Abstract
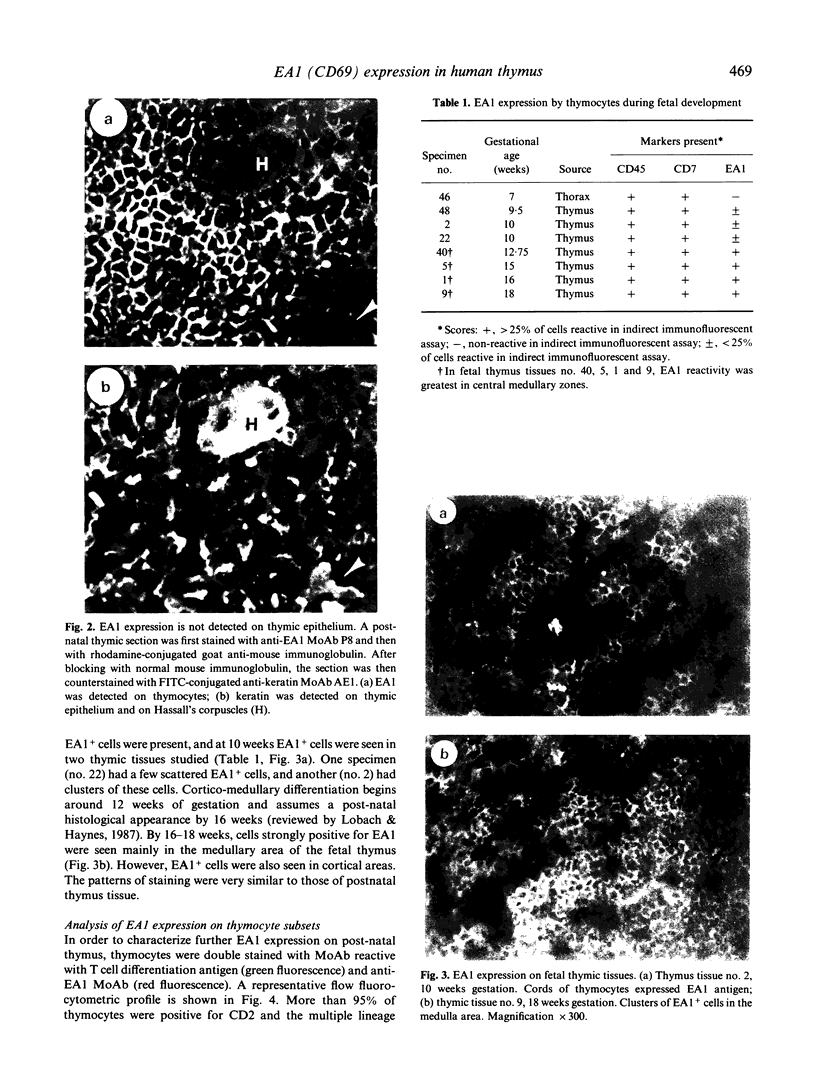
The novel early activation antigen, EA1, has been shown to be induced by mitogens, antigens and the tumour promoter, phorbol myristate acetate (PMA), on human lymphocytes. This antigen has been designated to be CD69. EA1 has also been shown to be expressed on thymocytes without exogenous activation stimuli. In order to characterize further the expression of EA1 on thymocytes, the ontogeny of its expression was studied. EA1 appeared between 7 and 9.5 weeks of gestation, after colonization of the thymic rudiment with CD7+ T cell precursors, but before the onset of compartmentalization of the thymus into cortical and medullary zones. After cortico-medullary differentiation, the majority of medullary thymocytes expressed EA1 while only a fraction of the cortical thymocytes expressed this antigen. In the fetal and post-natal cortex, EA1 expression appeared to cluster in the subcapsular cortex. EA1+ cells were also scattered throughout the inner cortex. By two-colour fluorocytometric analysis of post-natal thymocytes, it was shown that EA1 was expressed on 30 to 65% of thymocytes. EA1 was expressed on CD4+ CD8+ as well as on the more immature CD4- CD8- thymocytes. In contrast to circulating T cells, thymocytes were much less responsive to PMA stimulation for the expression of EA1. Molecular characterization showed that EA1 on thymocytes had the same structure as that of activated peripheral T cells. In addition, thymic EA1 was constitutively phosphorylated. Thus, EA1 expression is acquired early during thymic development after colonization of the thymic rudiment by CD7+ T cell precursors. However, the specific role that EA1 may play in the activation and function of developing thymocytes remains to be determined.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
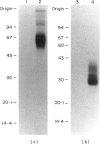
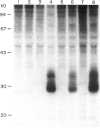
- Bjorndahl J. M., Nakamura S., Hara T., Jung L. K., Fu S. M. The 28-kDa/32-kDa activation antigen EA 1. Further characterization and signal requirements for its expression. J Immunol. 1988 Dec 15;141(12):4094–4100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blue M. L., Daley J. F., Levine H., Craig K. A., Schlossman S. F. Identification and isolation of a T4+T8+ cell with high T3 expression in human thymus: a possible late intermediate in thymocyte differentiation. J Immunol. 1987 Aug 15;139(4):1065–1069. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cebrián M., Yagüe E., Rincón M., López-Botet M., de Landázuri M. O., Sánchez-Madrid F. Triggering of T cell proliferation through AIM, an activation inducer molecule expressed on activated human lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1988 Nov 1;168(5):1621–1637. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.5.1621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delia D., Traversari C., Ballinari D., Cattoretti G., Fontanella E., Polli N., Della Porta G. Early lymphocyte activation molecule defined by the monoclonal antibody MLR-3: biochemical and functional studies. Immunology. 1988 Aug;64(4):593–598. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denning S. M., Tuck D. T., Singer K. H., Haynes B. F. Human thymic epithelial cells function as accessory cells for autologous mature thymocyte activation. J Immunol. 1987 Feb 1;138(3):680–686. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hara T., Fu S. M. Human T cell activation. I. Monocyte-independent activation and proliferation induced by anti-T3 monoclonal antibodies in the presence of tumor promoter 12-o-tetradecanoyl phorbol-13 acetate. J Exp Med. 1985 Apr 1;161(4):641–656. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.4.641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hara T., Jung L. K., Bjorndahl J. M., Fu S. M. Human T cell activation. III. Rapid induction of a phosphorylated 28 kD/32 kD disulfide-linked early activation antigen (EA 1) by 12-o-tetradecanoyl phorbol-13-acetate, mitogens, and antigens. J Exp Med. 1986 Dec 1;164(6):1988–2005. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.6.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynes B. F., Eisenbarth G. S., Fauci A. S. Human lymphocyte antigens: production of a monoclonal antibody that defines functional thymus-derived lymphocyte subsets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5829–5833. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynes B. F., Martin M. E., Kay H. H., Kurtzberg J. Early events in human T cell ontogeny. Phenotypic characterization and immunohistologic localization of T cell precursors in early human fetal tissues. J Exp Med. 1988 Sep 1;168(3):1061–1080. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.3.1061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynes B. F., Singer K. H., Denning S. M., Martin M. E. Analysis of expression of CD2, CD3, and T cell antigen receptor molecules during early human fetal thymic development. J Immunol. 1988 Dec 1;141(11):3776–3784. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgkin P. D., Bond M. W., O'Garra A., Frank G., Lee F., Coffman R. L., Zlotnik A., Howard M. Identification of IL-6 as a T cell-derived factor that enhances the proliferative response of thymocytes to IL-4 and phorbol myristate acetate. J Immunol. 1988 Jul 1;141(1):151–157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung L. K., Bjorndahl J. M., Fu S. M. Dissociation of TPA-induced down-regulation of T cell antigens from protein kinase C activation. Cell Immunol. 1988 Dec;117(2):352–359. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(88)90124-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung L. K., Fu S. M. Effect of tumor promoter 12-O-tetradecanoyl-phorbol 13-acetate on CD 7 expression by T lineage cells. Eur J Immunol. 1988 May;18(5):711–715. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung L. K., Hara T., Fu S. M. Detection and functional studies of p60-65 (Tac antigen) on activated human B cells. J Exp Med. 1984 Nov 1;160(5):1597–1602. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.5.1597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampson L. A., Levy R. Two populations of Ia-like molecules on a human B cell line. J Immunol. 1980 Jul;125(1):293–299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanier L. L., Buck D. W., Rhodes L., Ding A., Evans E., Barney C., Phillips J. H. Interleukin 2 activation of natural killer cells rapidly induces the expression and phosphorylation of the Leu-23 activation antigen. J Exp Med. 1988 May 1;167(5):1572–1585. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.5.1572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobach D. F., Haynes B. F. Ontogeny of the human thymus during fetal development. J Clin Immunol. 1987 Mar;7(2):81–97. doi: 10.1007/BF00916002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobach D. F., Hensley L. L., Ho W., Haynes B. F. Human T cell antigen expression during the early stages of fetal thymic maturation. J Immunol. 1985 Sep;135(3):1752–1759. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura S., Sung S. S., Bjorndahl J. M., Fu S. M. Human T cell activation. IV. T cell activation and proliferation via the early activation antigen EA 1. J Exp Med. 1989 Mar 1;169(3):677–689. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.3.677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palacios R., Sideras P., von Boehmer H. Recombinant interleukin 4/BSF-1 promotes growth and differentiation of intrathymic T cell precursors from fetal mice in vitro. EMBO J. 1987 Jan;6(1):91–95. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04723.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranges G. E., Zlotnik A., Espevik T., Dinarello C. A., Cerami A., Palladino M. A., Jr Tumor necrosis factor alpha/cachectin is a growth factor for thymocytes. Synergistic interactions with other cytokines. J Exp Med. 1988 Apr 1;167(4):1472–1478. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.4.1472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reem G. H., Yeh N. H. Regulation by interleukin 2 of interleukin 2 receptors and gamma-interferon synthesis by human thymocytes: augmentation of interleukin 2 receptors by interleukin 2. J Immunol. 1985 Feb;134(2):953–958. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risso A., Cosulich M. E., Rubartelli A., Mazza M. R., Bargellesi A. MLR3 molecule is an activation antigen shared by human B, T lymphocytes and T cell precursors. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Feb;19(2):323–328. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Madrid F., Krensky A. M., Ware C. F., Robbins E., Strominger J. L., Burakoff S. J., Springer T. A. Three distinct antigens associated with human T-lymphocyte-mediated cytolysis: LFA-1, LFA-2, and LFA-3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7489–7493. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spits H., Yssel H., Takebe Y., Arai N., Yokota T., Lee F., Arai K., Banchereau J., de Vries J. E. Recombinant interleukin 4 promotes the growth of human T cells. J Immunol. 1987 Aug 15;139(4):1142–1147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Testi R., Phillips J. H., Lanier L. L. Constitutive expression of a phosphorylated activation antigen (Leu 23) by CD3bright human thymocytes. J Immunol. 1988 Oct 15;141(8):2557–2563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A., Dazin P. F., Shields R., Fu S. M., Lanier L. L. Functional competency of T cell antigen receptors in human thymus. J Immunol. 1987 Nov 15;139(10):3245–3250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodcock-Mitchell J., Eichner R., Nelson W. G., Sun T. T. Immunolocalization of keratin polypeptides in human epidermis using monoclonal antibodies. J Cell Biol. 1982 Nov;95(2 Pt 1):580–588. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.2.580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wysocki L. J., Sato V. L. "Panning" for lymphocytes: a method for cell selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2844–2848. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zlotnik A., Ransom J., Frank G., Fischer M., Howard M. Interleukin 4 is a growth factor for activated thymocytes: possible role in T-cell ontogeny. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3856–3860. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3856. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vries J. E., Vyth-Dreese F. A., Figdor C. G., Spits H., Leemans J. M., Bont W. S. Induction of phenotypic differentiation, interleukin 2 production, and PHA responsiveness of "immature" human thymocytes by interleukin 1 and phorbol ester. J Immunol. 1983 Jul;131(1):201–206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Boehmer H. The developmental biology of T lymphocytes. Annu Rev Immunol. 1988;6:309–326. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.06.040188.001521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]