Abstract
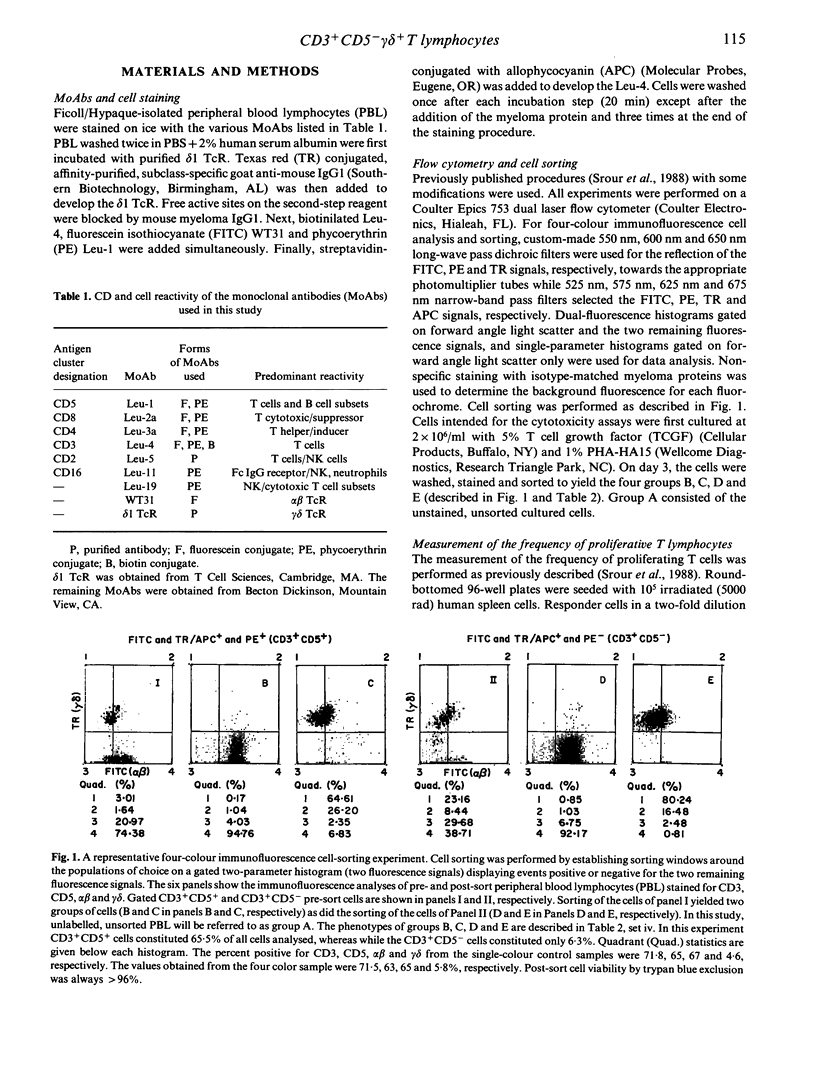
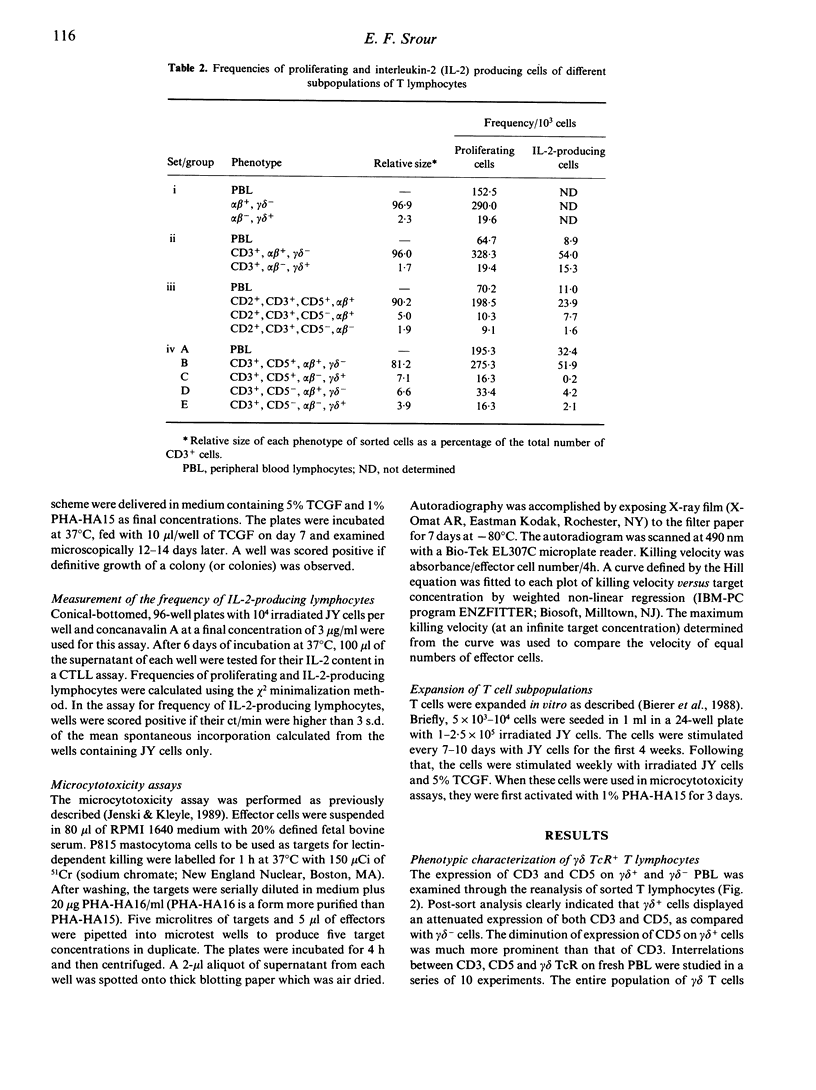
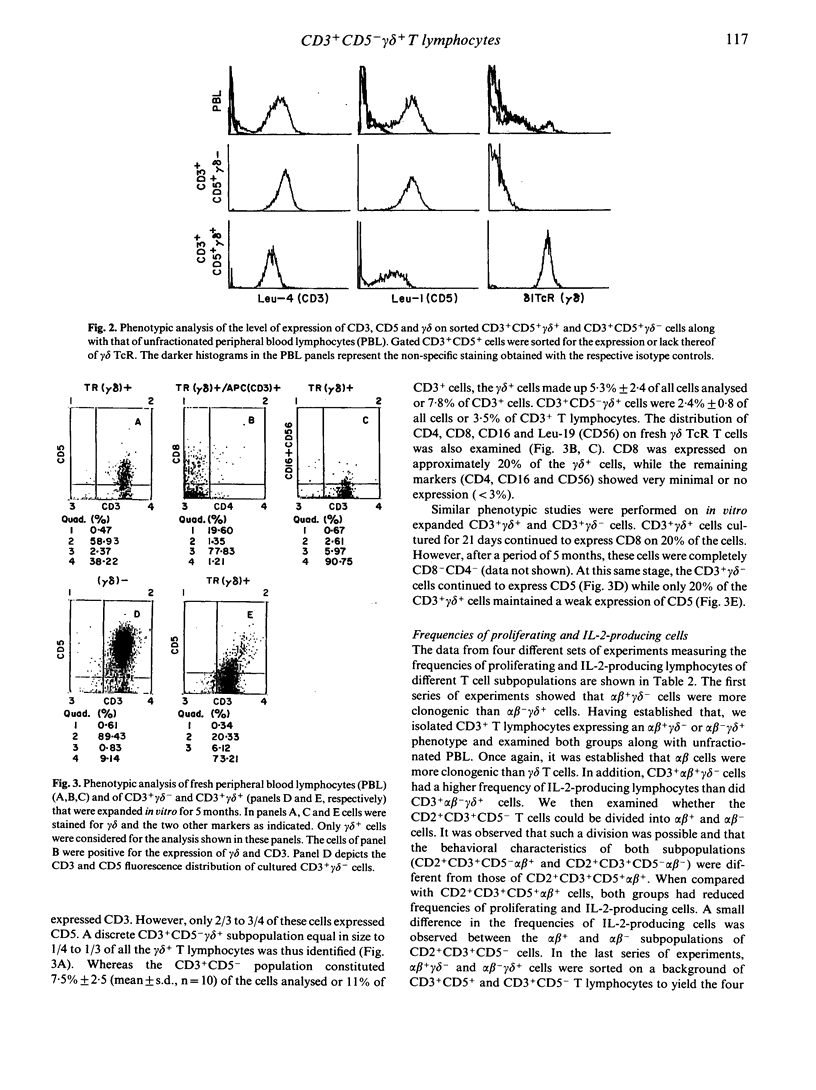
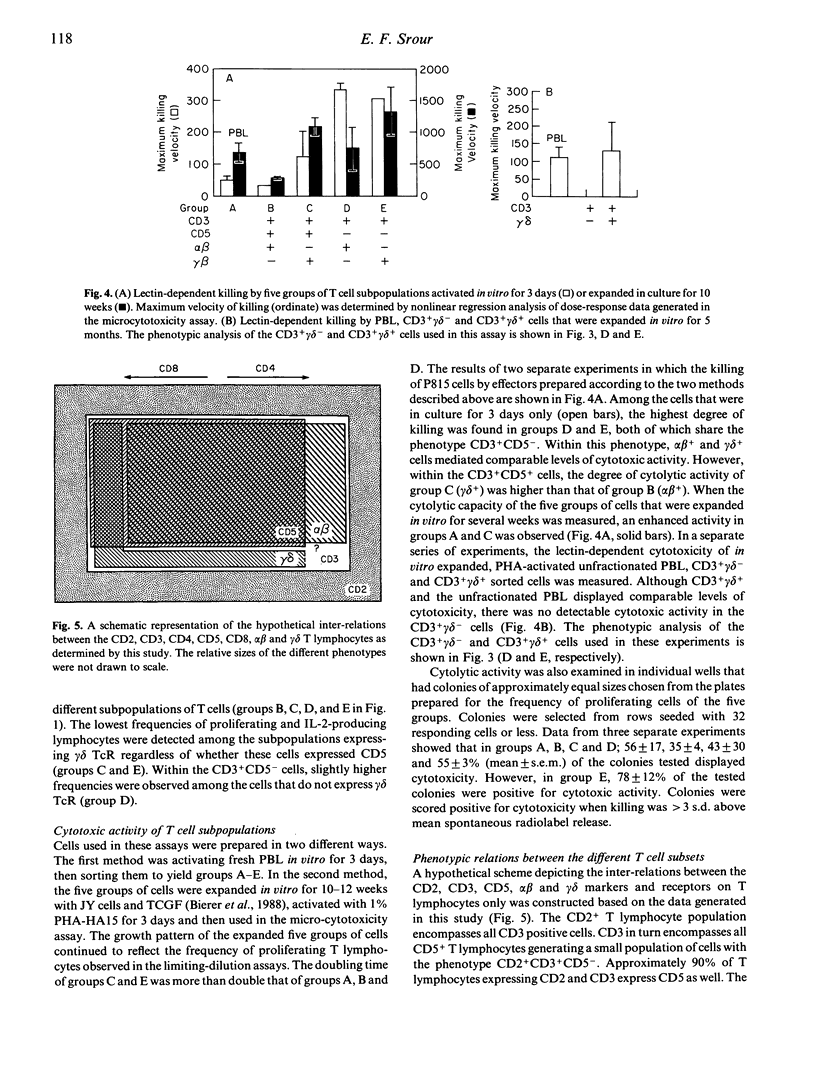
The functional and phenotypic properties of normal human CD3+CD5- T cells which have a higher frequency of cytotoxic cells than CD3+CD5+ T lymphocytes have been described. Using three- and four-colour immunofluorescence flow cytometric cell sorting, the CD3+CD5- and CD3+CD5+ populations were subdivided into alpha beta or gamma delta T cell receptor positive cells. The four subsets were examined for the in vitro cytotoxic activity and were also stimulated with mitogens in limiting-dilution assays to measure the frequencies of proliferating and interleukin-2 (IL-2) producing cells. CD3+CD5- alpha beta +, CD3+CD5- gamma delta + and CD3+CD5+ gamma delta + cells had lower frequencies of proliferating and IL-2-producing cells than did CD3+CD5+ alpha beta + cells. However, the cytotoxic activity of the different phenotypes was higher in the CD3+CD5- subsets, especially when these cells were gamma delta +. Expression of gamma delta or lack of expression of CD5 appeared to be associated with the acquisition of cytolytic potentials. CD8 was expressed on 20% of fresh CD3+ gamma delta + cells. Cultured gamma delta + cells retained the expression of gamma delta, but quickly lost that of CD8 and with time modulated the expression of CD5. The expression of CD5 was found to be higher on sorted CD3+CD5+ gamma delta - than on CD3+CD5+ gamma delta + cells. These observations indicate that gamma delta is preferentially expressed on CD5-negative or weakly positive T lymphocytes and that CD3+CD5- gamma delta + cells appear to constitute a discrete small subset of mature T lymphocytes which are cytotoxic in nature. However, the exact immunological function of these cells and their place in T cell ontogeny are yet to be elucidated.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bank I., DePinho R. A., Brenner M. B., Cassimeris J., Alt F. W., Chess L. A functional T3 molecule associated with a novel heterodimer on the surface of immature human thymocytes. Nature. 1986 Jul 10;322(6075):179–181. doi: 10.1038/322179a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bierer B. E., Burakoff S. J., Smith B. R. A large proportion of T lymphocytes lack CD5 expression after bone marrow transplantation. Blood. 1989 Apr;73(5):1359–1366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bierer B. E., Nishimura Y., Burakoff S. J., Smith B. R. Phenotypic and functional characterization of human cytolytic T cells lacking expression of CD5. J Clin Invest. 1988 May;81(5):1390–1397. doi: 10.1172/JCI113468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borst J., van de Griend R. J., van Oostveen J. W., Ang S. L., Melief C. J., Seidman J. G., Bolhuis R. L. A T-cell receptor gamma/CD3 complex found on cloned functional lymphocytes. Nature. 1987 Feb 19;325(6106):683–688. doi: 10.1038/325683a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner M. B., McLean J., Dialynas D. P., Strominger J. L., Smith J. A., Owen F. L., Seidman J. G., Ip S., Rosen F., Krangel M. S. Identification of a putative second T-cell receptor. Nature. 1986 Jul 10;322(6075):145–149. doi: 10.1038/322145a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner M. B., McLean J., Scheft H., Riberdy J., Ang S. L., Seidman J. G., Devlin P., Krangel M. S. Two forms of the T-cell receptor gamma protein found on peripheral blood cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Nature. 1987 Feb 19;325(6106):689–694. doi: 10.1038/325689a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ceuppens J. L., Baroja M. L. Monoclonal antibodies to the CD5 antigen can provide the necessary second signal for activation of isolated resting T cells by solid-phase-bound OKT3. J Immunol. 1986 Sep 15;137(6):1816–1821. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colamonici O. R., Ang S., Quinones R., Henkart P., Heikkila R., Gress R., Felix C., Kirsch I., Longo D., Marti G. IL-2-dependent expansion of CD3+ large granular lymphocytes expressing T cell receptor-gamma delta. Evidence for a functional receptor by anti-CD3 activation of cytolysis. J Immunol. 1988 Apr 15;140(8):2527–2533. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faure F., Jitsukawa S., Meuer S., Bohuon C., Triebel F., Hercend T. Identification of a CD2- CD3+ T cell receptor-gamma+ peripheral blood lymphocyte subpopulation. J Immunol. 1988 Apr 1;140(7):2128–2132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman T., Lefrançois L. Expression of the gamma-delta T-cell receptor on intestinal CD8+ intraepithelial lymphocytes. Nature. 1988 Jun 30;333(6176):855–858. doi: 10.1038/333855a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenski L. J., Kleyle R. M. Kinetic assay of cytotoxic T lymphocyte clones. I. Methodology and data analysis. J Immunol Methods. 1989 Feb 24;117(2):181–190. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(89)90139-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein J. R. Ontogeny of the Thy-1-, Lyt-2+ murine intestinal intraepithelial lymphocyte. Characterization of a unique population of thymus-independent cytotoxic effector cells in the intestinal mucosa. J Exp Med. 1986 Jul 1;164(1):309–314. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.1.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koning F., Lew A. M., Maloy W. L., Valas R., Coligan J. E. The biosynthesis and assembly of T cell receptor alpha- and beta-chains with the CD3 complex. J Immunol. 1988 May 1;140(9):3126–3134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koning F., Stingl G., Yokoyama W. M., Yamada H., Maloy W. L., Tschachler E., Shevach E. M., Coligan J. E. Identification of a T3-associated gamma delta T cell receptor on Thy-1+ dendritic epidermal Cell lines. Science. 1987 May 15;236(4803):834–837. doi: 10.1126/science.2883729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledbetter J. A., June C. H., Martin P. J., Spooner C. E., Hansen J. A., Meier K. E. Valency of CD3 binding and internalization of the CD3 cell-surface complex control T cell responses to second signals: distinction between effects on protein kinase C, cytoplasmic free calcium, and proliferation. J Immunol. 1986 Jun 1;136(11):3945–3952. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledbetter J. A., Martin P. J., Spooner C. E., Wofsy D., Tsu T. T., Beatty P. G., Gladstone P. Antibodies to Tp67 and Tp44 augment and sustain proliferative responses of activated T cells. J Immunol. 1985 Oct;135(4):2331–2336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marusić-Galesić S., Pardoll D. M., Saito T., Leo O., Fowlkes B. J., Coligan J., Germain R. N., Schwartz R. H., Kruisbeek A. M. Activation properties of T cell receptor-gamma delta hybridomas expressing diversity in both gamma- and delta-chains. J Immunol. 1988 Jan 15;140(2):411–418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moretta L., Pende D., Bottino C., Migone N., Ciccone E., Ferrini S., Mingari M. C., Moretta A. Human CD3+4-8-WT31- T lymphocyte populations expressing the putative T cell receptor gamma-gene product. A limiting dilution and clonal analysis. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Sep;17(9):1229–1234. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830170903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pantaleo G., Zocchi M. R., Ferrini S., Poggi A., Tambussi G., Bottino C., Moretta L., Moretta A. Human cytolytic cell clones lacking surface expression of T cell receptor alpha/beta or gamma/delta. Evidence that surface structures other than CD3 or CD2 molecules are required for signal transduction. J Exp Med. 1988 Jul 1;168(1):13–24. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.1.13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozans M. K., Smith B. R., Emerson S., Crimmins M., Laurent G., Reichert T., Burakoff S. J., Miller R. A. Functional assessment of T cell depletion from bone marrow prior to therapeutic transplantation using limiting dilution culture methods. Transplantation. 1986 Oct;42(4):380–387. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198610000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snodgrass H. R., Dembić Z., Steinmetz M., von Boehmer H. Expression of T-cell antigen receptor genes during fetal development in the thymus. Nature. 1985 May 16;315(6016):232–233. doi: 10.1038/315232a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srour E. F., Walker E. B., Walker D. E., Jansen J. Functional and phenotypical studies of the Leu-4 (CD3)+, Leu-1 (CD5)- T lymphocyte. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Jul;73(1):34–39. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sussman J. J., Bonifacino J. S., Lippincott-Schwartz J., Weissman A. M., Saito T., Klausner R. D., Ashwell J. D. Failure to synthesize the T cell CD3-zeta chain: structure and function of a partial T cell receptor complex. Cell. 1988 Jan 15;52(1):85–95. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90533-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas Y., Glickman E., DeMartino J., Wang J., Goldstein G., Chess L. Biologic functions of the OKT1 T cell surface antigen. I. The T1 molecule is involved in helper function. J Immunol. 1984 Aug;133(2):724–728. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vilmer E., Guglielmi P., David V., Leca G., Rabian C., Degos L., Boiron M., Bensussan A. Predominant expression of circulating CD3+ lymphocytes bearing gamma T cell receptor in a prolonged immunodeficiency after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. J Clin Invest. 1988 Sep;82(3):755–761. doi: 10.1172/JCI113675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Griend R. J., Tax W. J., van Krimpen B. A., Vreugdenhil R. J., Ronteltap C. P., Bolhuis R. L. Lysis of tumor cells by CD3+4-8-16+ T cell receptor alpha beta- clones, regulated via CD3 and CD16 activation sites, recombinant interleukin 2, and interferon beta 1. J Immunol. 1987 Mar 1;138(5):1627–1633. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


