Abstract
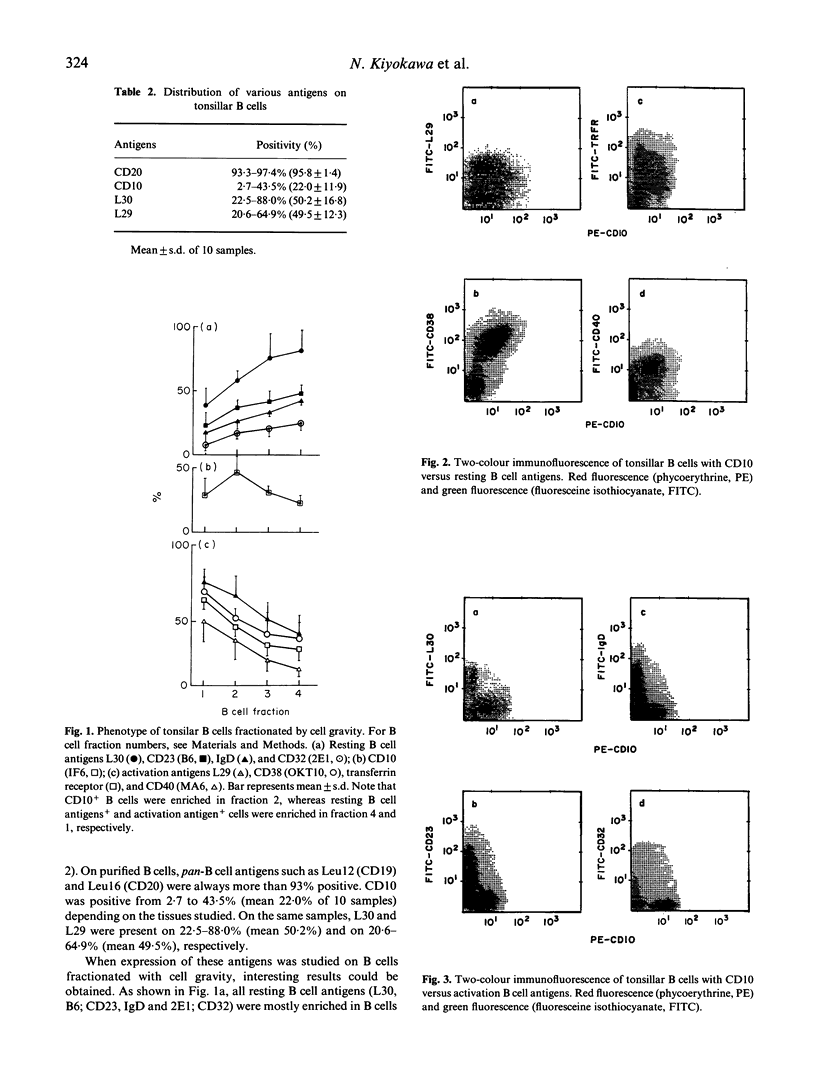
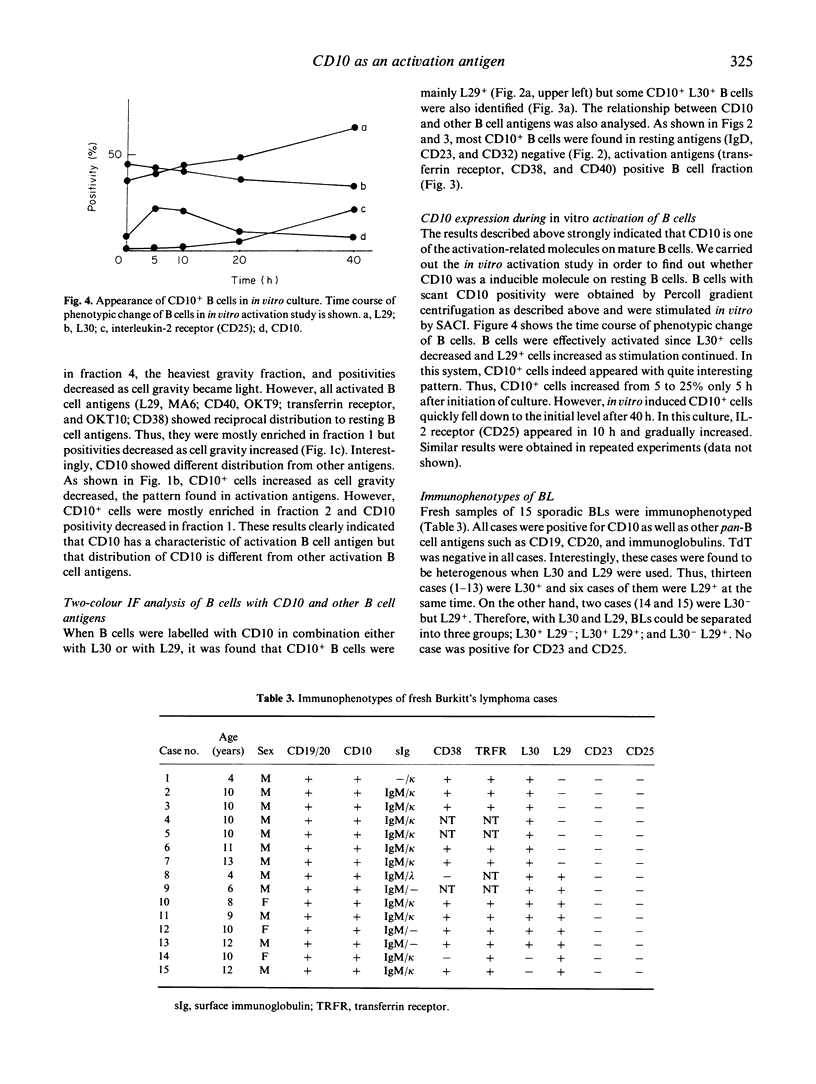
Distinct expression pattern of CD10 molecules during B cell activation was analysed using in vivo and in vitro systems. By two-colour flowcytometrical analysis, CD10 was found to be expressed at a specific stage of in vivo activating B cells. The expression of CD10 during B cell activation appeared to be unique from that of other activation-related B cell antigens including L29, MA6, OKT9 and OKT10. Although the expression of CD10 was associated with that of the activation-related B cell antigens, CD10+ B cells could be separated in the distinct fractions to those expressing other activation-related B cell antigens when fractionated by cell gravity. In particular, certain CD10+ B cells were detected positive for the resting B cell antigen, L30. In vitro studies revealed that CD10+ B cells arose from CD10- B cells at an early step of B cell activation, and disappeared lately when activated by Staphylococcus aureus Cowan I. Collectively, CD10 was an antigen transiently expressed at an early phase of B cell activation process. Expression of CD10 and other antigens on Burkitt's lymphomas (15 cases) was studied next. All cases were CD10+, and 87% (13 cases) were also L30+. In addition, six of CD10+ L30+ cases were L29+. This observation suggested that Burkitt's lymphomas were phenotypically similar to the B cells at an early phase of activation, those expressing CD10 and L30, simultaneously. The present study has dissected a precise expression pattern of CD10 on mature B cell activation in vitro and in vivo, and could be implicated for the histogenesis of one of the poorly characterized B cell lymphoma, namely Burkitt's lymphoma.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dagg M. K., Levitt D. Human B-lymphocyte subpopulations. I. Differentiation of density-separated B lymphocytes. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1981 Oct;21(1):39–49. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(81)90193-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dörken B., Moldenhauer G., Pezzutto A., Schwartz R., Feller A., Kiesel S., Nadler L. M. HD39 (B3), a B lineage-restricted antigen whose cell surface expression is limited to resting and activated human B lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1986 Jun 15;136(12):4470–4479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman A. S., Boyd A. W., Anderson K. C., Fisher D. C., Schlossman S. F., Nadler L. M. B5, a new B cell-restricted activation antigen. J Immunol. 1985 Apr;134(4):2228–2235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimoto J., Ishii Y., Koshiba H., Matsuura A., Ogasawara M., Uede T., Kikuchi K. Human thymus antigen: characterization and its expression on human leukemias. Am J Hematol. 1981;10(2):145–156. doi: 10.1002/ajh.2830100206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimoto J., Ishimoto K., Kiyokawa N., Tanaka S., Ishii E., Hata J. Immunocytological and immunochemical analysis on the common acute lymphoblastic leukemia antigen (CALLA): evidence that CALLA on ALL cells and granulocytes are structurally related. Hybridoma. 1988 Jun;7(3):227–236. doi: 10.1089/hyb.1988.7.227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gadol N., Peacock M. A., Ault K. A. Antigenic phenotype and functional characterization of human tonsil B cells. Blood. 1988 Apr;71(4):1048–1055. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaves M. F., Brown G., Rapson N. T., Lister T. A. Antisera to acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1975 May;4(1):67–84. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(75)90041-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaves M. F., Hariri G., Newman R. A., Sutherland D. R., Ritter M. A., Ritz J. Selective expression of the common acute lymphoblastic leukemia (gp 100) antigen on immature lymphoid cells and their malignant counterparts. Blood. 1983 Apr;61(4):628–639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregory C. D., Tursz T., Edwards C. F., Tetaud C., Talbot M., Caillou B., Rickinson A. B., Lipinski M. Identification of a subset of normal B cells with a Burkitt's lymphoma (BL)-like phenotype. J Immunol. 1987 Jul 1;139(1):313–318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hokland P., Nadler L. M., Griffin J. D., Schlossman S. F., Ritz J. Purification of common acute lymphoblastic leukemia antigen positive cells from normal human bone marrow. Blood. 1984 Sep;64(3):662–666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Jaffe E. S. Phenotypic expression of B-lymphocytes. 1. Identification with monoclonal antibodies in normal lymphoid tissues. Am J Pathol. 1984 Mar;114(3):387–395. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii E., Fujimoto J., Tanaka S., Hata J. Immunohistochemical analysis on normal nephrogenesis and Wilms' tumour using monoclonal antibodies reactive with lymphohaemopoietic antigens. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol. 1987;411(4):315–322. doi: 10.1007/BF00713375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii Y., Kon S., Takei T., Fujimoto J., Kikuchi K. Four distinct antigen systems on human thymus and T cells defined by monoclonal antibodies: immunohistological and immunochemical studies. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Jul;53(1):31–40. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii Y., Mori M., Onoé T. Studies on the germinal center. IV. Autoradiographic study of lymph node germinal centers in relation to zonal differentiation. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1972 Apr;11(4):383–393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kokai Y., Ishii Y., Kikuchi K. Characterization of two distinct antigens expressed on either resting or activated human B cells as defined by monoclonal antibodies. Clin Exp Immunol. 1986 May;64(2):382–391. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loken M. R., Shah V. O., Dattilio K. L., Civin C. I. Flow cytometric analysis of human bone marrow. II. Normal B lymphocyte development. Blood. 1987 Nov;70(5):1316–1324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann R. B., Jaffe E. S., Braylan R. C., Nanba K., Frank M. M., Ziegler J. L., Berard C. W. Non-endemic Burkitts's lymphoma. A B-cell tumor related to germinal centers. N Engl J Med. 1976 Sep 23;295(13):685–691. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197609232951301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritz J., Nadler L. M., Bhan A. K., Notis-McConarty J., Pesando J. M., Schlossman S. F. Expression of common acute lymphoblastic leukemia antigen (CALLA) by lymphomas of B-cell and T-cell lineage. Blood. 1981 Sep;58(3):648–652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritz J., Pesando J. M., Notis-McConarty J., Lazarus H., Schlossman S. F. A monoclonal antibody to human acute lymphoblastic leukaemia antigen. Nature. 1980 Feb 7;283(5747):583–585. doi: 10.1038/283583a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan D., Kossover S., Mitchell S., Frantz C., Hennessy L., Cohen H. Subpopulations of common acute lymphoblastic leukemia antigen-positive lymphoid cells in normal bone marrow identified by hematopoietic differentiation antigens. Blood. 1986 Aug;68(2):417–425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shipp M. A., Vijayaraghavan J., Schmidt E. V., Masteller E. L., D'Adamio L., Hersh L. B., Reinherz E. L. Common acute lymphoblastic leukemia antigen (CALLA) is active neutral endopeptidase 24.11 ("enkephalinase"): direct evidence by cDNA transfection analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(1):297–301. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsudo M., Uchiyama T., Uchino H. Expression of Tac antigen on activated normal human B cells. J Exp Med. 1984 Aug 1;160(2):612–617. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.2.612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokochi T., Holly R. D., Clark E. A. B lymphoblast antigen (BB-1) expressed on Epstein-Barr virus-activated B cell blasts, B lymphoblastoid cell lines, and Burkitt's lymphomas. J Immunol. 1982 Feb;128(2):823–827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


