Abstract
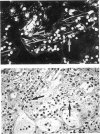
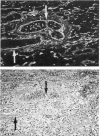
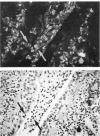
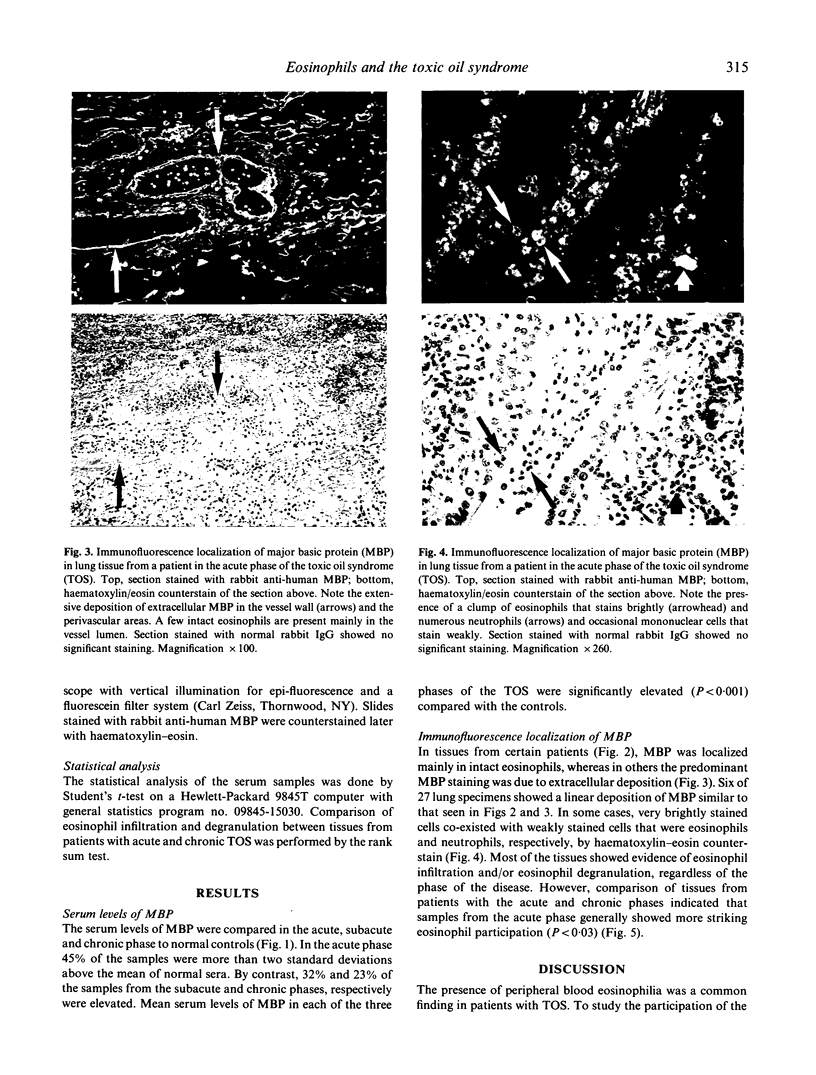
The participation of eosinophils in the Spanish toxic oil syndrome (TOS) was investigated. Eosinophil infiltration and degranulation in tissues from 52 patients with the TOS were examined by immunofluorescence staining for the eosinophil granule major basic protein (MBP). Serum MBP levels were determined in sera from 323 patients. Eosinophil infiltration and degranulation were found in several tissues, especially during the acute phase of the TOS, and serum MBP was significantly elevated during all phases of the disease, suggesting that eosinophils play a role in the pathogenesis of the TOS.
Full text
PDF
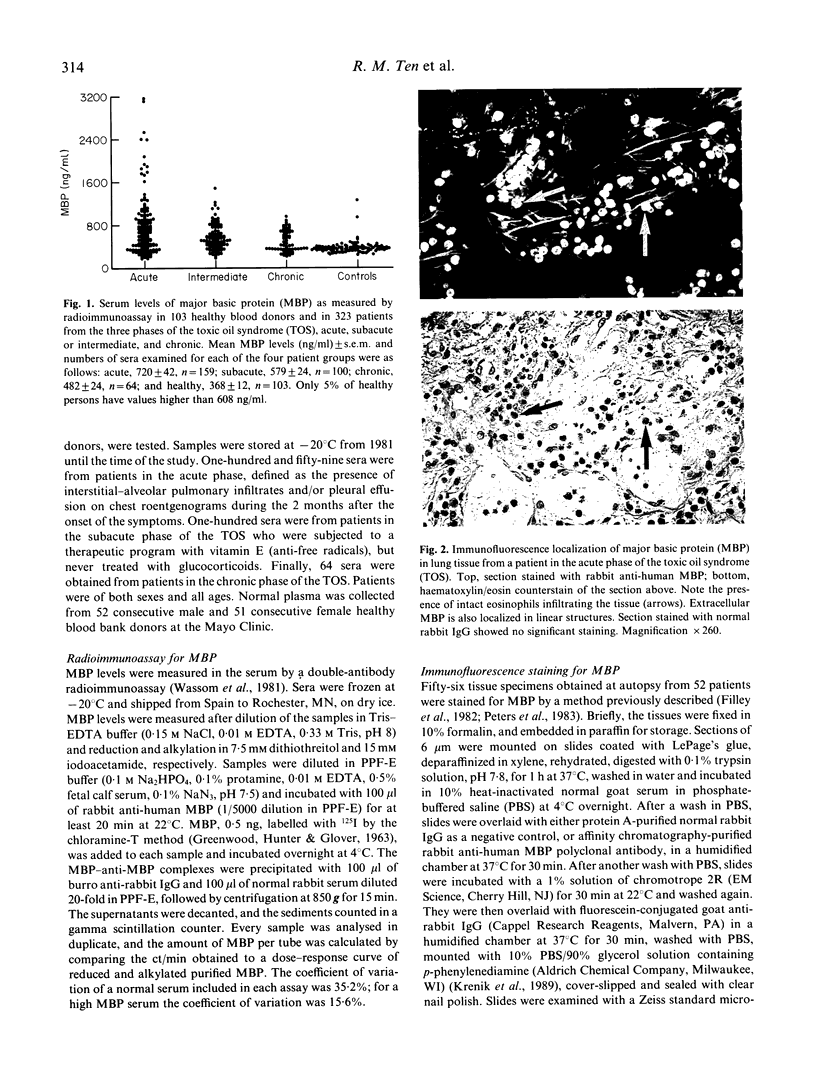


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernert J. T., Jr, Pendergrast A. H., Ashley D. L., Patterson D. G., Jr, Kilbourne E. M., Alexander L. R., Posada de la Paz M., Abaitua Borda I. Synthesis of N-(5-vinyl-1,3-thiazolidin-2-ylidene)phenylamine and analysis of oils implicated in the Spanish toxic oil syndrome for its presence. Food Chem Toxicol. 1989 Mar;27(3):159–164. doi: 10.1016/0278-6915(89)90064-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castro García M., Posada M., Diaz de Rojas F., Abaitua Borda I., Tabuenca Oliver J. M. Hypercoagulable states and the toxic oil syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 1986 May;104(5):730–730. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-104-5-730_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filley W. V., Holley K. E., Kephart G. M., Gleich G. J. Identification by immunofluorescence of eosinophil granule major basic protein in lung tissues of patients with bronchial asthma. Lancet. 1982 Jul 3;2(8288):11–16. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)91152-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENWOOD F. C., HUNTER W. M., GLOVER J. S. THE PREPARATION OF I-131-LABELLED HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE OF HIGH SPECIFIC RADIOACTIVITY. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:114–123. doi: 10.1042/bj0890114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabriel L. C., Escribano L. M., Villa E., Leiva C., Valdes M. D. Ultrastructural study of blood cells in toxic oil syndrome. Acta Haematol. 1986;75(3):165–170. doi: 10.1159/000206112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia Gil M., Traver J., Suarez C., Marin Cao D., Mato J. M. Evidence for generation of leukotriene B4 in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes treated with linoleylanilide. Biochem Pharmacol. 1984 Oct 15;33(20):3303–3306. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(84)90096-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gleich G. J., Adolphson C. R. The eosinophilic leukocyte: structure and function. Adv Immunol. 1986;39:177–253. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60351-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gleich G. J., Frigas E., Loegering D. A., Wassom D. L., Steinmuller D. Cytotoxic properties of the eosinophil major basic protein. J Immunol. 1979 Dec;123(6):2925–2927. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goetzl E. J. The conversion of leukotriene C4 to isomers of leukotriene B4 by human eosinophil peroxidase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 May 31;106(2):270–275. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91105-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutierrez C., Gaspar L., Muro R., Kreisler M., Ferriz P. Autoimmunnity in patients with Spanish toxic oil syndrome. Lancet. 1983 Mar 19;1(8325):644–644. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91812-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez Bronchud M. Toxic oil syndrome and vinyl chloride disease. Lancet. 1984 Oct 20;2(8408):931–931. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)90688-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kammüller M. E., Penninks A. H., Seinen W. Spanish toxic oil syndrome is a chemically induced GVHD-like epidemic. Lancet. 1984 May 26;1(8387):1174–1175. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)91412-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilbourne E. M., Bernert J. T., Jr, Posada de la Paz M., Hill R. H., Jr, Abaitua Borda I., Kilbourne B. W., Zack M. M. Chemical correlates of pathogenicity of oils related to the toxic oil syndrome epidemic in Spain. Am J Epidemiol. 1988 Jun;127(6):1210–1227. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a114914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilbourne E. M., Rigau-Perez J. G., Heath C. W., Jr, Zack M. M., Falk H., Martin-Marcos M., de Carlos A. Clinical epidemiology of toxic-oil syndrome. Manifestations of a New Illness. N Engl J Med. 1983 Dec 8;309(23):1408–1414. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198312083092302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krenik K. D., Kephart G. M., Offord K. P., Dunnette S. L., Gleich G. J. Comparison of antifading agents used in immunofluorescence. J Immunol Methods. 1989 Feb 8;117(1):91–97. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(89)90122-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Tello F. J., Navas-Palacios J. J., Ricoy J. R., Gil-Martín R., Conde-Zurita J. M., Colina-Ruiz Delgado F., Tellez I., Cabello A., Madero-García S. Pathology of a new toxic syndrome caused by ingestion of adulterated oil in Spain. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histol. 1982;397(3):261–285. doi: 10.1007/BF00496569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters M. S., Schroeter A. L., Kephart G. M., Gleich G. J. Localization of eosinophil granule major basic protein in chronic urticaria. J Invest Dermatol. 1983 Jul;81(1):39–43. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12538380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricoy J. R., Cabello A., Rodriguez J., Téllez I. Neuropathological studies on the toxic syndrome related to adulterated rapeseed oil in Spain. Brain. 1983 Dec;106(Pt 4):817–835. doi: 10.1093/brain/106.4.817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silberstein D. S., David J. R. Tumor necrosis factor enhances eosinophil toxicity to Schistosoma mansoni larvae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):1055–1059. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.1055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vicario J. L., Serrano-Rios M., San Andrés F., Arnaiz-Villena A. HLA-DR3, DR4 increase in chronic stage of Spanish oil disease. Lancet. 1982 Jan 30;1(8266):276–276. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)90994-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wassom D. L., Loegering D. A., Solley G. O., Moore S. B., Schooley R. T., Fauci A. S., Gleich G. J. Elevated serum levels of the eosinophil granule major basic protein in patients with eosinophilia. J Clin Invest. 1981 Mar;67(3):651–661. doi: 10.1172/JCI110080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheutlin L. M., Ackerman S. J., Gleich G. J., Thomas L. L. Stimulation of basophil and rat mast cell histamine release by eosinophil granule-derived cationic proteins. J Immunol. 1984 Oct;133(4):2180–2185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]