Abstract
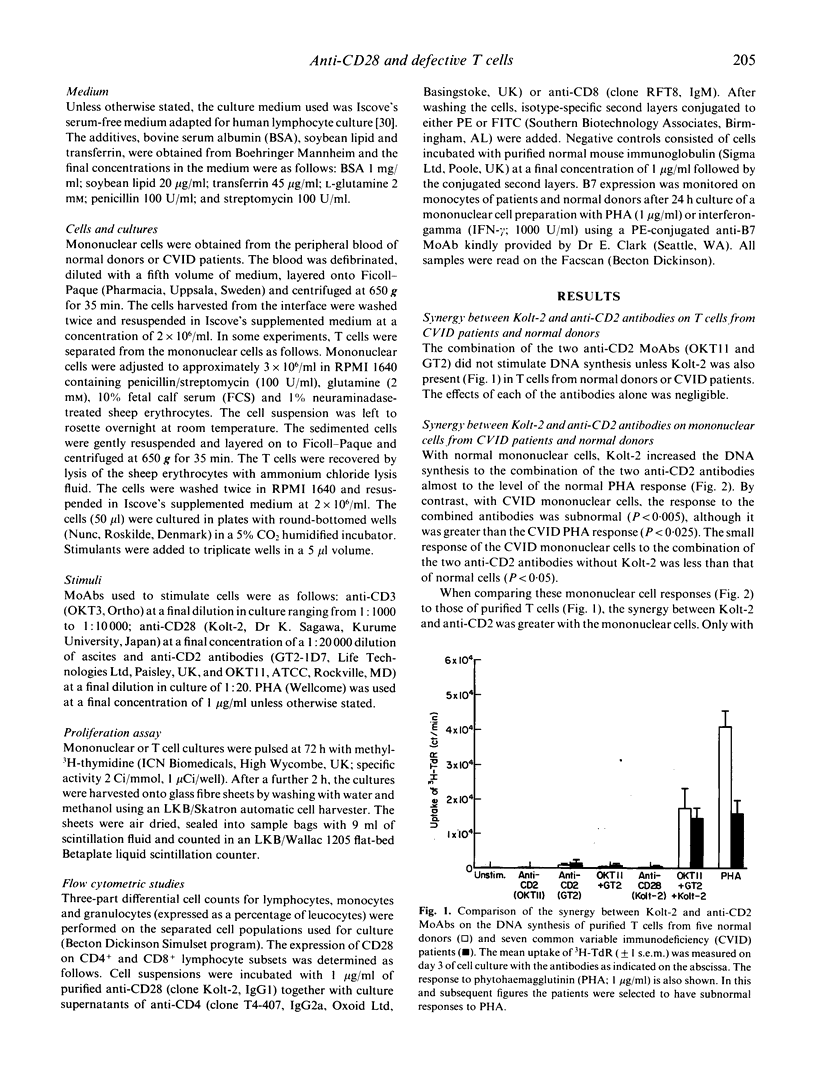
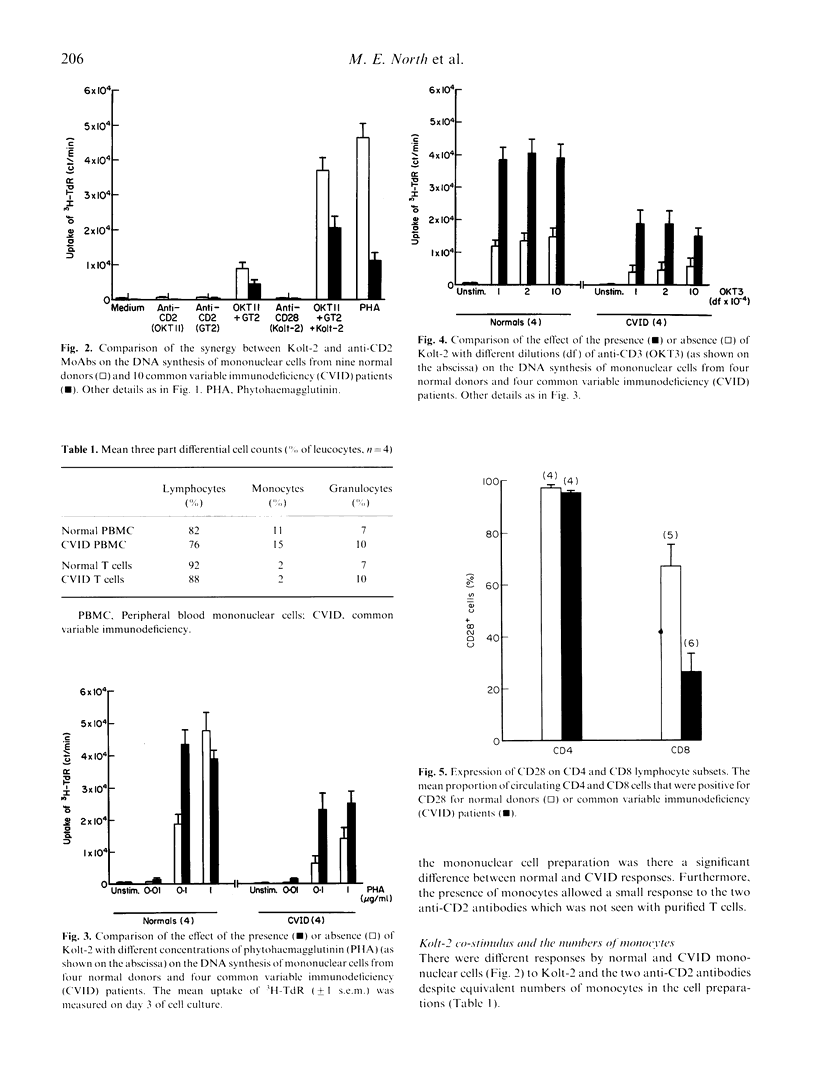
In normal T cells, an anti-CD28 MoAb (Kolt-2) will synergize with the mitogenic stimuli phytohaemagglutinin (PHA), anti-CD3 (OKT3) or a combination of anti-CD2 antibodies (OKT11 and GT2) in the induction of DNA synthesis. A subgroup of patients with common variable immunodeficiency (CVID) show a defect in DNA synthesis by T cells stimulated in vitro with the above mitogens. We have now investigated whether anti-CD28 will correct the defect. This strategy partially restored DNA synthesis, providing evidence that the CD28 co-stimulatory pathway in CVID T cells is normal. Ligation of CD28 acts through co-stimulating IL-2 secretion. The natural ligand (B7) for CD28 on antigen-presenting cells from CVID patients is expressed normally. We conclude that the defect in CVID T cells lies in pathways that lead to transcription of the IL-2 gene other than that induced by ligation of CD28 with Kolt-2.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atluru S., Atluru D. Evidence that genistein, a protein-tyrosine kinase inhibitor, inhibits CD28 monoclonal-antibody-stimulated human T cell proliferation. Transplantation. 1991 Feb;51(2):448–450. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199102000-00035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azuma M., Phillips J. H., Lanier L. L. CD28- T lymphocytes. Antigenic and functional properties. J Immunol. 1993 Feb 15;150(4):1147–1159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant A., Calver N. C., Toubi E., Webster A. D., Farrant J. Classification of patients with common variable immunodeficiency by B cell secretion of IgM and IgG in response to anti-IgM and interleukin-2. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1990 Aug;56(2):239–248. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(90)90145-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham-Rundles C. Clinical and immunologic analyses of 103 patients with common variable immunodeficiency. J Clin Immunol. 1989 Jan;9(1):22–33. doi: 10.1007/BF00917124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrant J., Newton C. A., North M. E., Weyman C., Brenner M. K. Production of antibody by human B cells under serum-free conditions. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Mar 30;68(1-2):25–34. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90133-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiedler W., Sykora K. W., Welte K., Kolitz J. E., Cunningham-Rundles C., Holloway K., Miller G. A., Souza L., Mertelsmann R. T-cell activation defect in common variable immunodeficiency: restoration by phorbol myristate acetate (PMA) or allogeneic macrophages. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1987 Aug;44(2):206–218. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(87)90066-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser J. D., Irving B. A., Crabtree G. R., Weiss A. Regulation of interleukin-2 gene enhancer activity by the T cell accessory molecule CD28. Science. 1991 Jan 18;251(4991):313–316. doi: 10.1126/science.1846244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gimmi C. D., Freeman G. J., Gribben J. G., Sugita K., Freedman A. S., Morimoto C., Nadler L. M. B-cell surface antigen B7 provides a costimulatory signal that induces T cells to proliferate and secrete interleukin 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 1;88(15):6575–6579. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.15.6575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gmünder H., Lesslauer W. A 45-kDa human T-cell membrane glycoprotein functions in the regulation of cell proliferative responses. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Jul 2;142(1):153–160. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08263.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding F. A., McArthur J. G., Gross J. A., Raulet D. H., Allison J. P. CD28-mediated signalling co-stimulates murine T cells and prevents induction of anergy in T-cell clones. Nature. 1992 Apr 16;356(6370):607–609. doi: 10.1038/356607a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jain J., Valge-Archer V. E., Sinskey A. J., Rao A. The AP-1 site at -150 bp, but not the NF-kappa B site, is likely to represent the major target of protein kinase C in the interleukin 2 promoter. J Exp Med. 1992 Mar 1;175(3):853–862. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.3.853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruger G., Welte K., Ciobanu N., Cunningham-Rundles C., Ralph P., Venuta S., Feldman S., Koziner B., Wang C. Y., Moore M. A. Interleukin-2 correction of defective in vitro T-cell mitogenesis in patients with common varied immunodeficiency. J Clin Immunol. 1984 Jul;4(4):295–303. doi: 10.1007/BF00915297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebranchu Y., Thibault G., Degenne D., Bardos P. Abnormalities in CD4+ T lymphocyte subsets in patients with common variable immunodeficiency. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1991 Oct;61(1):83–92. doi: 10.1016/s0090-1229(06)80009-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledbetter J. A., Martin P. J., Spooner C. E., Wofsy D., Tsu T. T., Beatty P. G., Gladstone P. Antibodies to Tp67 and Tp44 augment and sustain proliferative responses of activated T cells. J Immunol. 1985 Oct;135(4):2331–2336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindstein T., June C. H., Ledbetter J. A., Stella G., Thompson C. B. Regulation of lymphokine messenger RNA stability by a surface-mediated T cell activation pathway. Science. 1989 Apr 21;244(4902):339–343. doi: 10.1126/science.2540528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linsley P. S., Brady W., Grosmaire L., Aruffo A., Damle N. K., Ledbetter J. A. Binding of the B cell activation antigen B7 to CD28 costimulates T cell proliferation and interleukin 2 mRNA accumulation. J Exp Med. 1991 Mar 1;173(3):721–730. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.3.721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linsley P. S., Ledbetter J. A. The role of the CD28 receptor during T cell responses to antigen. Annu Rev Immunol. 1993;11:191–212. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.11.040193.001203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López-Botet M., Fontán G., Garcia Rodriguez M. C., de Landázuri M. O. Relationship between IL 2 synthesis and the proliferative response to PHA in different primary immunodeficiencies. J Immunol. 1982 Feb;128(2):679–683. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin P. J., Ledbetter J. A., Morishita Y., June C. H., Beatty P. G., Hansen J. A. A 44 kilodalton cell surface homodimer regulates interleukin 2 production by activated human T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1986 May 1;136(9):3282–3287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller D. L., Jenkins M. K., Schwartz R. H. Clonal expansion versus functional clonal inactivation: a costimulatory signalling pathway determines the outcome of T cell antigen receptor occupancy. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:445–480. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.07.040189.002305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North M. E., Spickett G. P., Allsop J., Webster A. D., Farrant J. Defective DNA synthesis by T cells in acquired 'common-variable' hypogammaglobulinaemia on stimulation with mitogens. Clin Exp Immunol. 1989 Apr;76(1):19–23. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North M. E., Webster A. D., Farrant J. Defects in proliferative responses of T cells from patients with common variable immunodeficiency on direct activation of protein kinase C. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991 Aug;85(2):198–201. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1991.tb05704.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North M. E., Webster A. D., Farrant J. Role of interleukin-2 and interleukin-6 in the mitogen responsiveness of T cells from patients with 'common-variable' hypogammaglobulinaemia. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 Sep;81(3):412–416. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb05348.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunès J., Klasen S., Ragueneau M., Pavon C., Couez D., Mawas C., Bagnasco M., Olive D. CD28 mAbs with distinct binding properties differ in their ability to induce T cell activation: analysis of early and late activation events. Int Immunol. 1993 Mar;5(3):311–315. doi: 10.1093/intimm/5.3.311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sneller M. C., Strober W. Abnormalities of lymphokine gene expression in patients with common variable immunodeficiency. J Immunol. 1990 May 15;144(10):3762–3769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spickett G. P., Matamoros N., Farrant J. Lymphocyte surface phenotype in common variable immunodeficiency. Dis Markers. 1992 Mar-Apr;10(2):67–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spickett G. P., Webster A. D., Farrant J. Cellular abnormalities in common variable immunodeficiency. Immunodefic Rev. 1990;2(3):199–219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Testi R., Lanier L. L. Functional expression of CD28 on T cell antigen receptor gamma/delta-bearing T lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Jan;19(1):185–188. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Lier R. A., Brouwer M., Aarden L. A. Signals involved in T cell activation. T cell proliferation induced through the synergistic action of anti-CD28 and anti-CD2 monoclonal antibodies. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Jan;18(1):167–172. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Lier R. A., Brouwer M., De Groot E. D., Kramer I., Aarden L. A., Verhoeven A. J. T cell receptor/CD3 and CD28 use distinct intracellular signaling pathways. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Jul;21(7):1775–1778. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verweij C. L., Geerts M., Aarden L. A. Activation of interleukin-2 gene transcription via the T-cell surface molecule CD28 is mediated through an NF-kB-like response element. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 5;266(22):14179–14182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


