Abstract
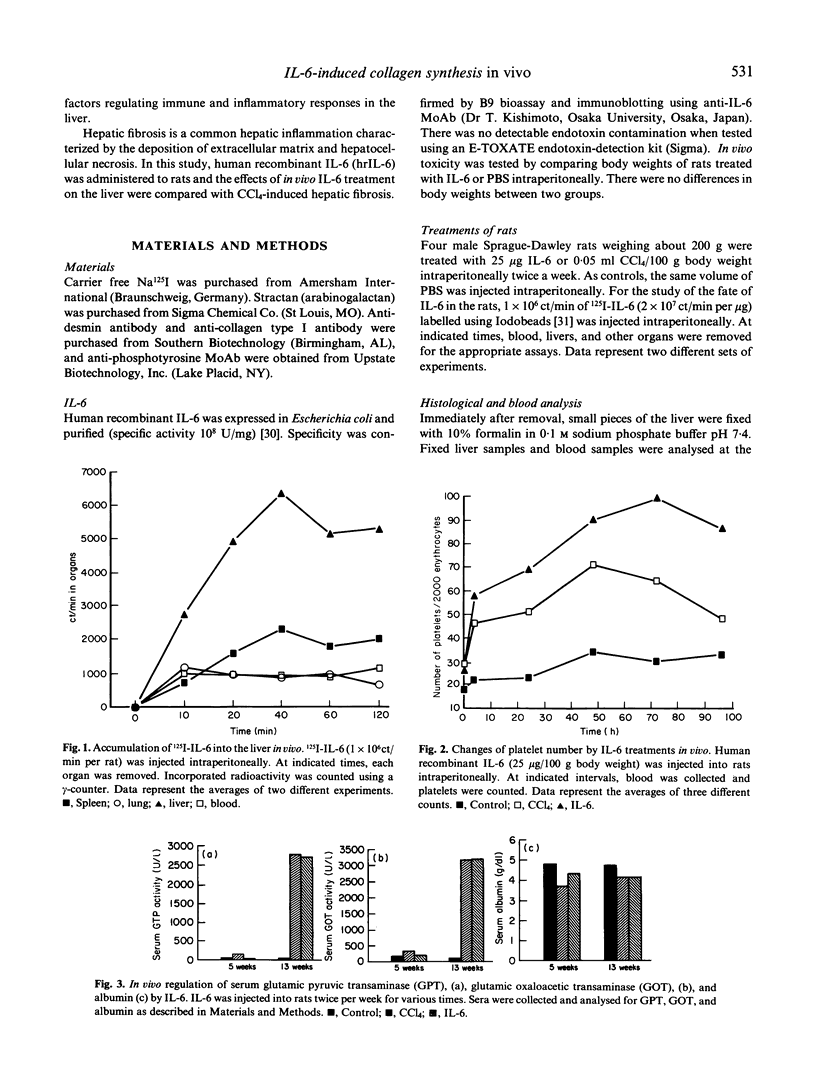
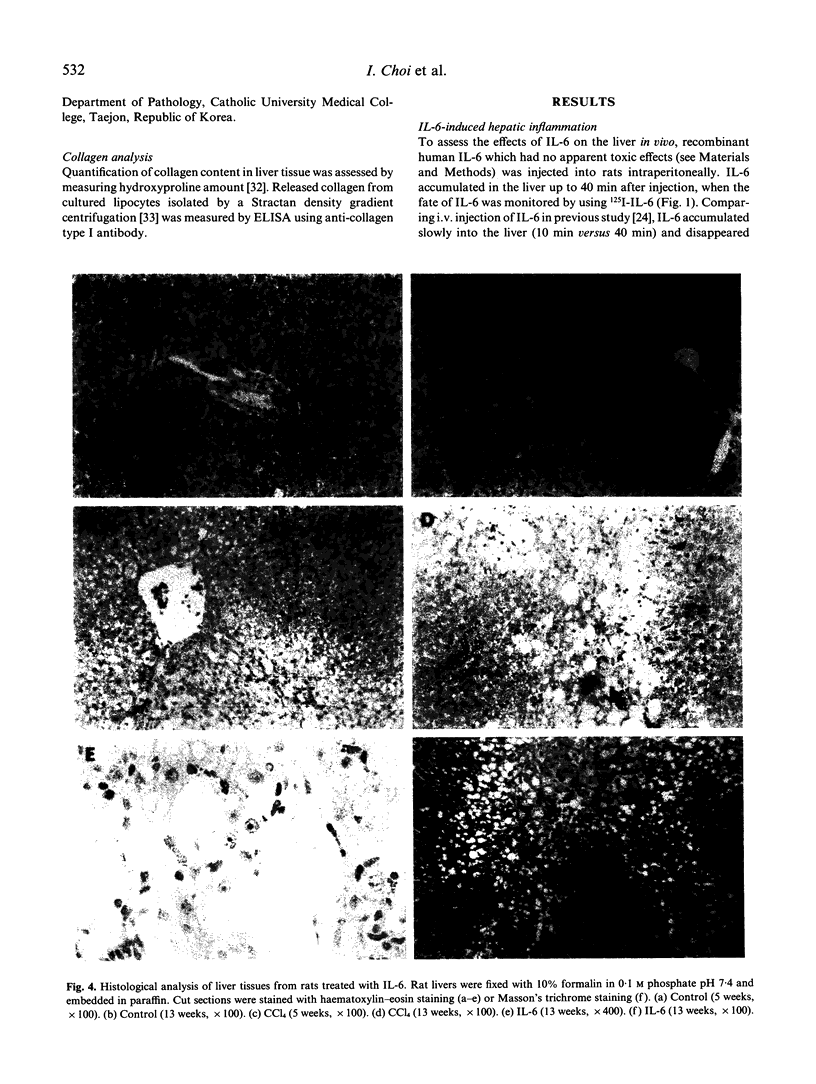
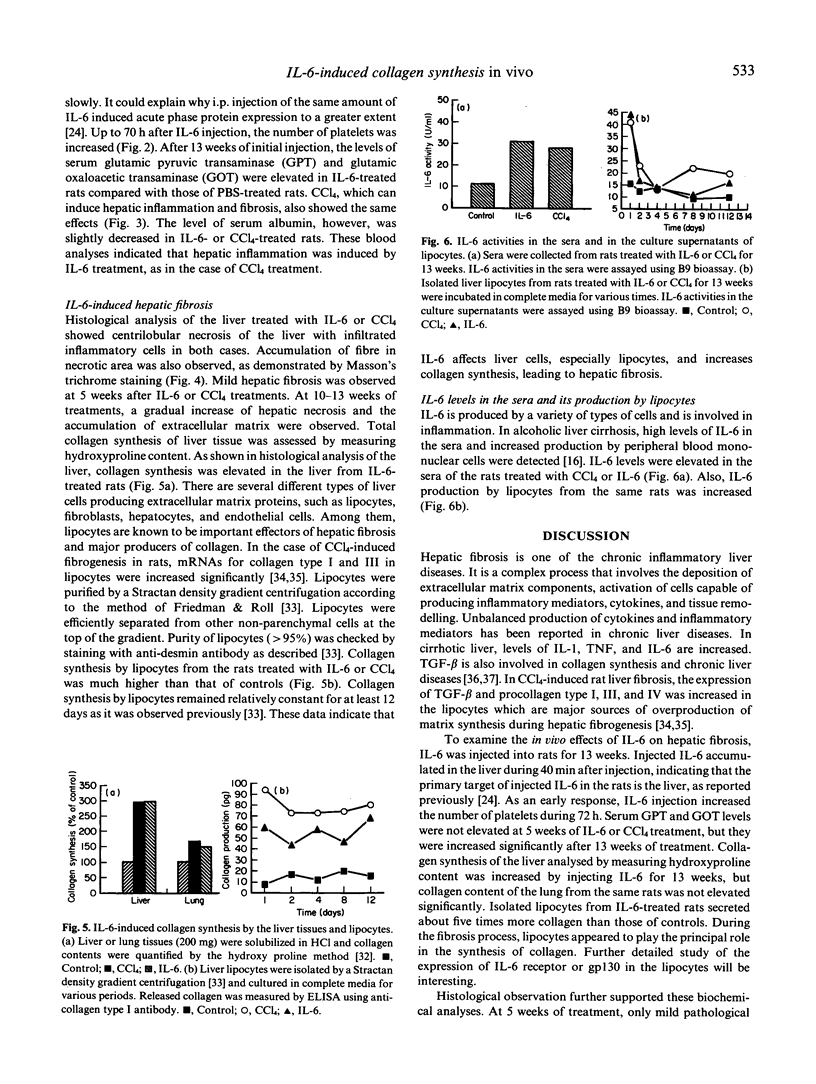
IL-6 regulates the synthesis of a broad spectrum of acute phase proteins in the liver. Also, it is involved in the pathogenesis of many fibrogenic diseases. To study the inflammatory effects of IL-6 on the liver in vivo, human rIL-6, produced in Escherichia coli, was injected intraperitoneally into rats (25 micrograms/100 g body weight). The major fraction of injected IL-6 was accumulated in the liver within 40 min, and the number of platelets was increased during 72 h after injection. After 5 weeks of injection, the levels of serum glutamine pyruvic transaminase (GPT) and glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase (GOT) were not changed, but they were significantly elevated at 13 weeks of treatment. Meanwhile, serum albumin levels were slightly decreased compared with those of controls. The same phenomena were observed in carbon tetrachloride-treated rats. Collagen synthesis was increased in the liver tissues and in the culture supernatants of hepatic lipocytes isolated from the rats treated with IL-6 for 13 weeks. Histological analysis correlated well with biochemical analysis. At 5 weeks of treatment, only mild pathological changes were observed, but severe hepatocyte necrosis and the accumulation of fibres in necrotic area were developed in the liver of IL-6-treated rats after 13 weeks of treatment, confirming that hepatic inflammation and fibrosis were developed. IL-6 activities in the sera and in the culture supernatants of lipocytes from IL-6-treated rats were elevated compared with those in controls. These biochemical and pathological data indicate that IL-6 can induce hepatic inflammation, and it has important roles in the pathogenesis of fibrosis and diseases of the liver in vivo. In addition, these results will provide useful information for the clinical trials of IL-6.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akira S., Isshiki H., Sugita T., Tanabe O., Kinoshita S., Nishio Y., Nakajima T., Hirano T., Kishimoto T. A nuclear factor for IL-6 expression (NF-IL6) is a member of a C/EBP family. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1897–1906. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08316.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andus T., Bauer J., Gerok W. Effects of cytokines on the liver. Hepatology. 1991 Feb;13(2):364–375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer J., Lengyel G., Bauer T. M., Acs G., Gerok W. Regulation of interleukin-6 receptor expression in human monocytes and hepatocytes. FEBS Lett. 1989 May 22;249(1):27–30. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80008-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner D. A., Koch K. S., Leffert H. L. Transforming growth factor-alpha stimulates proto-oncogene c-jun expression and a mitogenic program in primary cultures of adult rat hepatocytes. DNA. 1989 May;8(4):279–285. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1989.8.279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cairo M. S., Plunkett J. M., Clark S., van de Ven C. In vivo hematological effects of seven days of rhIL-6 in neonatal rats. Am J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 1992 Spring;14(1):44–47. doi: 10.1097/00043426-199221000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cairo M. S., Plunkett J. M., Nguyen A., Clark S., van de Ven C. Sequential administration of interleukin-6 and granulocyte-colony stimulating factor in newborn rats: modulation of newborn granulopoiesis and thrombopoiesis. Pediatr Res. 1991 Dec;30(6):554–559. doi: 10.1203/00006450-199112000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castilla A., Prieto J., Fausto N. Transforming growth factors beta 1 and alpha in chronic liver disease. Effects of interferon alfa therapy. N Engl J Med. 1991 Apr 4;324(14):933–940. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199104043241401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowl R. M., Stoller T. J., Conroy R. R., Stoner C. R. Induction of phospholipase A2 gene expression in human hepatoma cells by mediators of the acute phase response. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 5;266(4):2647–2651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czaja M. J., Weiner F. R., Flanders K. C., Giambrone M. A., Wind R., Biempica L., Zern M. A. In vitro and in vivo association of transforming growth factor-beta 1 with hepatic fibrosis. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;108(6):2477–2482. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.6.2477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deviere J., Content J., Denys C., Vandenbussche P., Schandene L., Wybran J., Dupont E. High interleukin-6 serum levels and increased production by leucocytes in alcoholic liver cirrhosis. Correlation with IgA serum levels and lymphokines production. Clin Exp Immunol. 1989 Aug;77(2):221–225. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman S. L., Roll F. J. Isolation and culture of hepatic lipocytes, Kupffer cells, and sinusoidal endothelial cells by density gradient centrifugation with Stractan. Anal Biochem. 1987 Feb 15;161(1):207–218. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90673-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson G. I., Baskin G. S., Horbach J., Porter P., Schenker S. Arrest of epidermal growth factor-dependent growth in fetal hepatocytes after ethanol exposure. J Clin Invest. 1989 Oct;84(4):1287–1294. doi: 10.1172/JCI114296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huszar G., Maiocco J., Naftolin F. Monitoring of collagen and collagen fragments in chromatography of protein mixtures. Anal Biochem. 1980 Jul 1;105(2):424–429. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90481-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansson J. O., Ekberg S., Hoath S. B., Beamer W. G., Frohman L. A. Growth hormone enhances hepatic epidermal growth factor receptor concentration in mice. J Clin Invest. 1988 Dec;82(6):1871–1876. doi: 10.1172/JCI113804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakumu S., Shinagawa T., Ishikawa T., Yoshioka K., Wakita T., Ida N. Interleukin 6 production by peripheral blood mononuclear cells in patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection and primary biliary cirrhosis. Gastroenterol Jpn. 1993 Feb;28(1):18–24. doi: 10.1007/BF02774999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakumu S., Shinagawa T., Ishikawa T., Yoshioka K., Wakita T., Ito Y., Takayanagi M., Ida N. Serum interleukin 6 levels in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Am J Gastroenterol. 1991 Dec;86(12):1804–1808. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kan M., Huang J. S., Mansson P. E., Yasumitsu H., Carr B., McKeehan W. L. Heparin-binding growth factor type 1 (acidic fibroblast growth factor): a potential biphasic autocrine and paracrine regulator of hepatocyte regeneration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(19):7432–7436. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khoruts A., Stahnke L., McClain C. J., Logan G., Allen J. I. Circulating tumor necrosis factor, interleukin-1 and interleukin-6 concentrations in chronic alcoholic patients. Hepatology. 1991 Feb;13(2):267–276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinoshita S., Akira S., Kishimoto T. A member of the C/EBP family, NF-IL6 beta, forms a heterodimer and transcriptionally synergizes with NF-IL6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 15;89(4):1473–1476. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.4.1473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto T., Akira S., Taga T. Interleukin-6 and its receptor: a paradigm for cytokines. Science. 1992 Oct 23;258(5082):593–597. doi: 10.1126/science.1411569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto T. The biology of interleukin-6. Blood. 1989 Jul;74(1):1–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koga M., Ogasawara H. Induction of hepatocyte mitosis in intact adult rat by interleukin-1 alpha and interleukin-6. Life Sci. 1991;49(17):1263–1270. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(91)90139-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maher J. J., McGuire R. F. Extracellular matrix gene expression increases preferentially in rat lipocytes and sinusoidal endothelial cells during hepatic fibrosis in vivo. J Clin Invest. 1990 Nov;86(5):1641–1648. doi: 10.1172/JCI114886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marinkovic S., Jahreis G. P., Wong G. G., Baumann H. IL-6 modulates the synthesis of a specific set of acute phase plasma proteins in vivo. J Immunol. 1989 Feb 1;142(3):808–812. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A. A new solid-state reagent to iodinate proteins. I. Conditions for the efficient labeling of antiserum. Anal Biochem. 1982 Sep 15;125(2):427–432. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90025-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyazawa K., Tsubouchi H., Naka D., Takahashi K., Okigaki M., Arakaki N., Nakayama H., Hirono S., Sakiyama O., Takahashi K. Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of cDNA for human hepatocyte growth factor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Sep 15;163(2):967–973. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92316-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Teramoto H., Ichihara A. Purification and characterization of a growth factor from rat platelets for mature parenchymal hepatocytes in primary cultures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6489–6493. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakatsukasa H., Nagy P., Evarts R. P., Hsia C. C., Marsden E., Thorgeirsson S. S. Cellular distribution of transforming growth factor-beta 1 and procollagen types I, III, and IV transcripts in carbon tetrachloride-induced rat liver fibrosis. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jun;85(6):1833–1843. doi: 10.1172/JCI114643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Presta M., Statuto M., Rusnati M., Dell'Era P., Ragnotti G. Characterization of a Mr 25,000 basic fibroblast growth factor form in adult, regenerating, and fetal rat liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Nov 15;164(3):1182–1189. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91794-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schooltink H., Stoyan T., Lenz D., Schmitz H., Hirano T., Kishimoto T., Heinrich P. C., Rose-John S. Structural and functional studies on the human hepatic interleukin-6 receptor. Molecular cloning and overexpression in HepG2 cells. Biochem J. 1991 Aug 1;277(Pt 3):659–664. doi: 10.1042/bj2770659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shalaby M. R., Halgunset J., Haugen O. A., Aarset H., Aarden L., Waage A., Matsushima K., Kvithyll H., Boraschi D., Lamvik J. Cytokine-associated tissue injury and lethality in mice: a comparative study. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1991 Oct;61(1):69–82. doi: 10.1016/s0090-1229(06)80008-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheron N., Bird G., Goka J., Alexander G., Williams R. Elevated plasma interleukin-6 and increased severity and mortality in alcoholic hepatitis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991 Jun;84(3):449–453. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyers L., De Wit L., Content J. Glucocorticoid up-regulation of high-affinity interleukin 6 receptors on human epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2838–2842. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strain A. J., Frazer A., Hill D. J., Milner R. D. Transforming growth factor beta inhibits DNA synthesis in hepatocytes isolated from normal and regenerating rat liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 May 29;145(1):436–442. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91340-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun Y., Tokushige K., Isono E., Yamauchi K., Obata H. Elevated serum interleukin-6 levels in patients with acute hepatitis. J Clin Immunol. 1992 May;12(3):197–200. doi: 10.1007/BF00918089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Snick J. Interleukin-6: an overview. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:253–278. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.001345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollenberg G. K., Semple E., Quinn B. A., Hayes M. A. Inhibition of proliferation of normal, preneoplastic, and neoplastic rat hepatocytes by transforming growth factor-beta. Cancer Res. 1987 Dec 15;47(24 Pt 1):6595–6599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]