Abstract
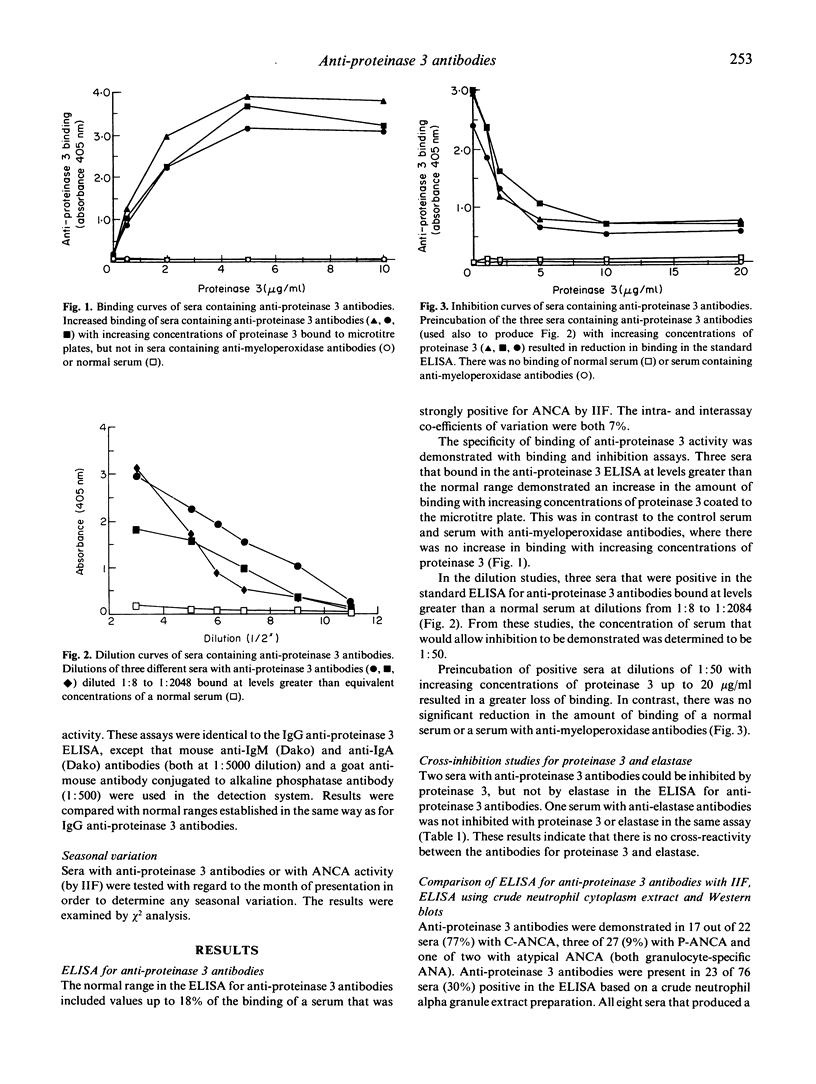
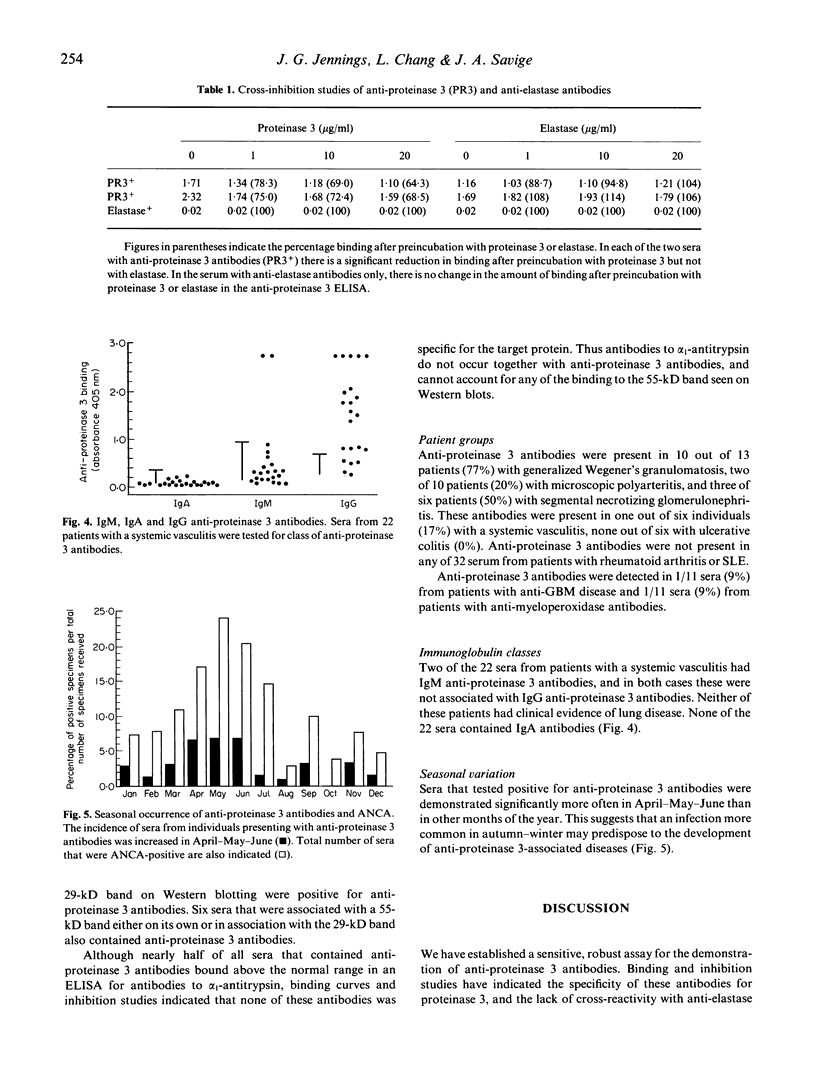
Anti-proteinase 3 antibodies are a subgroup of anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (ANCA), and we have established an ELISA for their detection using high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC)-purified protein. This assay is sensitive and specific: inhibition studies have shown that despite the homology between proteinase 3 and elastase there is no cross-reactivity between the corresponding antibodies for their targets. Anti-proteinase 3 antibodies were associated most often with cytoplasmic fluorescence (17/22, 77%), but occasionally with a perinuclear (3/22, 14%) or atypical pattern (1/2). These antibodies were found in 23 out of 76 sera (30%) that were positive in an ELISA based on a crude neutrophil cytoplasmic extract, and they were associated with both 29 and 55 kD bands on Western blots. Anti-proteinase 3 antibodies were found in most individuals with active Wegener's granulomatosis (10/13, 77%), but less often in individuals with microscopic polyarteritis (2/10, 20%) or segmental necrotizing glomerulonephritis (3/6, 50%). However, anti-proteinase 3 antibodies were not detected in any of 32 sera from individuals with rheumatoid arthritis or systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Occasionally anti-proteinase 3 antibodies were associated with anti-glomerular basement membrane antibodies (1/11, 9%) or with anti-myeloperoxidase antibodies (1/11, 9%). IgM anti-proteinase 3 antibodies were uncommon (2/22 sera, 9%), and no IgA antibodies were demonstrated in any of 22 sera from patients with active systemic vasculitis. Significantly more individuals presented with anti-proteinase 3 antibodies in April-May-June, suggesting that an infective agent prevalent in Autumn might have a causative role in the associated diseases. Anti-proteinase 3 antibodies are the most common target antigen associated with Wegener's granulomatosis and cytoplasmic fluorescence.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bini P., Gabay J. E., Teitel A., Melchior M., Zhou J. L., Elkon K. B. Antineutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibodies in Wegener's granulomatosis recognize conformational epitope(s) on proteinase 3. J Immunol. 1992 Aug 15;149(4):1409–1415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bories D., Raynal M. C., Solomon D. H., Darzynkiewicz Z., Cayre Y. E. Down-regulation of a serine protease, myeloblastin, causes growth arrest and differentiation of promyelocytic leukemia cells. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):959–968. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90752-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Csernok E., Lüdemann J., Gross W. L., Bainton D. F. Ultrastructural localization of proteinase 3, the target antigen of anti-cytoplasmic antibodies circulating in Wegener's granulomatosis. Am J Pathol. 1990 Nov;137(5):1113–1120. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies D. J., Moran J. E., Niall J. F., Ryan G. B. Segmental necrotising glomerulonephritis with antineutrophil antibody: possible arbovirus aetiology? 1982 Aug 28-Sep 4Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 285(6342):606–606. doi: 10.1136/bmj.285.6342.606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk R. J., Jennette J. C. Anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibodies with specificity for myeloperoxidase in patients with systemic vasculitis and idiopathic necrotizing and crescentic glomerulonephritis. N Engl J Med. 1988 Jun 23;318(25):1651–1657. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198806233182504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabay J. E., Scott R. W., Campanelli D., Griffith J., Wilde C., Marra M. N., Seeger M., Nathan C. F. Antibiotic proteins of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5610–5614. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschmeding R., van der Schoot C. E., ten Bokkel Huinink D., Hack C. E., van den Ende M. E., Kallenberg C. G., von dem Borne A. E. Wegener's granulomatosis autoantibodies identify a novel diisopropylfluorophosphate-binding protein in the lysosomes of normal human neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 1989 Nov;84(5):1577–1587. doi: 10.1172/JCI114335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jayne D. R., Jones S. J., Severn A., Shaunak S., Murphy J., Lockwood C. M. Severe pulmonary hemorrhage and systemic vasculitis in association with circulating anti-neutrophil cytoplasm antibodies of IgM class only. Clin Nephrol. 1989 Sep;32(3):101–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennette J. C. Antineutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibody-associated diseases: a pathologist's perspective. Am J Kidney Dis. 1991 Aug;18(2):164–170. doi: 10.1016/s0272-6386(12)80874-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao R. C., Wehner N. G., Skubitz K. M., Gray B. H., Hoidal J. R. Proteinase 3. A distinct human polymorphonuclear leukocyte proteinase that produces emphysema in hamsters. J Clin Invest. 1988 Dec;82(6):1963–1973. doi: 10.1172/JCI113816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klaassen R. J., Goldschmeding R., Dolman K. M., Vlekke A. B., Weigel H. M., Eeftinck Schattenkerk J. K., Mulder J. W., Westedt M. L., von dem Borne A. E. Anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibodies in patients with symptomatic HIV infection. Clin Exp Immunol. 1992 Jan;87(1):24–30. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1992.tb06408.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koderisch J., Andrassy K., Rasmussen N., Hartmann M., Tilgen W. "False-positive" anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies in HIV infection. Lancet. 1990 May 19;335(8699):1227–1228. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)92755-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüdemann J., Utecht B., Gross W. L. Anti-neutrophil cytoplasm antibodies in Wegener's granulomatosis recognize an elastinolytic enzyme. J Exp Med. 1990 Jan 1;171(1):357–362. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.1.357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niles J. L., McCluskey R. T., Ahmad M. F., Arnaout M. A. Wegener's granulomatosis autoantigen is a novel neutrophil serine proteinase. Blood. 1989 Nov 1;74(6):1888–1893. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nässberger L., Jonsson H., Sjöholm A. G., Sturfelt G., Heubner A. Circulating anti-elastase in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lancet. 1989 Mar 4;1(8636):509–509. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)91420-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinching A. J., Lockwood C. M., Pussell B. A., Rees A. J., Sweny P., Evans D. J., Bowley N., Peters D. K. Wegener's granulomatosis: observations on 18 patients with severe renal disease. Q J Med. 1983 Autumn;52(208):435–460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinching A. J., Rees A. J., Pussell B. A., Lockwood C. M., Mitchison R. S., Peters D. K. Relapses in Wegener's granulomatosis: the role of infection. Br Med J. 1980 Sep 27;281(6244):836–838. doi: 10.1136/bmj.281.6244.836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage C. O., Winearls C. G., Evans D. J., Rees A. J., Lockwood C. M. Microscopic polyarteritis: presentation, pathology and prognosis. Q J Med. 1985 Aug;56(220):467–483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savige J. A., Gallicchio M. C., Stockman A., Cunningham T. J., Rowley M. J., Georgiou T., Davies D. Anti-neutrophil cytoplasm antibodies in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991 Oct;86(1):92–98. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1991.tb05779.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savige J. A., Gallicchio M. IgA antimyeloperoxidase antibodies associated with crescentic IgA glomerulonephritis. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1992;7(9):952–955. doi: 10.1093/ndt/7.9.952. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savige J. A., Yeung S. P., Gallicchio M., Davies D. J. Two ELISAs to detect anti-neutrophil cytoplasm antibodies (ANCA) in various vasculitides. Pathology. 1989 Oct;21(4):282–287. doi: 10.3109/00313028909061076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxon A., Shanahan F., Landers C., Ganz T., Targan S. A distinct subset of antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies is associated with inflammatory bowel disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1990 Aug;86(2):202–210. doi: 10.1016/s0091-6749(05)80067-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wathen C. W., Harrison D. J. Circulating anti-neutrophil antibodies in systemic vasculitis. Lancet. 1987 May 2;1(8540):1037–1037. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)92310-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilde C. G., Snable J. L., Griffith J. E., Scott R. W. Characterization of two azurphil granule proteases with active-site homology to neutrophil elastase. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 5;265(4):2038–2041. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Woude F. J., Rasmussen N., Lobatto S., Wiik A., Permin H., van Es L. A., van der Giessen M., van der Hem G. K., The T. H. Autoantibodies against neutrophils and monocytes: tool for diagnosis and marker of disease activity in Wegener's granulomatosis. Lancet. 1985 Feb 23;1(8426):425–429. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)91147-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


