Abstract
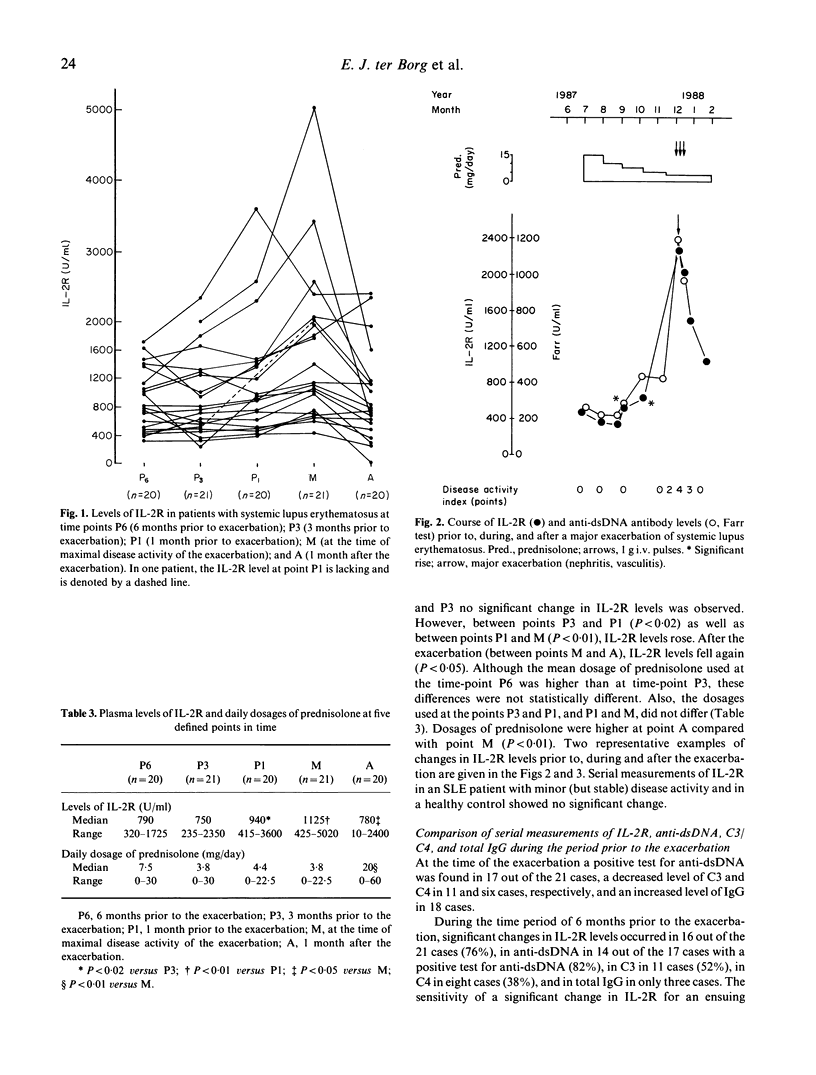
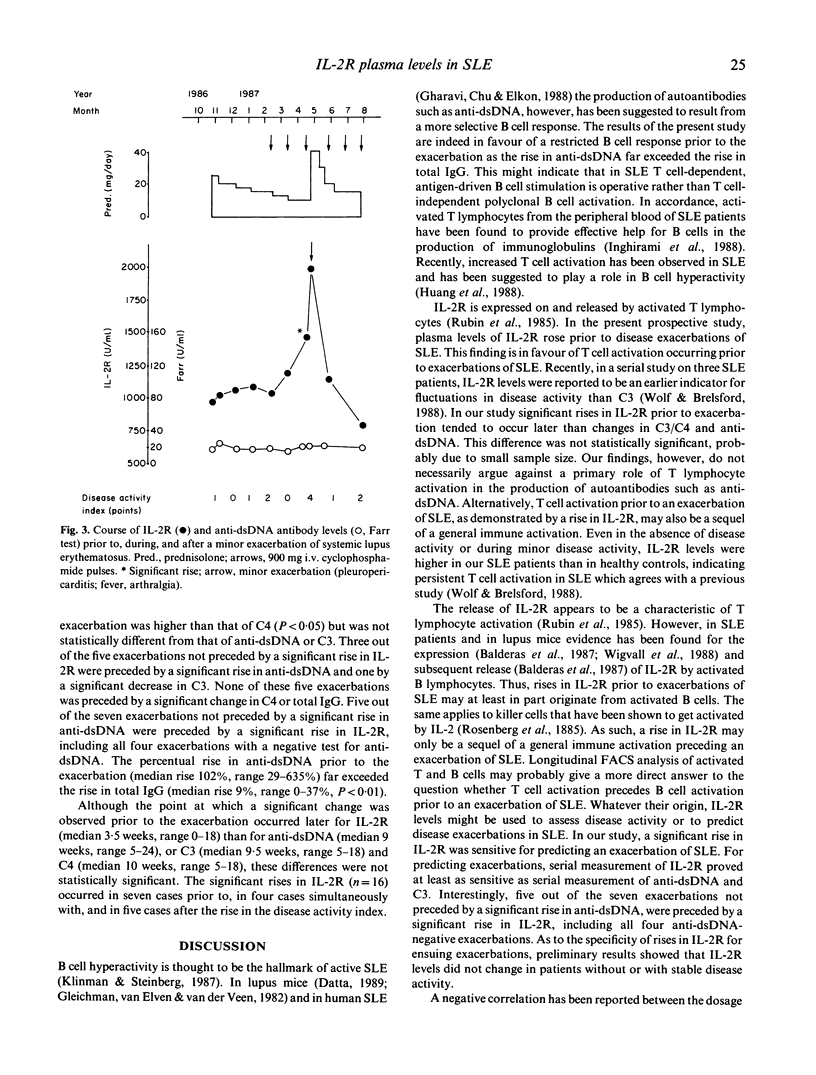
Interleukin-2 receptor (IL-2R) is expressed and released predominantly by activated T cells. In order to investigate whether disease exacerbations of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) are preceded by T cell activation, we prospectively measured levels of IL-2R once a month, from 6 months prior to exacerbations until 1 month afterwards. To assess the temporal relation between T cell activation and B cell activation, we measured, in addition, levels of anti-dsDNA, complement C3/C4, and total IgG. During a mean follow-up period of 23 months, 40 exacerbations occurred in 21 out of the 71 participating patients. For the present study one exacerbation per patient was evaluated. During exacerbation levels of IL-2R were increased in 18 out of the 21 cases and correlated with levels of anti-dsDNA (P less than 0.02), C3 (P less than 0.02), and C4 (P less than 0.01), but not with the score of the disease activity index. Levels of IL-2R rose prior to the exacerbation (P less than 0.02) and fell afterwards following treatment (P less than 0.05). Even in the absence of disease activity or during minor disease symptoms IL-2R levels were higher (P less than 0.01) than in healthy controls. Sixteen out of the 21 exacerbations (76%) were preceded by a significant increase in IL-2R. Changes in levels of anti-dsDNA and complement C3/C4 tended to precede changes in levels of IL-2R. We conclude that increased levels of IL-2R, compatible with T cell activation, are present in SLE already during inactive disease. These levels further increased prior to exacerbations of disease. As such, IL-2R is an indicator of disease activity in SLE. Serial measurement of IL-2R is a sensitive test for predicting disease exacerbations of SLE.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balderas R. S., Josimovic-Alasevic O., Diamantstein T., Dixon F. J., Theofilopoulos A. N. Elevated titers of cell-free interleukin 2 receptor in serum of lupus mice. J Immunol. 1987 Sep 1;139(5):1496–1500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campen D. H., Horwitz D. A., Quismorio F. P., Jr, Ehresmann G. R., Martin W. J. Serum levels of interleukin-2 receptor and activity of rheumatic diseases characterized by immune system activation. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Nov;31(11):1358–1364. doi: 10.1002/art.1780311103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta S. K. A search for the underlying mechanisms of systemic autoimmune disease in the NZB x SWR model. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1989 May;51(2):141–156. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(89)90015-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauci A. S., Steinberg A. D., Haynes B. F., Whalen G. Immunoregulatory aberrations in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. 1978 Oct;121(4):1473–1479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feltkamp T. E., Kirkwood T. B., Maini R. N., Aarden L. A. The first international standard for antibodies to double stranded DNA. Ann Rheum Dis. 1988 Sep;47(9):740–746. doi: 10.1136/ard.47.9.740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gharavi A. E., Chu J. L., Elkon K. B. Autoantibodies to intracellular proteins in human systemic lupus erythematosus are not due to random polyclonal B cell activation. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Nov;31(11):1337–1345. doi: 10.1002/art.1780311101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gleichmann E., Van Elven E. H., Van der Veen J. P. A systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)-like disease in mice induced by abnormal T-B cell cooperation. Preferential formation of autoantibodies characteristic of SLE. Eur J Immunol. 1982 Feb;12(2):152–159. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830120210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamzaoui K., Ayed K. Soluble interleukin 2 receptors in patients with Behçet's disease. J Rheumatol. 1989 Jun;16(6):852–853. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang Y. P., Perrin L. H., Miescher P. A., Zubler R. H. Correlation of T and B cell activities in vitro and serum IL-2 levels in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. 1988 Aug 1;141(3):827–833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inghirami G., Simon J., Balow J. E., Tsokos G. C. Activated T lymphocytes in the peripheral blood of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus induce B cells to produce immunoglobulin. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1988 Jul-Sep;6(3):269–276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klinman D. M., Steinberg A. D. Systemic autoimmune disease arises from polyclonal B cell activation. J Exp Med. 1987 Jun 1;165(6):1755–1760. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.6.1755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd W., Schur P. H. Immune complexes, complement, and anti-DNA in exacerbations of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Medicine (Baltimore) 1981 May;60(3):208–217. doi: 10.1097/00005792-198105000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manoussakis M. N., Papadopoulos G. K., Drosos A. A., Moutsopoulos H. M. Soluble interleukin 2 receptor molecules in the serum of patients with autoimmune diseases. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1989 Mar;50(3):321–332. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(89)90140-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg S. A., Lotze M. T., Muul L. M., Leitman S., Chang A. E., Ettinghausen S. E., Matory Y. L., Skibber J. M., Shiloni E., Vetto J. T. Observations on the systemic administration of autologous lymphokine-activated killer cells and recombinant interleukin-2 to patients with metastatic cancer. N Engl J Med. 1985 Dec 5;313(23):1485–1492. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198512053132327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin L. A., Kurman C. C., Fritz M. E., Biddison W. E., Boutin B., Yarchoan R., Nelson D. L. Soluble interleukin 2 receptors are released from activated human lymphoid cells in vitro. J Immunol. 1985 Nov;135(5):3172–3177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semenzato G., Bambara L. M., Biasi D., Frigo A., Vinante F., Zuppini B., Trentin L., Feruglio C., Chilosi M., Pizzolo G. Increased serum levels of soluble interleukin-2 receptor in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Immunol. 1988 Nov;8(6):447–452. doi: 10.1007/BF00916949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M., Cohen A. S., Fries J. F., Masi A. T., McShane D. J., Rothfield N. F., Schaller J. G., Talal N., Winchester R. J. The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Nov;25(11):1271–1277. doi: 10.1002/art.1780251101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theofilopoulos A. N., Dixon F. J. Murine models of systemic lupus erythematosus. Adv Immunol. 1985;37:269–390. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60342-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigfall D. R., Sakai R. S., Wallace D. J., Jordan S. C. Interleukin-2 receptor expression in peripheral blood lymphocytes from systemic lupus erythematosus patients: relationship to clinical activity. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1988 Jun;47(3):354–362. doi: 10.1016/s0090-1229(88)80012-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf R. E., Brelsford W. G. Soluble interleukin-2 receptors in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Jun;31(6):729–735. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ter Borg E. J., Horst G., Hummel E. J., Limburg P. C., Kallenberg C. G. Measurement of increases in anti-double-stranded DNA antibody levels as a predictor of disease exacerbation in systemic lupus erythematosus. A long-term, prospective study. Arthritis Rheum. 1990 May;33(5):634–643. doi: 10.1002/art.1780330505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


