Abstract
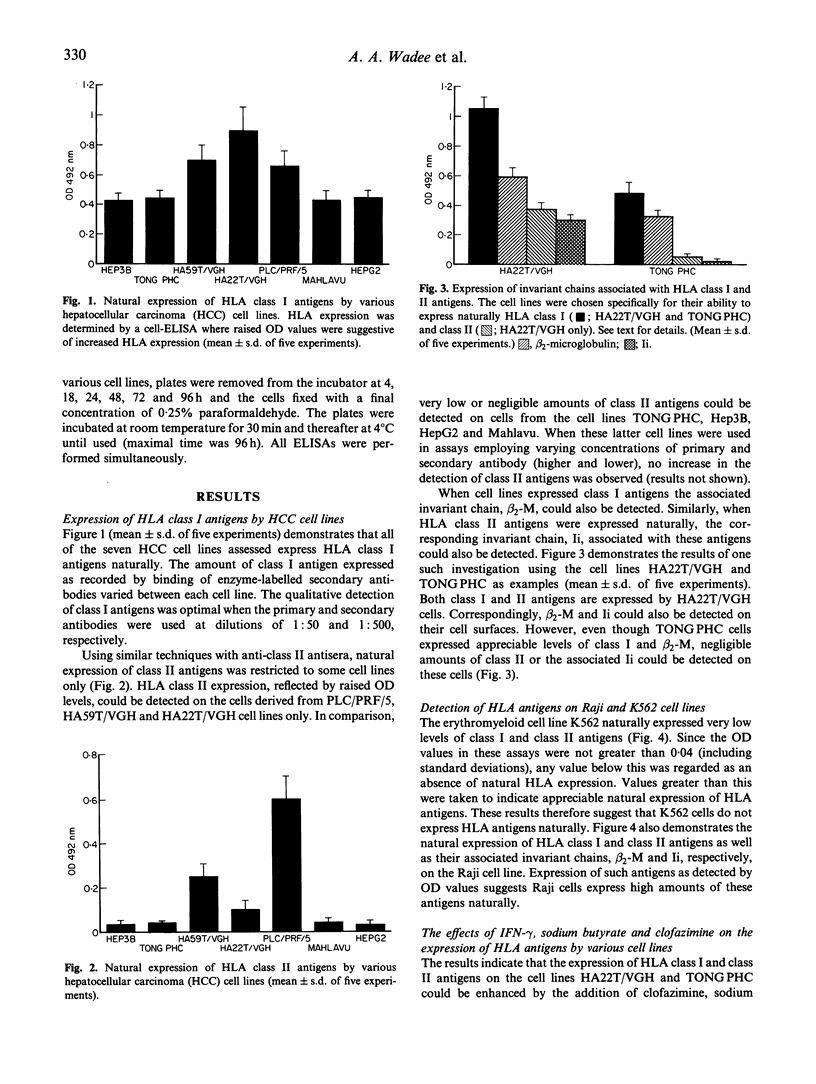
The present study undertook to investigate the biological significance of human leucocyte antigen expression in hepatocellular carcinoma and to elucidate the role of potential modulating agents on human leucocyte antigen expression. These studies used several hepatic tumour-derived cell lines as in vitro model systems. The cell lines included PLC/PRF/5 (Alexander cell line), Hep3B, HepG2, TONG PHC, HA22T/VGH, HA59T/VGH and Mahlavu. The cell lines K562 and Raji were used as negative and positive controls, respectively. K562, a B lymphoid-derived cell line, was shown to express negligible amounts of human leucocyte antigens, while Raji, an erythromyeloid-derived cell line, expressed both class I and class II human leucocyte antigens as well as their respective invariant chains, beta 2-microglobulin and Ii. Using an ELISA, experiments performed on these cell lines confirmed the natural expression of class I and class II antigens by the HA22T/VGH and HA59T/VGH cell lines, whereas PLC/PRF/5 displayed class II surface antigens only. The effects of modulating agents such as interferon-gamma sodium butyrate and clofazimine on human leucocyte antigen expression were investigated using the HA22T/VGH, HA59T/VGH and TONG PHC cell lines. These agents increased class II and class II human leucocyte antigen expression on HA22T/VGH and TONG PHC cells, but had no effect on the HA59T/VGH cell line. The results suggest a potential use for these agents as modulators of human leucocyte antigen expression by human heptocellular cell lines.
Full text
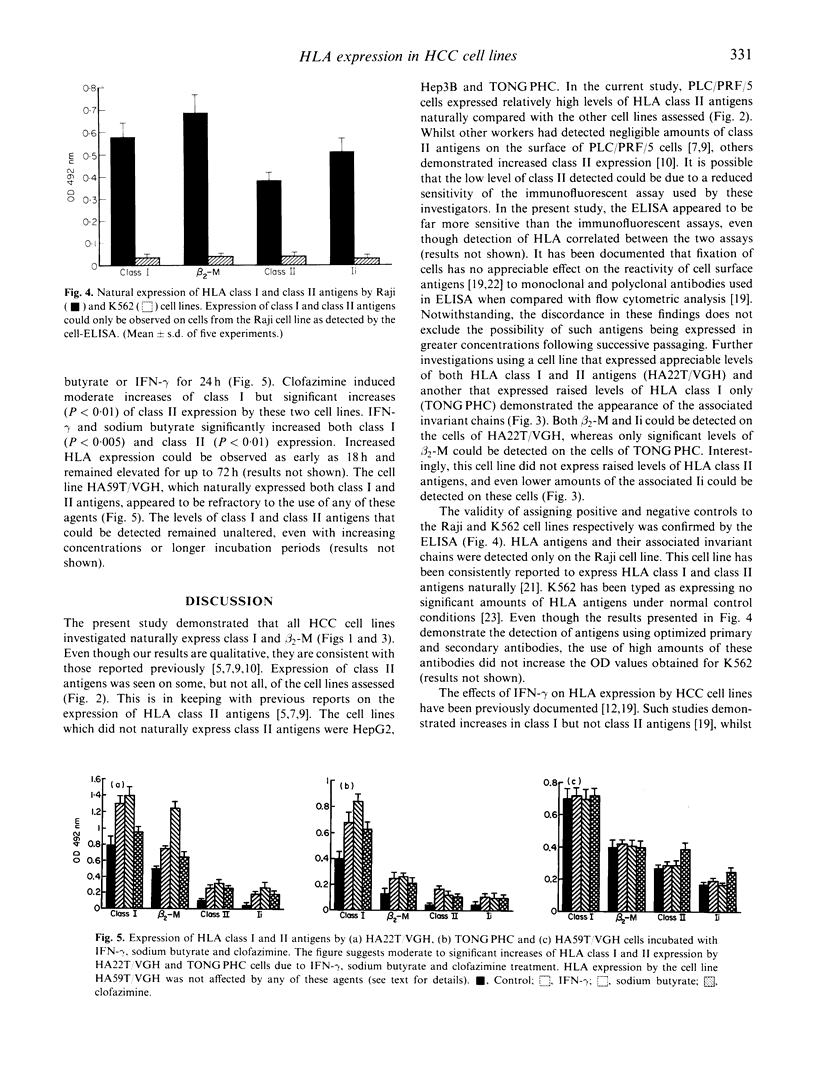
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson R. Enhancement by clofazimine and inhibition by dapsone of production of prostaglandin E2 by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes in vitro. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Feb;27(2):257–262. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.2.257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson R., Lukey P., Van Rensburg C., Dippenaar U. Clofazimine-mediated regulation of human polymorphonuclear leukocyte migration by pro-oxidative inactivation of both leukoattractants and cellular migratory responsiveness. Int J Immunopharmacol. 1986;8(6):605–620. doi: 10.1016/0192-0561(86)90033-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARRY V. C., BELTON J. G., CONALTY M. L., DENNENY J. M., EDWARD D. W., O'SULLIVAN J. F., TWOMEY D., WINDER F. A new series of phenazines (rimino-compounds) with high antituberculosis activity. Nature. 1957 May 18;179(4568):1013–1015. doi: 10.1038/1791013a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt L., Svensson B. Stimulation of macrophage phagocytosis by clofazimine. Scand J Haematol. 1973;10(4):261–264. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1973.tb00070.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cline M. J. Drug potentiation of macrophage function. Infect Immun. 1970 Nov;2(5):601–605. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.5.601-605.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook J. R., Schwartz C. E., Fausel E. D., Chiu J. F. Effect of sodium butyrate on alpha-fetoprotein gene expression in rat hepatoma cells in vitro. Cancer Res. 1985 Jul;45(7):3215–3219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darlington G. J. Liver cell lines. Methods Enzymol. 1987;151:19–38. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(87)51006-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelmann G. L., Staecker J. L., Richardson A. G. Effect of sodium butyrate on primary cultures of adult rat hepatocytes. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol. 1987 Feb;23(2):86–92. doi: 10.1007/BF02623587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franco A., Barnaba V., Natali P., Balsano C., Musca A., Balsano F. Expression of class I and class II major histocompatibility complex antigens on human hepatocytes. Hepatology. 1988 May-Jun;8(3):449–454. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840080302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukusato T., Gerber M. A., Thung S. N., Ferrone S., Schaffner F. Expression of HLA class I antigens on hepatocytes in liver disease. Am J Pathol. 1986 May;123(2):264–270. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukusato T., Mohamad A., Gerber M. A., Thung S. N. Synergistic effect of 5-azacytidine and gamma-interferon or dimethyl sulfoxide on expression of HLA class I antigens by PLC-PRF-5 cells. Tohoku J Exp Med. 1988 Jun;155(2):117–128. doi: 10.1620/tjem.155.117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatner E. M., Anderson R., van Remsburg C. E., Imkamp F. M. The in vitro and in vivo effects of clofazimine on the motility of neutrophils and transformation of lymphocytes from normal individuals. Lepr Rev. 1982 Jun;53(2):85–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko Y., Nakayama T., Tsukamoto A., Kurokawa K. Alteration of differentiation state of human hepatocytes cultured with novobiocin and butyrate. Cancer Res. 1990 May 15;50(10):3101–3105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leder A., Leder P. Butyric acid, a potent inducer of erythroid differentiation in cultured erythroleukemic cells. Cell. 1975 Jul;5(3):319–322. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90107-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lozzio C. B., Lozzio B. B. Human chronic myelogenous leukemia cell-line with positive Philadelphia chromosome. Blood. 1975 Mar;45(3):321–334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. A., Kurschel E., Osieka R., Schmidt C. G. Clinical pharmacology of sodium butyrate in patients with acute leukemia. Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol. 1987 Sep;23(9):1283–1287. doi: 10.1016/0277-5379(87)90109-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montano L., Miescher G. C., Goodall A. H., Wiedmann K. H., Janossy G., Thomas H. C. Hepatitis B virus and HLA antigen display in the liver during chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatology. 1982 Sep-Oct;2(5):557–561. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840020508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore M., Ghosh A. K. "Aberrant" MHC class II expression in epithelia. Lancet. 1987 Jan 17;1(8525):165–165. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)92004-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagawa T., Nakao Y., Matsui T., Koizumi T., Matsuda S., Maeda S., Fujita T. Effects of sodium n-butyrate on alpha-fetoprotein and albumin secretion in the human hepatoma cell line PLC/PRF/5. Br J Cancer. 1985 Mar;51(3):357–363. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1985.47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nibbering P. H., Van de Gevel J. S., Van Furth R. A cell-ELISA for the quantification of adherent murine macrophages and the surface expression of antigens. J Immunol Methods. 1990 Jul 20;131(1):25–32. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(90)90228-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson K., Evrin P. E., Welsh K. I. Production of beta 2-microglobulin by normal and malignant human cell lines and peripheral lymphocytes. Transplant Rev. 1974;21(0):53–84. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1974.tb01546.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PULVERTAFT J. V. A STUDY OF MALIGNANT TUMOURS IN NIGERIA BY SHORT-TERM TISSUE CULTURE. J Clin Pathol. 1965 May;18:261–273. doi: 10.1136/jcp.18.3.261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parak R. B., Wadee A. A. The synergistic effects of gamma interferon and clofazimine on phagocyte function: restoration of inhibition due to a 25 kilodalton fraction from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Biotherapy. 1991;3(3):265–272. doi: 10.1007/BF02171691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson A. C., Sciot R., Kew M. C., Callea F., Dusheiko G. M., Desmet V. J. HLA expression in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 1988 Apr;57(4):369–373. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1988.84. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters M., Vierling J., Gershwin M. E., Milich D., Chisari F. V., Hoofnagle J. H. Immunology and the liver. Hepatology. 1991 May;13(5):977–994. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggs M. G., Whittaker R. G., Neumann J. R., Ingram V. M. n-Butyrate causes histone modification in HeLa and Friend erythroleukaemia cells. Nature. 1977 Aug 4;268(5619):462–464. doi: 10.1038/268462a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders M. E., Makgoba M. W., Sharrow S. O., Stephany D., Springer T. A., Young H. A., Shaw S. Human memory T lymphocytes express increased levels of three cell adhesion molecules (LFA-3, CD2, and LFA-1) and three other molecules (UCHL1, CDw29, and Pgp-1) and have enhanced IFN-gamma production. J Immunol. 1988 Mar 1;140(5):1401–1407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarracent J., Finlay C. M. The action of Clofazimine on the level of lysosomal enzymes of cultured macrophages. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Apr;48(1):261–267. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimonkevitz R., Kappler J., Marrack P., Grey H. Antigen recognition by H-2-restricted T cells. I. Cell-free antigen processing. J Exp Med. 1983 Aug 1;158(2):303–316. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.2.303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sung C. H., Hu C. P., Hsu H. C., Ng A. K., Chou C. K., Ting L. P., Su T. S., Han S. H., Chang C. M. Expression of class I and class II major histocompatibility antigens on human hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin Invest. 1989 Feb;83(2):421–429. doi: 10.1172/JCI113900. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ucer U., Bartsch H., Scheurich P., Pfizenmaier K. Biological effects of gamma-interferon on human tumor cells: quantity and affinity of cell membrane receptors for gamma-IFN in relation to growth inhibition and induction of HLA-DR expression. Int J Cancer. 1985 Jul 15;36(1):103–108. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910360116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Rensburg C. E., Van Staden A. M., Anderson R. The riminophenazine agents clofazimine and B669 inhibit the proliferation of cancer cell lines in vitro by phospholipase A2-mediated oxidative and nonoxidative mechanisms. Cancer Res. 1993 Jan 15;53(2):318–323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vischer W. A. The experimental properties of G 30 320 (B 663)--a new anti-leprotic agent. Lepr Rev. 1969 Apr;40(2):107–110. doi: 10.5935/0305-7518.19690021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volpes R., van den Oord J. J., Desmet V. J. Can hepatocytes serve as 'activated' immunomodulating cells in the immune response? J Hepatol. 1992 Sep;16(1-2):228–240. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(05)80121-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadee A. A., Anderson R., Rabson A. R. Clofazimine reverses the inhibitory effect of Mycobacterium tuberculosis derived factors on phagocyte intracellular killing mechanisms. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1988 Jan;21(1):65–74. doi: 10.1093/jac/21.1.65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadee A. A., Cohen J. D., Rabson A. R. Gamma interferon reverses inhibition of leukocyte bactericidal activity by a 25-kilodalton fraction from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Infect Immun. 1987 Nov;55(11):2777–2782. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.11.2777-2782.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yawalkar S. J., Vischer W. Lamprene (clofazimine) in leprosy. Basic information. Lepr Rev. 1979 Jun;50(2):135–144. doi: 10.5935/0305-7518.19790020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshioka K., Kakumu S., Tahara H., Arao M., Fuji A. Effect of interferon alpha, gamma, and tumor necrosis factor alpha on the HLA-A, B, C expression of cell lines derived from human liver. Liver. 1989 Feb;9(1):14–19. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0676.1989.tb00372.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou D. X., Taraboulos A., Ou J. H., Yen T. S. Activation of class I major histocompatibility complex gene expression by hepatitis B virus. J Virol. 1990 Aug;64(8):4025–4028. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.8.4025-4028.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Haan J. B., Gevers W., Parker M. I. Effects of sodium butyrate on the synthesis and methylation of DNA in normal cells and their transformed counterparts. Cancer Res. 1986 Feb;46(2):713–716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Oord J. J., de Vos R., Desmet V. J. In situ distribution of major histocompatibility complex products and viral antigens in chronic hepatitis B virus infection: evidence that HBc-containing hepatocytes may express HLA-DR antigens. Hepatology. 1986 Sep-Oct;6(5):981–989. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840060529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


