Abstract
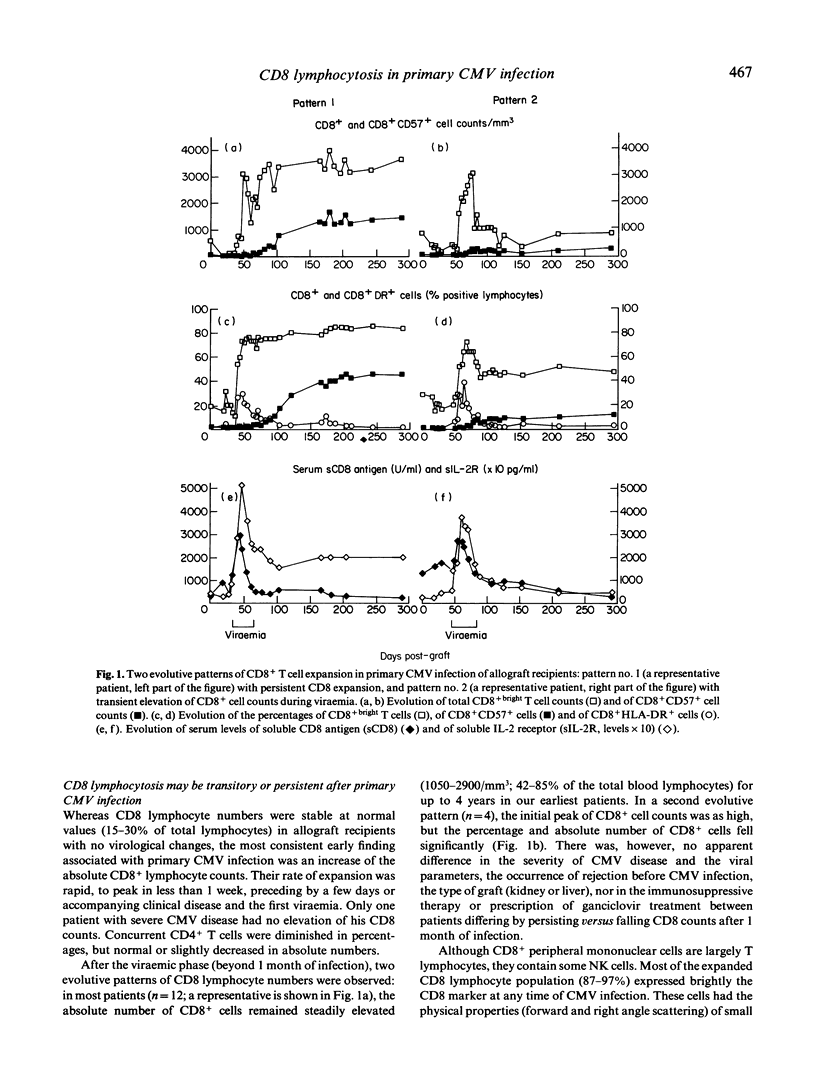
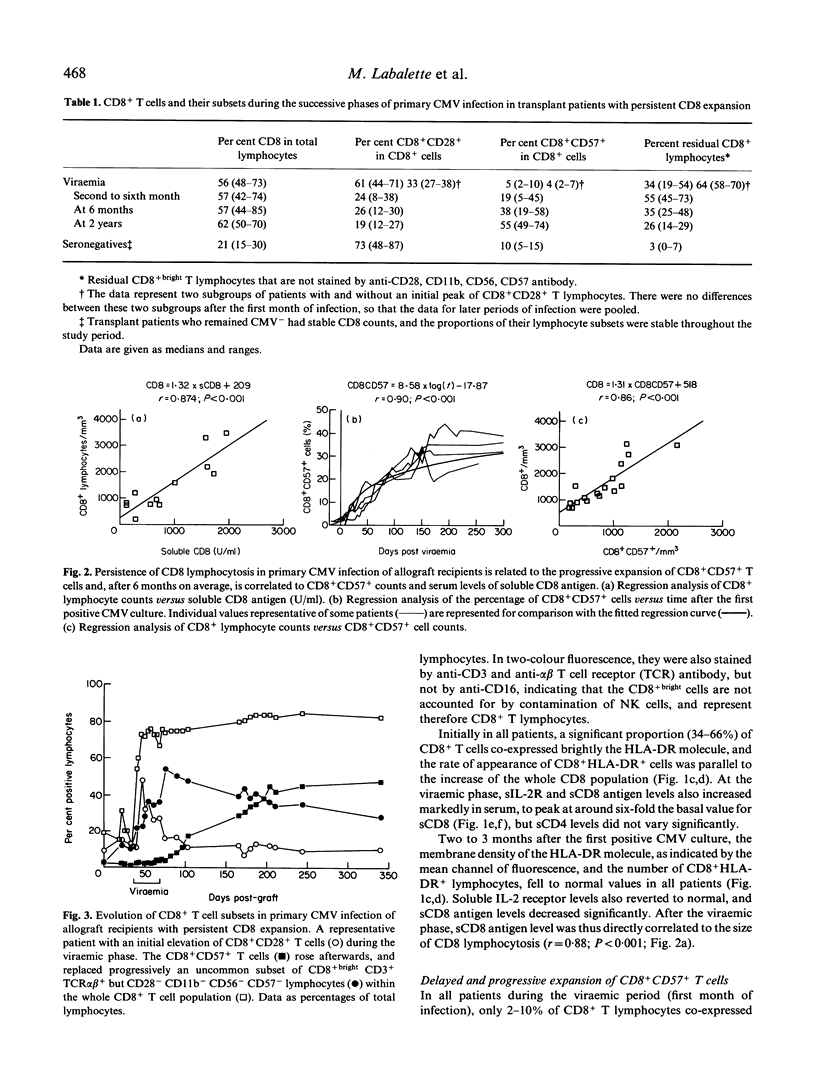
Allograft recipients undergoing cytomegalovirus infection present increased proportions of circulating CD8+ lymphocytes. A longitudinal study of 11 kidney and five liver allograft recipients with primary CMV infection but no other etiological factor of graft dysfunction revealed selective imbalances of peripheral blood CD8+ T cell subsets. Initially, CMV viraemia is associated with elevated CD8+bright T cell numbers and T cell activation. Activation markers fall to normal when viral cultures become negative (before the end of the first month). During the second to sixth month, most (12/16) patients keep up high CD8+ T cell counts (1050-2900 CD8+ cells/mm3), comprising an uncommon CD8+ T cell subset, as 45-73% of CD8+bright lymphocytes were CD3+ and TCR alpha beta+, but were not stained by anti-CD28, CD11b, CD16, CD56, and CD57 antibody. Unexpectedly, CD8+CD57+ T cells, a hallmark of CMV infection, do not appear until the second to sixth month of primary CMV infection, and their numbers increase progressively thereafter. They become the predominant CD8+ T cell subset after 6 months of infection and their persistence for several (up to 4) years is strongly correlated (r = 0.87) with expansion of CD8+ cells. By analysis with MoAbs, there was no bias towards the use of particular TCR-V beta gene families at any time of primary CMV infection. Persistence of CD8 lymphocytosis is thus directly related to the rate of expansion of an uncommon CD8+CD57- subset and its progressive replacement by CD8+CD57+ T cells that are chronically elicited by CMV.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Azuma M., Phillips J. H., Lanier L. L. CD28- T lymphocytes. Antigenic and functional properties. J Immunol. 1993 Feb 15;150(4):1147–1159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borysiewicz L. K., Graham S., Hickling J. K., Mason P. D., Sissons J. G. Human cytomegalovirus-specific cytotoxic T cells: their precursor frequency and stage specificity. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Feb;18(2):269–275. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun R. W., Reiser H. C. Replication of human cytomegalovirus in human peripheral blood T cells. J Virol. 1986 Oct;60(1):29–36. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.1.29-36.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carney W. P., Rubin R. H., Hoffman R. A., Hansen W. P., Healey K., Hirsch M. S. Analysis of T lymphocyte subsets in cytomegalovirus mononucleosis. J Immunol. 1981 Jun;126(6):2114–2116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Divine M., Lecouedic J. P., Gourdin M. F., Oudhriri N., Zohair M., Henni T., Beaujan F., Vernant J. P., Reyes F., Farcet J. P. Functional analysis of CD8 lymphocytes in long-term surviving patients after bone marrow transplantation. J Clin Immunol. 1988 Mar;8(2):140–147. doi: 10.1007/BF00917902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forman S. J., Zaia J. A., Wright C., Gallagher M. T., Blume K. G. Increased Leu-7-positive T lymphocytes during cytomegalovirus infection following allogeneic bone marrow transplantation for hematologic malignancies. Transplantation. 1986 Feb;41(2):268–271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimoto J., Levy S., Levy R. Spontaneous release of the Leu-2 (T8) molecule from human T cells. J Exp Med. 1983 Sep 1;158(3):752–766. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.3.752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gratama J. W., Kardol M., Naipal A. M., Slats J., Den Ouden A., Stijnen T., D'Amaro J., The T. H., Bruning J. W. The influence of cytomegalovirus carrier status on lymphocyte subsets and natural immunity. Clin Exp Immunol. 1987 Jul;69(1):16–24. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gratama J. W., Kluin-Nelemans H. C., Langelaar R. A., den Ottolander G. J., Stijnen T., D'Amaro J., Torensma R., Tanke H. J. Flow cytometric and morphologic studies of HNK1+ (Leu 7+) lymphocytes in relation to cytomegalovirus carrier status. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Nov;74(2):190–195. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gratama J. W., Langelaar R. A., Oosterveer M. A., van der Linden J. A., den Ouden-Noordermeer A., Naipal A. M., Visser J. W., de Gast G. C., Tanke H. J. Phenotypic study of CD4+ and CD8+ lymphocyte subsets in relation to cytomegalovirus carrier status and its correlate with pokeweed mitogen-induced B lymphocyte differentiation. Clin Exp Immunol. 1989 Aug;77(2):245–251. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruse J., Mailhammer R., Wernecke H., Faissner A., Sommer I., Goridis C., Schachner M. Neural cell adhesion molecules and myelin-associated glycoprotein share a common carbohydrate moiety recognized by monoclonal antibodies L2 and HNK-1. Nature. 1984 Sep 13;311(5982):153–155. doi: 10.1038/311153a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linsley P. S., Bradshaw J., Urnes M., Grosmaire L., Ledbetter J. A. CD28 engagement by B7/BB-1 induces transient down-regulation of CD28 synthesis and prolonged unresponsiveness to CD28 signaling. J Immunol. 1993 Apr 15;150(8 Pt 1):3161–3169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maher P., O'Toole C. M., Wreghitt T. G., Spiegelhalter D. J., English T. A. Cytomegalovirus infection in cardiac transplant recipients associated with chronic T cell subset ratio inversion with expansion of a Leu-7+ TS-C+ subset. Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 Dec;62(3):515–524. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFarland H. I., Nahill S. R., Maciaszek J. W., Welsh R. M. CD11b (Mac-1): a marker for CD8+ cytotoxic T cell activation and memory in virus infection. J Immunol. 1992 Aug 15;149(4):1326–1333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers J. D., Ljungman P., Fisher L. D. Cytomegalovirus excretion as a predictor of cytomegalovirus disease after marrow transplantation: importance of cytomegalovirus viremia. J Infect Dis. 1990 Aug;162(2):373–380. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.2.373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy M. M., Lange M., Grieco M. H. Elevated soluble CD8 levels in sera of human immunodeficiency virus-infected populations. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Feb;27(2):257–260. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.2.257-260.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees J. C., Lifton M. A., Light J. A. Changes in lymphocyte subset distribution aid in the differential diagnosis of renal allograft dysfunction. J Clin Lab Anal. 1989;3(4):222–231. doi: 10.1002/jcla.1860030406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reipert B., Scheuch C., Lukowsky A., Reinke P., Fietze E., Döcke W. D., Staffa G., Czerlinksi S., Hetzer R., Volk H. D. CD3+ CD57+ lymphocytes are not likely to be involved in antigen-specific rejection processes in long-term allograft recipients. Clin Exp Immunol. 1992 Jul;89(1):143–147. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1992.tb06893.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renzi P., Ginns L. C. Analysis of T cell subsets in normal adults. Comparison of whole blood lysis technique to Ficoll-Hypaque separation by flow cytometry. J Immunol Methods. 1987 Apr 2;98(1):53–56. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(87)90434-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reusser P., Riddell S. R., Meyers J. D., Greenberg P. D. Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte response to cytomegalovirus after human allogeneic bone marrow transplantation: pattern of recovery and correlation with cytomegalovirus infection and disease. Blood. 1991 Sep 1;78(5):1373–1380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rocha B., Dautigny N., Pereira P. Peripheral T lymphocytes: expansion potential and homeostatic regulation of pool sizes and CD4/CD8 ratios in vivo. Eur J Immunol. 1989 May;19(5):905–911. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin R. H., Carney W. P., Schooley R. T., Colvin R. B., Burton R. C., Hoffman R. A., Hansen W. P., Cosimi A. B., Russell P. S., Hirsch M. S. The effect of infection on T lymphocyte subpopulations: a preliminary report. Int J Immunopharmacol. 1981;3(3):307–312. doi: 10.1016/0192-0561(81)90024-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadat-Sowti B., Debré P., Idziorek T., Guillon J. M., Hadida F., Okzenhendler E., Katlama C., Mayaud C., Autran B. A lectin-binding soluble factor released by CD8+CD57+ lymphocytes from AIDS patients inhibits T cell cytotoxicity. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Mar;21(3):737–741. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrier R. D., Nelson J. A., Oldstone M. B. Detection of human cytomegalovirus in peripheral blood lymphocytes in a natural infection. Science. 1985 Nov 29;230(4729):1048–1051. doi: 10.1126/science.2997930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel D. L., Fox I., Dafoe D. C., Power M., Asplund M., Zellers L., Barker C. F., Prystowsky M. B. Discriminating rejection from CMV infection in renal allograft recipients using flow cytometry. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1989 May;51(2):157–171. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(89)90016-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilden A. B., Abo T., Balch C. M. Suppressor cell function of human granular lymphocytes identified by the HNK-1 (Leu 7) monoclonal antibody. J Immunol. 1983 Mar;130(3):1171–1175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Würsch A. M., Gratama J. W., Middeldorp J. M., Nissen C., Gratwohl A., Speck B., Jansen J., D'Amaro J., The T. H., De Gast G. C. The effect of cytomegalovirus infection on T lymphocytes after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 Nov;62(2):278–287. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada H., Martin P. J., Bean M. A., Braun M. P., Beatty P. G., Sadamoto K., Hansen J. A. Monoclonal antibody 9.3 and anti-CD11 antibodies define reciprocal subsets of lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1985 Dec;15(12):1164–1168. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830151204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Berg A. P., van Son W. J., Haagsma E. B., Klompmaker I. J., Tegzess A. M., Schirm J., Dijkstra G., van der Giessen M., Slooff M. J., The T. H. Prediction of recurrent cytomegalovirus disease after treatment with ganciclovir in solid-organ transplant recipients. Transplantation. 1993 Apr;55(4):847–851. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199304000-00031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Berg A. P., van Son W. J., Janssen R. A., Brons N. H., Heyn A. A., Scholten-Sampson A., Postma S., van der Giessen M., Tegzess A. M., de Leij L. H. Recovery from cytomegalovirus infection is associated with activation of peripheral blood lymphocytes. J Infect Dis. 1992 Dec;166(6):1228–1235. doi: 10.1093/infdis/166.6.1228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


