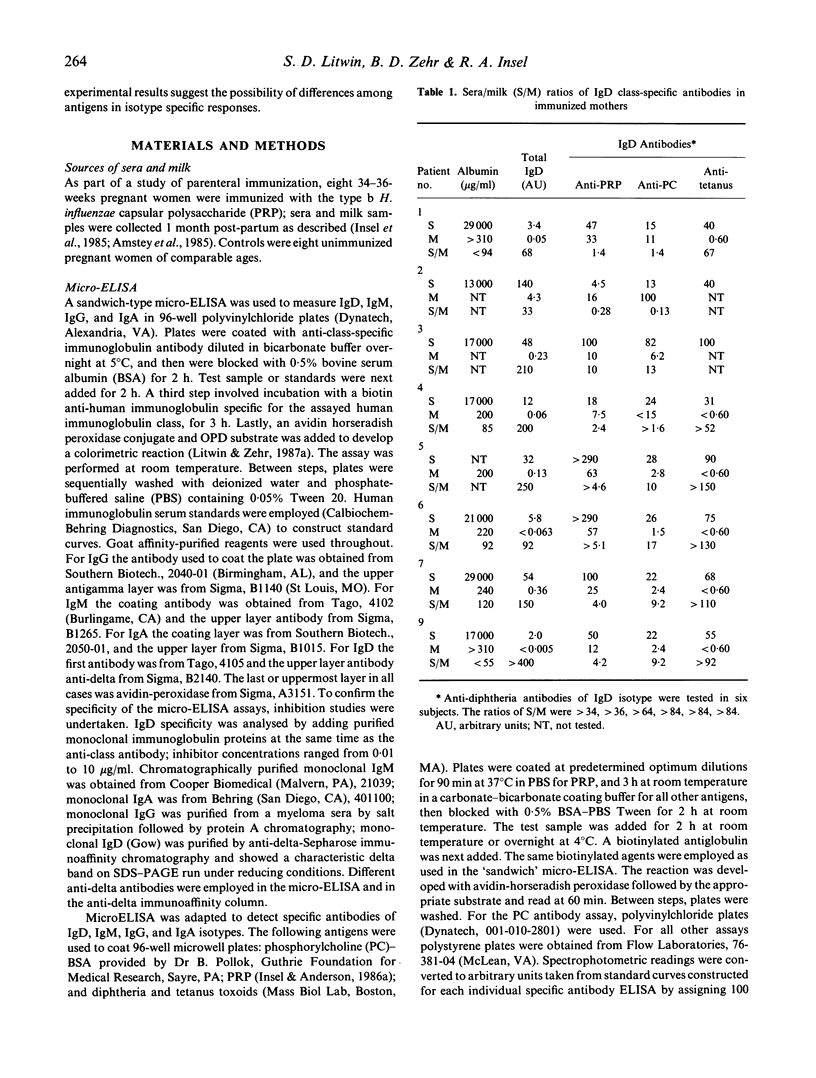
Abstract
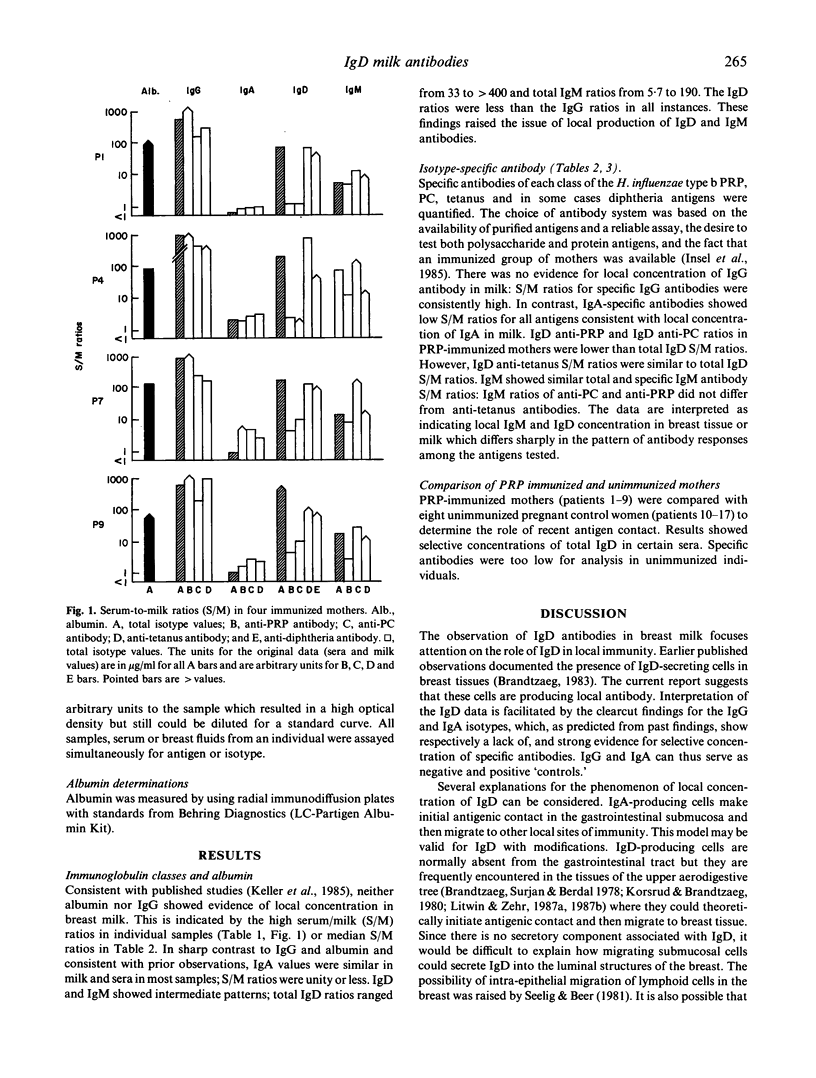
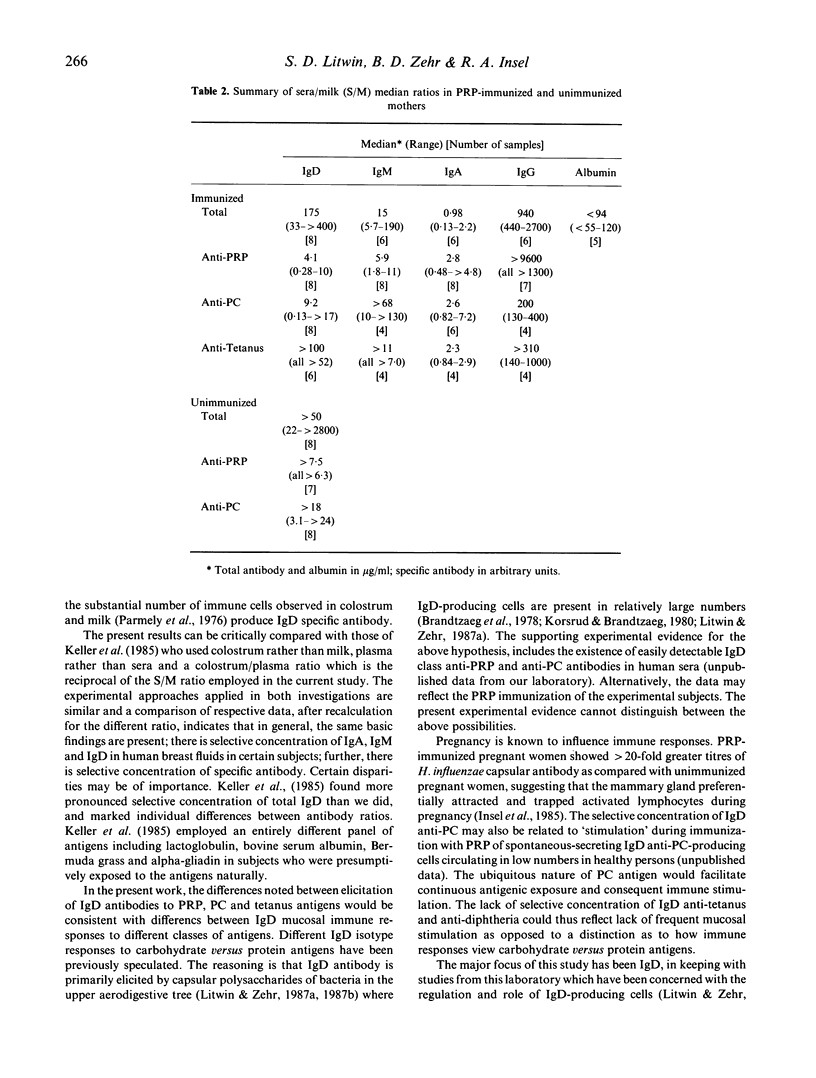
The participation of human IgD class antibody in local immune responses of breast tissue was studied by analysing the sera-to-milk ratios of total IgD, IgM, IgA, IgG isotypes and albumin found in matched samples, and by analysing the sera-to-milk (S/M) ratios of IgD, IgM, IgA, IgG antibodies against Haemophilus influenzae capsular polysaccharide (PRP), phosphorylcholine, tetanus and in some cases diphtheria antigens. The study group consisted of eight women immunized during pregnancy with PRP, and control, unimmunized women. Albumin, and total IgG showed high S/M ratios. IgA had a low S/M ratio as expected, consistent with reports that IgA is locally concentrated. Total IgD and IgM isotype ratio values were intermediate between IgG and IgA suggesting they were selectively concentrated in breast fluids due to local production or transport mechanisms, or both. Ratios for specific antibodies of IgA and IgM isotypes and for total IgA and IgM isotype showed parallel data. Among the IgD antibodies, those specific for PRP and phosphorylcholine suggested a higher degree of selective concentration as compared with tetanus antigen. In the group of unimmunized women, although selective concentration of total IgD was observed, specific antibody studies were inconclusive due to the low milk IgD antibody levels encountered. The results indicate that IgD (and also IgM) may participate in local immune responses of human breast tissues and fluids; possibly influenced by the nature of the antigen, the state of immunization and the hormonal environment (pregnancy).
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amstey M. S., Insel R., Munoz J., Pichichero M. Fetal-neonatal passive immunization against Hemophilus influenzae, type b. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1985 Nov 15;153(6):607–611. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(85)80243-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bahna S. L., Keller M. A., Heiner D. C. IgE and IgD in human colostrum and plasma. Pediatr Res. 1982 Aug;16(8):604–607. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198208000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandtzaeg P., Surjan L., Jr, Berdal P. Immunoglobulin systems of human tonsils. I. Control subjects of various ages: quantification of Ig-producing cells, tonsillar morphometry and serum Ig concentrations. Clin Exp Immunol. 1978 Mar;31(3):367–381. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandtzaeg P. The secretory immune system of lactating human mammary glands compared with other exocrine organs. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1983 Jun 30;409:353–382. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1983.tb26883.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin R. M., Prendergast R. A., Silverstein A. M. Nonspecific signals for B-cell localization and activation. J Exp Med. 1978 Dec 1;148(6):1705–1710. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.6.1705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Insel R. A., Amstey M., Pichichero M. E. Postimmunization antibody to the Haemophilus influenzae type b capsule in breast milk. J Infect Dis. 1985 Aug;152(2):407–408. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.2.407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Insel R. A., Anderson P. W. Response to oligosaccharide-protein conjugate vaccine against Hemophilus influenzae b in two patients with IgG2 deficiency unresponsive to capsular polysaccharide vaccine. N Engl J Med. 1986 Aug 21;315(8):499–503. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198608213150807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller M. A., Heiner D. C., Myers A. S., Reisinger D. M. IgD in human colostrum. Pediatr Res. 1985 Jan;19(1):122–126. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198501000-00032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korsrud F. R., Brandtzaeg P. Immune systems of human nasopharyngeal and palatine tonsils: histomorphometry of lymphoid components and quantification of immunoglobulin-producing cells in health and disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Feb;39(2):361–370. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litwin S. D., Zehr B. D. In vitro studies on human IgD. I. Sources and characteristics of "externalized" IgD in tonsil lymphocyte cultures. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Apr;17(4):483–489. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830170408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litwin S. D., Zehr B. D. In vitro studies on human IgD. II. IgD-secreting cells preferentially elaborate IgD, lambda molecules. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Apr;17(4):491–495. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830170409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litwin S. D., Zehr B. D. Membrane IgD-positive B cells of "low-IgD serum phenotype" individuals fail to secrete IgD and fail to shift to preferential lambda light-chain expression in vitro. J Clin Immunol. 1987 Mar;7(2):114–120. doi: 10.1007/BF00916005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mestecky J. The common mucosal immune system and current strategies for induction of immune responses in external secretions. J Clin Immunol. 1987 Jul;7(4):265–276. doi: 10.1007/BF00915547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parmely M. J., Beer A. E., Billingham R. E. In vitro studies on the T-lymphocyte population of human milk. J Exp Med. 1976 Aug 1;144(2):358–370. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.2.358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seelig L. L., Jr, Beer A. E. Intraepithelial leukocytes in the human mammary gland. Biol Reprod. 1981 Jun;24(5):1157–1163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steele M. G., Leslie G. A. Immunoglobulin D in rat serum, saliva and milk. Immunology. 1985 Aug;55(4):571–577. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


