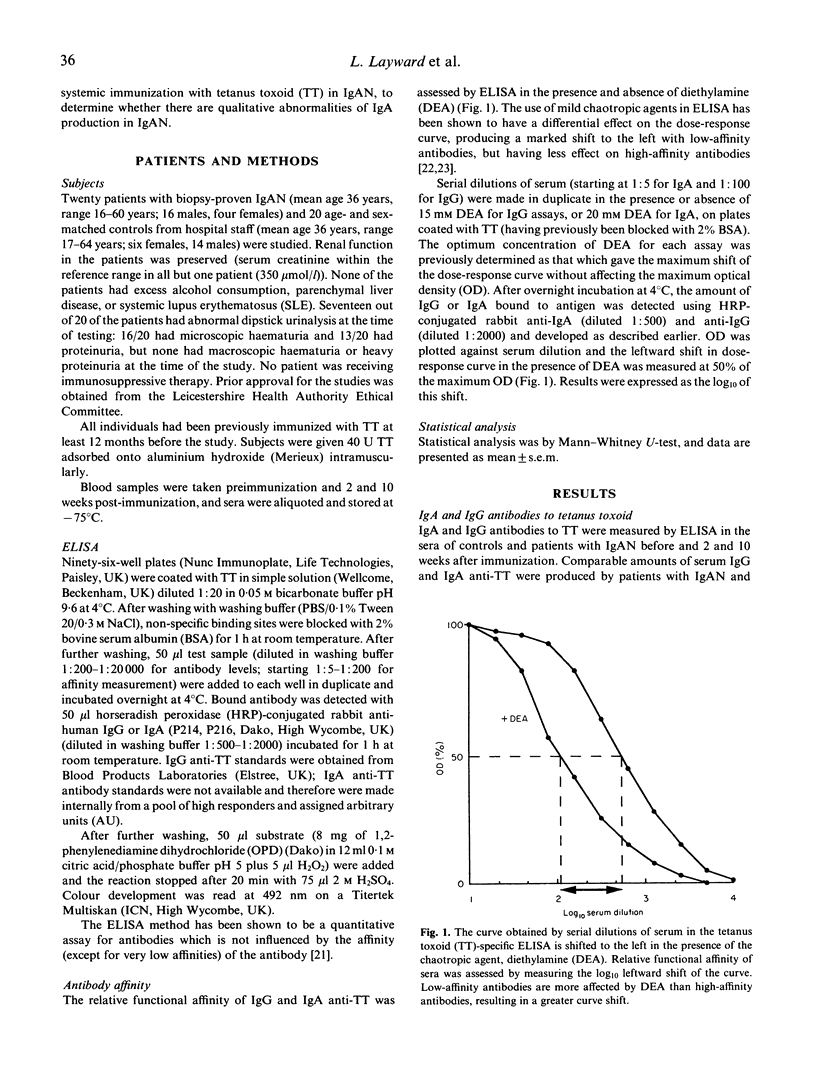
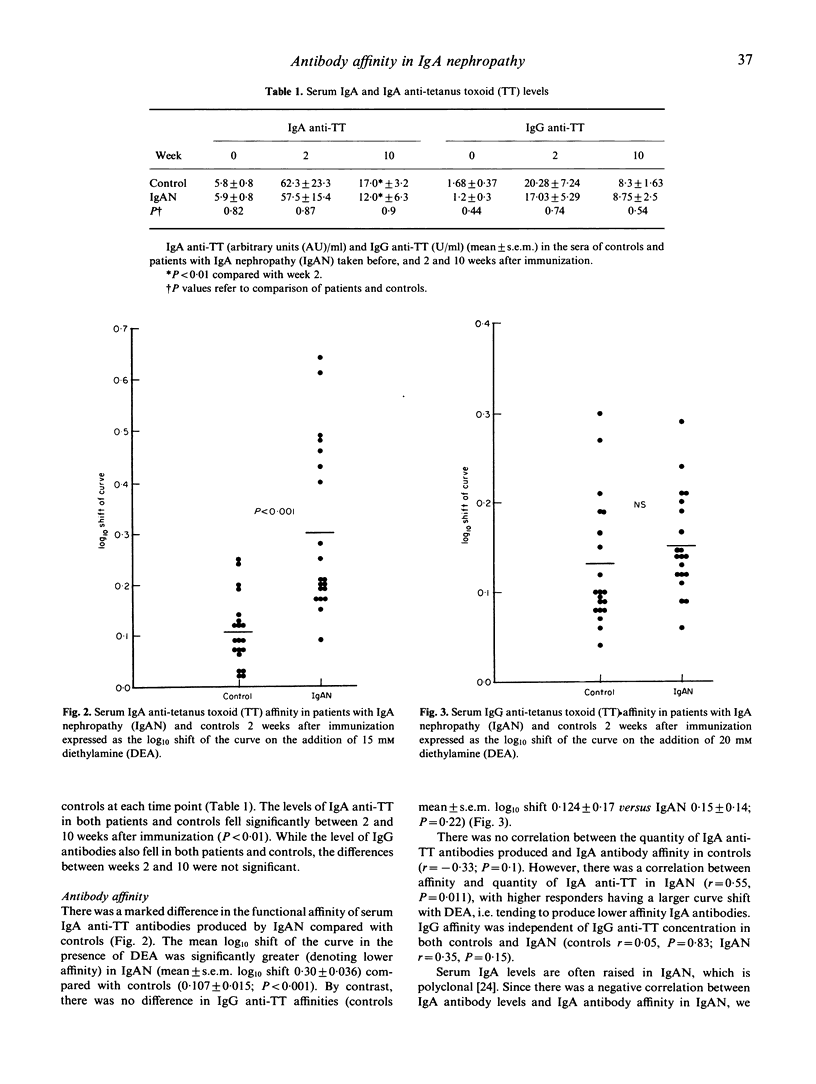
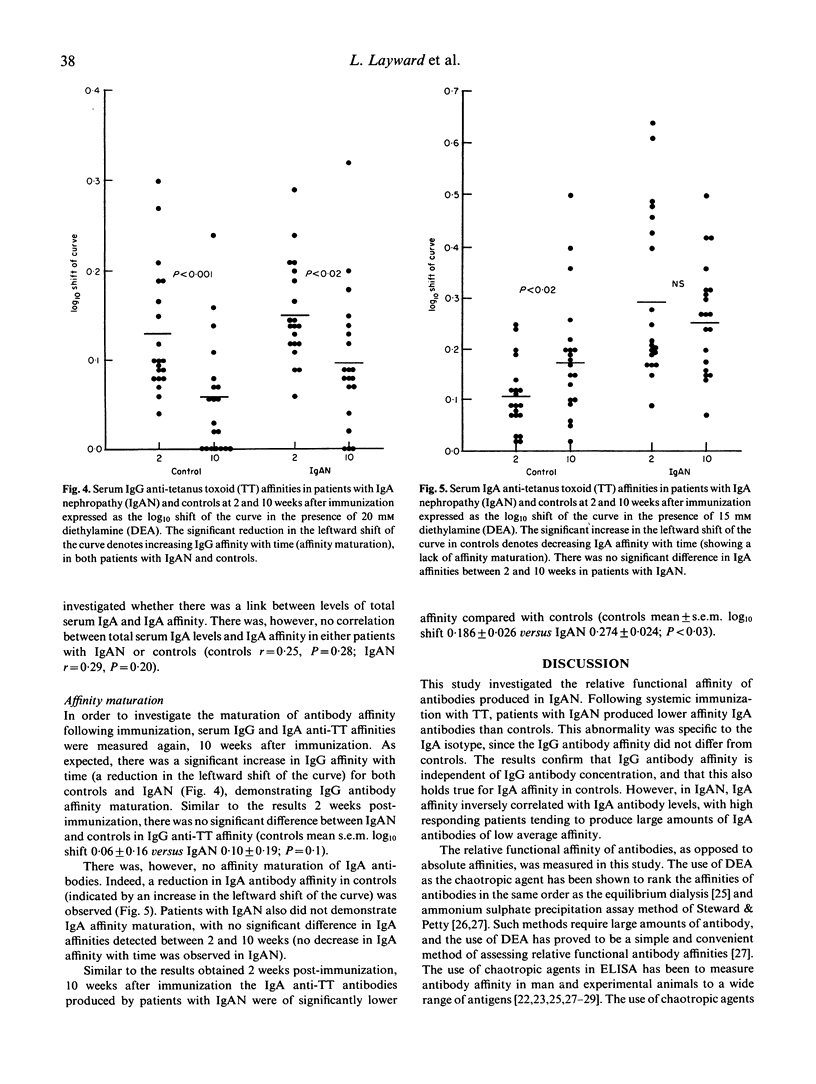
Antibody affinity affects the handling and behaviour of immune complexes, and experimental studies have shown that animals which produce predominantly low-affinity antibody are prone to immune complex deposition resulting in glomerulonephritis. In order to investigate the potential role of antibody affinity in the pathogenesis of IgA nephropathy, affinity of both IgA and IgG antibody isotypes during secondary response to systemic immunization with tetanus toxoid was studied in 20 patients with IgA nephropathy. Patients with IgA nephropathy produced IgA antibodies of significantly lower affinity than controls (P < 0.001), whereas IgG antibody affinities were similar. Contrasting with controls, patients' IgA antibody affinity was inversely related to antibody concentration, with higher responders producing large amounts of low-affinity antibody. IgG antibody affinity increased with time, and maturation of IgG antibody affinity was similar in both controls and patients. IgA affinity in controls decreased with time, and this lack of IgA affinity maturation may explain the relative unimportance of IgA in normal systemic immunity. This temporal decrease in IgA affinity was not observed in patients with IgA nephropathy. The production of low-affinity IgA in IgA nephropathy may provide an explanation for the predominant deposition of IgA in this disease.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alpers J. H., Steward M. W., Soothill J. F. Differences in immune elimination in inbred mice. The role of low affinity antibody. Clin Exp Immunol. 1972 Sep;12(1):121–132. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron J. S., Clark W. F. A role for insoluble antibody-antigen complexes in glomerulonephritis? Clin Nephrol. 1982 Aug;18(2):55–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conley M. E., Briles D. E. Lack of IgA subclass restriction in antibody response to phosphorylcholine, beta lactoglobulin and tetanus toxoid. Immunology. 1984 Nov;53(3):419–426. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeKruyff R., Siskind G. W. Studies on the control of antibody synthesis. XIV. Role of T cells in regulating antibody affinity. Cell Immunol. 1979 Sep 15;47(1):134–142. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(79)90321-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devey M. E., Bleasdale-Barr K. M., Bird P., Amlot P. L. Antibodies of different human IgG subclasses show distinct patterns of affinity maturation after immunization with keyhole limpet haemocyanin. Immunology. 1990 Jun;70(2):168–174. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devey M. E., Bleasdale K. M., French M. A., Harrison G. The IgG4 subclass is associated with a low affinity antibody response to tetanus toxoid in man. Immunology. 1985 Jul;55(3):565–567. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devey M. E., Bleasdale K., Collins M., Steward M. W. Experimental antigen-antibody complex disease in mice. The role of antibody levels, antibody affinity and circulating antigen-antibody complexes. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1982;68(1):47–53. doi: 10.1159/000233066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devey M. E., Bleasdale K., Isenberg D. A. Antibody affinity and IgG subclass of responses to tetanus toxoid in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1987 Jun;68(3):562–569. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devey M. E., Bleasdale K., Lee S., Rath S. Determination of the functional affinity of IgG1 and IgG4 antibodies to tetanus toxoid by isotype-specific solid-phase assays. J Immunol Methods. 1988 Jan 21;106(1):119–125. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(88)90279-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devey M. E., Bleasdale K., Stanley C., Steward M. W. Failure of affinity maturation leads to increased susceptibility to immune complex glomerulonephritis. Immunology. 1984 Jun;52(2):377–383. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devey M. E., Major P. J., Bleasdale-Barr K. M., Holland G. P., Dal Canto M. C., Paterson P. Y. Experimental allergic encephalomyelitis (EAE) in mice selectively bred to produce high affinity (HA) or low affinity (LA) antibody responses. Immunology. 1990 Apr;69(4):519–524. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devey M. E., Steward M. W. The induction of chronic antigen-antibody complex disease in selectively bred mice producing either high or low affinity antibody to protein antigens. Immunology. 1980 Oct;41(2):303–311. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebling F., Hahn B. H. Restricted subpopulations of DNA antibodies in kidneys of mice with systemic lupus. Comparison of antibodies in serum and renal eluates. Arthritis Rheum. 1980 Apr;23(4):392–403. doi: 10.1002/art.1780230402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feehally J. Immune mechanisms in glomerular IgA deposition. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1988;3(4):361–378. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.ndt.a091683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germuth F. G., Jr, Rodriguez E., Lorelle C. A., Trump E. I., Milano L. L., Wise O. Passive immune complex glomerulonephritis in mice: models for various lesions found in human disease. II. Low avidity complexes and diffuse proliferative glomerulonephritis with subepithelial deposits. Lab Invest. 1979 Oct;41(4):366–371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germuth F. G., Rodriguez E., Wise O. L. Passive immune complex glomerulonephritis in mice. III. Clearance kinetics and properties of circulating complexes. Lab Invest. 1982 May;46(5):515–519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregory M. C., Hammond M. E., Brewer E. D. Renal deposition of cytomegalovirus antigen in immunoglobulin-A nephropathy. Lancet. 1988 Jan 2;1(8575-6):11–14. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)91000-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths G. M., Berek C., Kaartinen M., Milstein C. Somatic mutation and the maturation of immune response to 2-phenyl oxazolone. Nature. 1984 Nov 15;312(5991):271–275. doi: 10.1038/312271a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland G. P., Steward M. W. Antibody affinity maturation: the role of CD8+ cells. Clin Exp Immunol. 1989 Dec;78(3):488–493. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye S., Hasegawa A., Matsuno S., Katow S. Changes in antibody avidity after virus infections: detection by an immunosorbent assay in which a mild protein-denaturing agent is employed. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Sep;20(3):525–529. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.3.525-529.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kocks C., Rajewsky K. Stepwise intraclonal maturation of antibody affinity through somatic hypermutation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):8206–8210. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.8206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koyama A., Inage H., Kobayashi M., Ohta Y., Narita M., Tojo S., Cameron J. S. Role of antigenic charge and antibody avidity on the glomerular immune complex localization in serum sickness of mice. Clin Exp Immunol. 1986 Jun;64(3):606–614. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai K. N., Lai F. M., Tam J. S., Vallance-Owen J. Strong association between IgA nephropathy and hepatitis B surface antigenemia in endemic areas. Clin Nephrol. 1988 May;29(5):229–234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Layward L., Allen A. C., Harper S. J., Hattersley J. M., Feehally J. Increased and prolonged production of specific polymeric IgA after systemic immunization with tetanus toxoid in IgA nephropathy. Clin Exp Immunol. 1992 Jun;88(3):394–398. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1992.tb06460.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luxton R. W., Thompson E. J. Affinity distributions of antigen-specific IgG in patients with multiple sclerosis and in patients with viral encephalitis. J Immunol Methods. 1990 Aug 7;131(2):277–282. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(90)90199-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mascart-Lemone F., Duchateau J., Conley M. E., Delacroix D. L. A polymeric IgA response in serum can be produced by parenteral immunization. Immunology. 1987 Aug;61(4):409–413. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donoghue D. J., Darvill A., Ballardie F. W. Mesangial cell autoantigens in immunoglobulin A nephropathy and Henoch-Schönlein purpura. J Clin Invest. 1991 Nov;88(5):1522–1530. doi: 10.1172/JCI115462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petty R. E., Steward M. W. Relative affinity of anti-protein antibodies in New Zealand mice. Clin Exp Immunol. 1972 Nov;12(3):343–350. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pullen G. R., Fitzgerald M. G., Hosking C. S. Antibody avidity determination by ELISA using thiocyanate elution. J Immunol Methods. 1986 Jan 22;86(1):83–87. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(86)90268-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rifai A. Characteristics of nephritogenic IgA immune complexes. Am J Kidney Dis. 1988 Nov;12(5):402–405. doi: 10.1016/s0272-6386(88)80034-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato M., Kojima H., Takayama K., Koshikawa S. Glomerular deposition of food antigens in IgA nephropathy. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Aug;73(2):295–299. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siskind G. W., Benacerraf B. Cell selection by antigen in the immune response. Adv Immunol. 1969;10:1–50. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60414-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sodoyez J. C., Koch M., Lemaire I., Sodoyez-Goffaux F., Rapaille A., François-Gérard C., Sondag D. Influence of affinity of antibodies upon their detection by liquid phase radiobinding assay and solid phase enzyme linked immunosorbent assay. Demonstration using monoclonal antibodies raised against rDNA human proinsulin. Diabetologia. 1991 Jul;34(7):463–468. doi: 10.1007/BF00403281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soothill J. F., Steward M. W. The immunopathological significance of the heterogeneity of antibody affinity. Clin Exp Immunol. 1971 Aug;9(2):193–199. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staines N. A., Ekong T. A., Thompson H. S., Isaacs A. B., Loryman B., Major P. J., Hobbs S. M., Devey M. E. Low affinity antibodies against collagen type II are associated with pathology in collagen-induced arthritis in mice. J Autoimmun. 1990 Dec;3(6):643–657. doi: 10.1016/s0896-8411(05)80032-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steward M. W. Chronic immune complex disease in mice: the role of antibody affinity. Clin Exp Immunol. 1979 Dec;38(3):414–423. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steward M. W., Reinhardt M. C., Staines N. A. The genetic control of antibody affinity. Evidence from breeding studies with mice selectively bred for either high or low affinity antibody production. Immunology. 1979 Jul;37(3):697–703. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takemori T., Tada T. Selective roles of thymus-derived lymphocytes in the antibody response. II. Preferential suppression of high-affinity antibody-forming cells by carrier-primed suppressor T cells. J Exp Med. 1974 Jul 1;140(1):253–266. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.1.253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vignali D. A., Devey M. E., Bickle Q. D., Taylor M. G. The role of antibody affinity and titre in immunity to Schistosoma mansoni following vaccination with highly irradiated cercariae. Immunology. 1990 Feb;69(2):195–201. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wen Y. M., Duan S. C., Howard C. R., Frew A. F., Steward M. W. The affinity of anti-HBc antibodies in acute and chronic hepatitis B infection. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 Jan;79(1):83–86. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb05131.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodroffe A. J., Gormly A. A., McKenzie P. E., Wootton A. M., Thompson A. J., Seymour A. E., Clarkson A. R. Immunologic studies in IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int. 1980 Sep;18(3):366–374. doi: 10.1038/ki.1980.147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Wall Bake A. W., Beyer W. E., Evers-Schouten J. H., Hermans J., Daha M. R., Masurel N., van Es L. A. Humoral immune response to influenza vaccination in patients with primary immunoglobulin A nephropathy. An analysis of isotype distribution and size of the influenza-specific antibodies. J Clin Invest. 1989 Oct;84(4):1070–1075. doi: 10.1172/JCI114269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


