Abstract
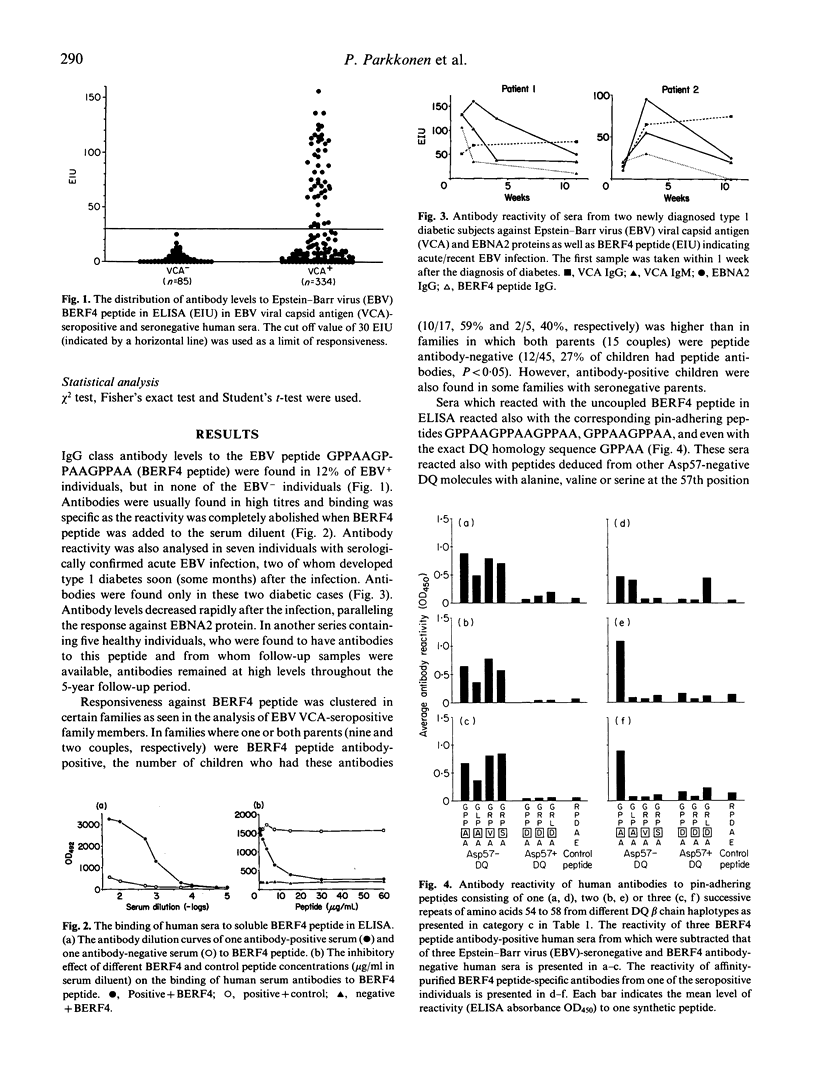
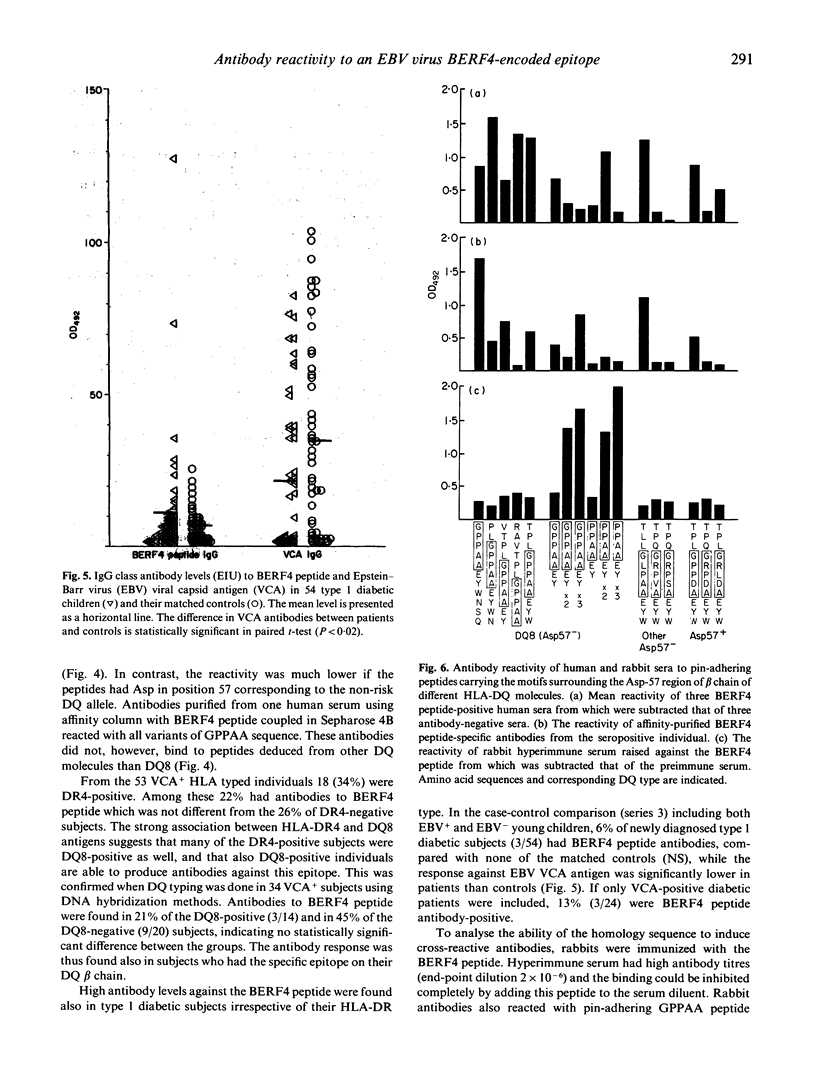
A five amino acids-long sequence (GPPAA) in the region of the 57th amino acid of HLA-DQ8 beta chain, which seems to be important in defining the risk for type 1 diabetes, occurs also in the BERF4-encoded EBNA3C protein of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) in six successive repeats. The antigenicity of this region was analysed using synthetic peptides containing different modifications of the GPPAA sequence. Two of the seven individuals who had acute EBV infection produced antibodies against an EBV-derived peptide (GPPAAGPPAAGPPAA) paralleling the EBNA2 antibodies. These two cases also contracted type 1 diabetes immediately after the infection. High antibody levels against this peptide were found in a total of 12% of EBV+ individuals, and in most cases antibodies remained at high levels for several years. Human sera as well as affinity-purified antibodies specific for the GPPAAGPPAAGPPAA peptide reacted also with shorter peptide analogues (GPPAAGPPAA and GPPAA), as well as with peptides containing the surrounding motifs from DQ8 beta chains. However, none of these antibodies bound to denatured DQ8 beta chains in immunoblotting. The charge of the 57th amino acid modulated the antigenicity of this epitope, as peptides from Asp-57-negative DQ molecules were reactive, while peptides from Asp-57-positive DQ molecules were not. The responsiveness was seen in both HLA-DQ8-positive and -negative subjects as well as in type 1 diabetic individuals. The results suggest that some individuals who carry the GPPAA sequence in their HLA-DQ molecule recognize this epitope in EBV. This phenomenon may have potential importance in EBV-induced immune abnormalities, although cross-reactivity against DQ molecules could not be demonstrated in the present study.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atar D., Dyrberg T., Michelsen B., Karlsen A., Kofod H., Mølvig J., Lernmark A. Site-specific antibodies distinguish single amino acid substitutions in position 57 in HLA-DQ beta-chain alleles associated with insulin-dependent diabetes. J Immunol. 1989 Jul 15;143(2):533–538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bordier C. Phase separation of integral membrane proteins in Triton X-114 solution. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1604–1607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess J. A., Kirkpatrick K. L., Menser M. A. Fulminant onset of diabetes mellitus during an attack of infectious mononucleosis. Med J Aust. 1974 Nov 9;2(19):706–707. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1974.tb71105.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derynck R., Jarrett J. A., Chen E. Y., Eaton D. H., Bell J. R., Assoian R. K., Roberts A. B., Sporn M. B., Goeddel D. V. Human transforming growth factor-beta complementary DNA sequence and expression in normal and transformed cells. Nature. 1985 Aug 22;316(6030):701–705. doi: 10.1038/316701a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujinami R. S., Nelson J. A., Walker L., Oldstone M. B. Sequence homology and immunologic cross-reactivity of human cytomegalovirus with HLA-DR beta chain: a means for graft rejection and immunosuppression. J Virol. 1988 Jan;62(1):100–105. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.1.100-105.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujinami R. S., Oldstone M. B. Molecular mimicry as a mechanism for virus-induced autoimmunity. Immunol Res. 1989;8(1):3–15. doi: 10.1007/BF02918552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geysen H. M., Rodda S. J., Mason T. J., Tribbick G., Schoofs P. G. Strategies for epitope analysis using peptide synthesis. J Immunol Methods. 1987 Sep 24;102(2):259–274. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(87)90085-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giguère V., Yang N., Segui P., Evans R. M. Identification of a new class of steroid hormone receptors. Nature. 1988 Jan 7;331(6151):91–94. doi: 10.1038/331091a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glerum M., Robinson B. H., Martin J. M. Could bovine serum albumin be the initiating antigen ultimately responsible for the development of insulin dependent diabetes mellitus? Diabetes Res. 1989 Mar;10(3):103–107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haspel M. V., Onodera T., Prabhakar B. S., Horita M., Suzuki H., Notkins A. L. Virus-induced autoimmunity: monoclonal antibodies that react with endocrine tissues. Science. 1983 Apr 15;220(4594):304–306. doi: 10.1126/science.6301002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirayama K., Matsushita S., Kikuchi I., Iuchi M., Ohta N., Sasazuki T. HLA-DQ is epistatic to HLA-DR in controlling the immune response to schistosomal antigen in humans. Nature. 1987 Jun 4;327(6121):426–430. doi: 10.1038/327426a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn G. T., Bugawan T. L., Long C. M., Erlich H. A. Allelic sequence variation of the HLA-DQ loci: relationship to serology and to insulin-dependent diabetes susceptibility. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):6012–6016. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.6012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyöty H., Parkkonen P., Rode M., Bakke O., Leinikki P. Common peptide epitope in mumps virus nucleocapsid protein and MHC class II-associated invariant chain. Scand J Immunol. 1993 May;37(5):550–558. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1993.tb02571.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyöty H., Räsänen L., Hiltunen M., Lehtinen M., Huupponen T., Leinikki P. Decreased antibody reactivity to Epstein-Barr virus capsid antigen in type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus. APMIS. 1991 Apr;99(4):359–363. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1991.tb05162.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehtinen T., Lumio J., Dillner J., Hakama M., Knekt P., Lehtinen M., Teppo L., Leinikki P. Increased risk of malignant lymphoma indicated by elevated Epstein-Barr virus antibodies--a prospective study. Cancer Causes Control. 1993 May;4(3):187–193. doi: 10.1007/BF00051312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J., Dolan A., Frame M. C. DNA sequence of the region in the genome of herpes simplex virus type 1 containing the exonuclease gene and neighbouring genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Apr 25;14(8):3435–3448. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.8.3435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misko I. S., Schmidt C., Moss D. J., Burrows S. R., Sculley T. B. Cytotoxic T lymphocyte discrimination between type A Epstein-Barr virus transformants is mapped to an immunodominant epitope in EBNA 3. J Gen Virol. 1991 Feb;72(Pt 2):405–409. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-72-2-405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musiani M., Zerbini M., Ferri S., Plazzi M., Gentilomi G., La Placa M. Comparison of the immune response to Epstein-Barr virus and cytomegalovirus in sera and synovial fluids of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1987 Nov;46(11):837–842. doi: 10.1136/ard.46.11.837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nieda M., Juji T., Imao S., Minami M. A role of HLA-DQ molecules of stimulator-adherent cells in the regulation of human autologous mixed lymphocyte reaction. J Immunol. 1988 Nov 1;141(9):2975–2979. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikoskelainen J., Hänninen P. Antibody response to Epstein-Barr virus in infectious mononucleosis. Infect Immun. 1975 Jan;11(1):42–51. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.1.42-51.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poli V., Mancini F. P., Cortese R. IL-6DBP, a nuclear protein involved in interleukin-6 signal transduction, defines a new family of leucine zipper proteins related to C/EBP. Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):643–653. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90459-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reijonen H., Ilonen J., Knip M., Akerblom H. K. HLA-DQB1 alleles and absence of Asp 57 as susceptibility factors of IDDM in Finland. Diabetes. 1991 Dec;40(12):1640–1644. doi: 10.2337/diab.40.12.1640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reijonen H., Ilonen J., Knip M., Michelsen B., Akerblom H. K. HLA-DQ beta-chain restriction fragment length polymorphism as a risk marker in type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus: a Finnish family study. Diabetologia. 1990 Jun;33(6):357–362. doi: 10.1007/BF00404640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roudier J., Rhodes G., Petersen J., Vaughan J. H., Carson D. A. The Epstein-Barr virus glycoprotein gp110, a molecular link between HLA DR4, HLA DR1, and rheumatoid arthritis. Scand J Immunol. 1988 Apr;27(4):367–371. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1988.tb02359.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe M., Young L. S., Cadwallader K., Petti L., Kieff E., Rickinson A. B. Distinction between Epstein-Barr virus type A (EBNA 2A) and type B (EBNA 2B) isolates extends to the EBNA 3 family of nuclear proteins. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1031–1039. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1031-1039.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sairenji T., Daibata M., Sorli C. H., Qvistbäck H., Humphreys R. E., Ludvigsson J., Palmer J., Landin-Olsson M., Sundkvist G., Michelsen B. Relating homology between the Epstein-Barr virus BOLF1 molecule and HLA-DQw8 beta chain to recent onset type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia. 1991 Jan;34(1):33–39. doi: 10.1007/BF00404022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sample J., Young L., Martin B., Chatman T., Kieff E., Rickinson A., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus types 1 and 2 differ in their EBNA-3A, EBNA-3B, and EBNA-3C genes. J Virol. 1990 Sep;64(9):4084–4092. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.9.4084-4092.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt S. K., Tatsuno G. P., Sommer A. Cloning and characterization of bovine insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 (bIGFBP-3). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Jun 28;177(3):1025–1032. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)90641-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surcel H. M., Ilonen J., Kär M. L., Hyöty H., Leinikki P. Infection by multiple viruses and lymphocyte abnormalities at the diagnosis of diabetes. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1988 May;77(3):471–474. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1988.tb10684.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd J. A., Bell J. I., McDevitt H. O. HLA-DQ beta gene contributes to susceptibility and resistance to insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Nature. 1987 Oct 15;329(6140):599–604. doi: 10.1038/329599a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuomilehto J., Lounamaa R., Tuomilehto-Wolf E., Reunanen A., Virtala E., Kaprio E. A., Akerblom H. K. Epidemiology of childhood diabetes mellitus in Finland--background of a nationwide study of type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus. The Childhood Diabetes in Finland (DiMe) Study Group. Diabetologia. 1992 Jan;35(1):70–76. doi: 10.1007/BF00400854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuomilehto J., Rewers M., Reunanen A., Lounamaa P., Lounamaa R., Tuomilehto-Wolf E., Akerblom H. K. Increasing trend in type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus in childhood in Finland. Analysis of age, calendar time and birth cohort effects during 1965 to 1984. Diabetologia. 1991 Apr;34(4):282–287. doi: 10.1007/BF00405089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turunen H., Vuorio K. A., Leinikki P. O. Determination of IgG, IgM and IgA antibody responses in human toxoplasmosis by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Scand J Infect Dis. 1983;15(3):307–311. doi: 10.3109/inf.1983.15.issue-3.12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weston K., Barrell B. G. Sequence of the short unique region, short repeats, and part of the long repeats of human cytomegalovirus. J Mol Biol. 1986 Nov 20;192(2):177–208. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90359-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Duin M., de Wit J., Odijk H., Westerveld A., Yasui A., Koken M. H., Hoeijmakers J. H., Bootsma D. Molecular characterization of the human excision repair gene ERCC-1: cDNA cloning and amino acid homology with the yeast DNA repair gene RAD10. Cell. 1986 Mar 28;44(6):913–923. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90014-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


