Abstract
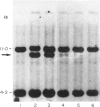
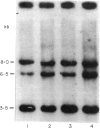
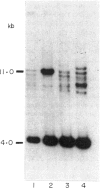
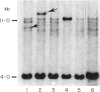
The dominant presence of specific T-cell populations in the rheumatoid joint as detected by Southern blot analysis of T cell receptor (TCR) gene rearrangements would indicate local antigen recognition and T cell proliferation. We therefore studied TCR beta chain gene rearrangements using a C beta 2 probe in paired samples of T cell populations from synovial tissue and peripheral blood (n = 6) as well as synovial fluid (n = 16) and peripheral blood (n = 18) of patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Peripheral blood mononuclear cells from healthy donors (n = 7) served as a control. T cells were studied directly after isolation or after non-specific expansion with OKT3 monoclonal antibody (MoAb) and T cell growth factor (TCGF). DNA samples were digested with EcoRI and HindIII to detect rearrangements to C beta 1 and C beta 2, respectively. Extra bands were detected in all EcoRI-digested DNA samples prepared from both freshly isolated and non-specifically expanded T cell populations of patients and healthy donors, possibly representing 'common' (V-) D-J rearrangements. Dominant rearrangements were found in only two out of 16 synovial fluid T cell populations (one freshly isolated and one expanded) and not in peripheral blood or synovial tissue derived T cell populations. No extra bands were detected in HindIII-digested DNA samples. To investigate the effect of in vitro culture techniques on rearrangement patterns we studied DNA samples prepared from synovial tissue T cells obtained both by outgrowth from tissue with TCGF or by enzyme digestion and subsequent expansion either with TCGF or with OKT3 MoAb and TCGF. Whereas the latter T cell population yielded 'common' rearrangements, the former T cell populations yielded different dominant rearrangements. These data indicate that oligoclonality of the T cell populations in synovial tissue and synovial fluid of patients with RA is a rare event. The data also show the influence of in vitro culture techniques on the result of TCR gene rearrangement analysis.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acha-Orbea H., Steinman L., McDevitt H. O. T cell receptors in murine autoimmune diseases. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:371–405. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.07.040189.002103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan F. M., Allard S., Londei M., Savill C., Boylston A., Carrel S., Maini R. N., Feldmann M. Heterogeneity of T cell receptor idiotypes in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Sep;73(3):417–423. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cush J. J., Lipsky P. E. Phenotypic analysis of synovial tissue and peripheral blood lymphocytes isolated from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Oct;31(10):1230–1238. doi: 10.1002/art.1780311003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duby A. D., Sinclair A. K., Osborne-Lawrence S. L., Zeldes W., Kan L., Fox D. A. Clonal heterogeneity of synovial fluid T lymphocytes from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6206–6210. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duke O., Panayi G. S., Janossy G., Poulter L. W. An immunohistological analysis of lymphocyte subpopulations and their microenvironment in the synovial membranes of patients with rheumatoid arthritis using monoclonal antibodies. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Jul;49(1):22–30. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaston J. S., Life P. F., Bailey L. C., Bacon P. A. In vitro responses to a 65-kilodalton mycobacterial protein by synovial T cells from inflammatory arthritis patients. J Immunol. 1989 Oct 15;143(8):2494–2500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holoshitz J., Klajman A., Drucker I., Lapidot Z., Yaretzky A., Frenkel A., van Eden W., Cohen I. R. T lymphocytes of rheumatoid arthritis patients show augmented reactivity to a fraction of mycobacteria cross-reactive with cartilage. Lancet. 1986 Aug 9;2(8502):305–309. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)90003-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Indiveri F., Huddlestone J., Pellegrino M. A., Ferrone S. Isolation of human T lymphocytes: comparison between nylon wool filtration and rosetting with neuraminidase (VCN) and 2-aminoethylisothiouronium bromide (AET)-treated sheep red blood cells (SRBC). J Immunol Methods. 1980;34(2):107–115. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90164-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keystone E. C., Minden M., Klock R., Poplonski L., Zalcberg J., Takadera T., Mak T. W. Structure of T cell antigen receptor beta chain in synovial fluid cells from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Dec;31(12):1555–1557. doi: 10.1002/art.1780311213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laffon A., Sánchez-Madrid F., Ortíz de Landázuri M., Jiménez Cuesta A., Ariza A., Ossorio C., Sabando P. Very late activation antigen on synovial fluid T cells from patients with rheumatoid arthritis and other rheumatic diseases. Arthritis Rheum. 1989 Apr;32(4):386–392. doi: 10.1002/anr.1780320405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meijer C. J., de Graaff-Reitsma C. B., Lafeber G. J., Cats A. In situ localization of lymphocyte subsets in synovial membranes of patients with rheumatoid arthritis with monoclonal antibodies. J Rheumatol. 1982 May-Jun;9(3):359–365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miceli M. C., Finn O. J. T cell receptor beta-chain selection in human allograft rejection. J Immunol. 1989 Jan 1;142(1):81–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miltenburg A. M., Meijer-Paape M. E., Daha M. R., Paul L. C. Endothelial cell lysis induced by lymphokine-activated human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Sep;17(9):1383–1386. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830170926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miltenburg A. M., van Laar J. M., Daha M. R., de Vries R. R., van den Elsen P. J., Breedveld F. C. Dominant T-cell receptor beta-chain gene rearrangements indicate clonal expansion in the rheumatoid joint. Scand J Immunol. 1990 Jan;31(1):121–126. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1990.tb02750.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pope R. M., Pahlavani M. A., LaCour E., Sambol S., Desai B. V. Antigenic specificity of rheumatoid synovial fluid lymphocytes. Arthritis Rheum. 1989 Nov;32(11):1371–1380. doi: 10.1002/anr.1780321105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Res P. C., Schaar C. G., Breedveld F. C., van Eden W., van Embden J. D., Cohen I. R., de Vries R. R. Synovial fluid T cell reactivity against 65 kD heat shock protein of mycobacteria in early chronic arthritis. Lancet. 1988 Aug 27;2(8609):478–480. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)90123-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savill C. M., Delves P. J., Kioussis D., Walker P., Lydyard P. M., Colaco B., Shipley M., Roitt I. M. A minority of patients with rheumatoid arthritis show a dominant rearrangement of T-cell receptor beta chain genes in synovial lymphocytes. Scand J Immunol. 1987 Jun;25(6):629–635. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1987.tb01089.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamenkovic I., Stegagno M., Wright K. A., Krane S. M., Amento E. P., Colvin R. B., Duquesnoy R. J., Kurnick J. T. Clonal dominance among T-lymphocyte infiltrates in arthritis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):1179–1183. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.1179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamenkovic I., Stegagno M., Wright K. A., Krane S. M., Amento E. P., Colvin R. B., Duquesnoy R. J., Kurnick J. T. T lymphocyte infiltrates in inflammatory synovia are oligoclonal. Transplant Proc. 1988 Apr;20(2):315–319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart J. M., Postlethwaite A. E., Townes A. S., Kang A. H. Cell-mediated immunity to collagen and collagen alpha chains in rheumatoid arthritis and other rheumatic diseases. Am J Med. 1980 Jul;69(1):13–18. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(80)90494-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoen J., Waalen K., Førre O., Kvarnes L., Natvig J. B. Inflammatory synovial T cells in different activity subgroups of patients with rheumatoid arthritis and juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Scand J Rheumatol. 1989;18(2):77–88. doi: 10.3109/03009748909099922. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldmann T. A., Davis M. M., Bongiovanni K. F., Korsmeyer S. J. Rearrangements of genes for the antigen receptor on T cells as markers of lineage and clonality in human lymphoid neoplasms. N Engl J Med. 1985 Sep 26;313(13):776–783. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198509263131303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber W. E., Buurman W. A., Vandermeeren M. M., Raus J. C. Activation through CD3 molecule leads to clonal expansion of all human peripheral blood T lymphocytes: functional analysis of clonally expanded cells. J Immunol. 1985 Oct;135(4):2337–2342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikai Y., Anatoniou D., Clark S. P., Yanagi Y., Sangster R., Van den Elsen P., Terhorst C., Mak T. W. Sequence and expression of transcripts of the human T-cell receptor beta-chain genes. Nature. 1984 Dec 6;312(5994):521–524. doi: 10.1038/312521a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vries F., Meijer C. J., Lafeber G. J., Cnossen J., Cats A. Lymphocyte subpopulations in rheumatoid arthritis. An immunological, enzyme histochemical and morphological study. Rheumatol Int. 1984;4(2):91–94. doi: 10.1007/BF00541203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]